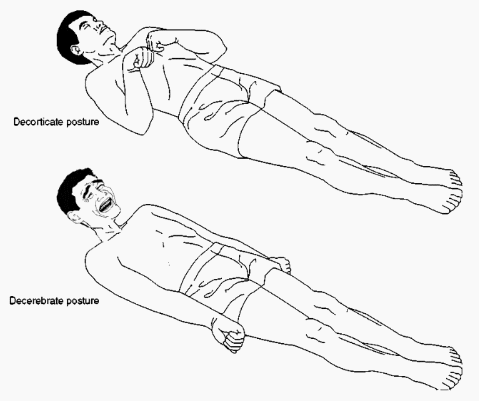
Description of decorticate posturing
What is a form of posturing where the patient presents with plantar flexion of legs and flexion of arms over chest .
This scale assesses Level of Consciousness after a brain injury. The score is calculated by adding the scores for three components: best eye response (E), best verbal response (V), and best motor response (M).
Whats the Scale, whats the best score , whats the lowest score?

A nurse working in the nursery bumps into the bassinette of a newborn causing this reflex. Name the reflex and describe how the infant would react
What is the Moro Reflex also known as the startle reflex or embrace reflex, is a normal, involuntary reflex in newborns that occurs when they are startled or feel like they are falling. It's a primitive protective response to sudden stimulation or disruption of balance
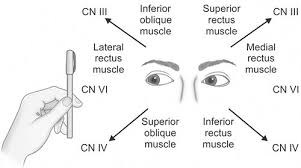
Extraocular movements controlled by these nerves are tested by asking the patient to follow a moving target (eg, examiner's finger, penlight) to all 4 quadrants (including across the midline) and toward the tip of the nose; this test can detect nystagmus and palsies of ocular muscles.
Six Cardinal Fields of Gaze
For the 3rd (ocolomotor), 4th (trochlear), and 6th (abducens) cranial nerves, eyes are observed for symmetry of movement, globe position, asymmetry or droop of the eyelids (ptosis), and twitches or flutters of globes or lids.
Decreased cognitive function and the aging process.
What is not associated with the normal aging process?
Explain Babinski Reflex and what it may indicate
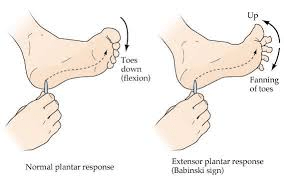 Toes up and fanning after plantar stroke is a positive Babinski .
Toes up and fanning after plantar stroke is a positive Babinski .
In adults and children over the age of 2 years, the Babinski reflex may be a sign of an underlying central nervous system disorder or another issue in the cortical spinal tract. Possible associated disorders include: spinal cord injury. tumors in the spinal cord.
Nerve tested in face with the sharp and dull test.
What is the trigeminal nerve test assessing the function of the trigeminal nerve, also known as cranial nerve V
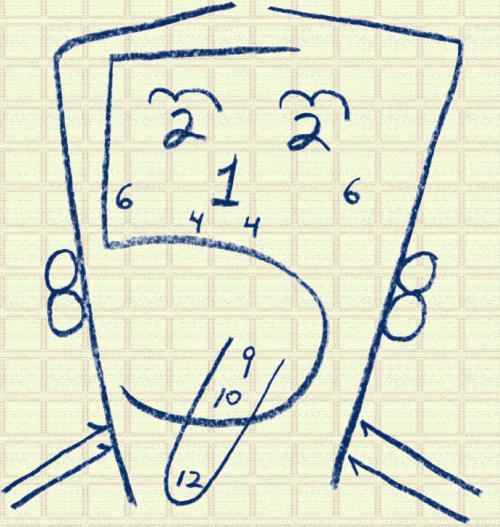
The most visual way to remember what the cranial nerves are associated with on the head and shoulders
Safety is priority with patients with neurological diseases. Testing Gag reflex and saying "ah" tests which nerves that protect the client's airway.
Safety is key in Maslow's hierarchy of needs for a client with diseases such as multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic sclerosis, and Guillain-Barre syndrome. The gag reflex is a protective response that prevents oral contents from entering the throat. It is controlled by the glossopharyngeal (CN IX) and vagus (CN X) nerves
Asking a patient to say "ahh" can be used to test the vagus nerve and test the gag reflex as part of a cranial nerve examination.
Double Jeopardy!!
Cranial nerve mnemonics are memory devices to help you remember the names of the nerves in order of one through 12 or remember whether nerves are sensory, motor or both. Name two mnemonics for both and be sure to know their function!
Cranial nerve mnemonics to remember the names of the nerves in order include:
- On old Olympus’s towering top, a Finn and German viewed some hops.
- Ooh, ooh, ooh to touch and feel very good velvet. Such heaven!
To remember cranial nerve functions, the words in the mnemonic start with:
- S for sensory.
- M for motor.
- B for both.
The word order mirrors the numerical order of nerves one through 12:
- Some say marry money, but my brother says big brains matter more.
- Some say my mother bought my brother some bad beer, my, my.
Broca's area.
What is the area of the brain affected by a CVA when the patient can only speak gibberish or profanity?
Areas assessed include eye opening, verbal response, and motor response.
What is assessed on the Glascow Coma Scale?
This test is used to test Postural instability and the inability to remain balanced during the test, It can trace back to potential neurological conditions. One condition may be cerebellar ataxia, determined by a lesion to the cerebellum
The client is asked to remove his shoes and stand with his two feet together. The arms are held next to the body or crossed in front of the body. The clinician asks the client to first stand quietly with eyes open, and subsequently with eyes closed. The client tries to maintain his balance.
The patient should be able to stand still with her feet less than shoulder-width apart. The patient should be able to walk with a smooth, coordinated motion There should be normal associated movement of the upper extremities. What is this test called and what are some conditions you may see an abnormal one?
What is GAIT analysis, abnormalities are often caused by an underlying condition or disease, such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, stroke, muscle disease (myopathy), brain or head trauma, congenital hip dysplasia, and joint pain or conditions (such as arthritis). Symptoms may include ataxia ( unsteady gait) widened base, crooked line, uneven arm swing, and slapping foot.
Unsteady gait which is a normal change associated with aging.
What is a normal finding in a patients gait who is 99 years old?
A common abnormal assessment finding if the third cranial nerve has compromised oculomotor function
What is Ptosis
Ptosis, or drooping of the eyelid, can be caused by damage to the third cranial nerve (oculomotor nerve). This nerve controls eye movements, pupil constriction, and upper eyelid elevation.

Name 3 infant reflexes different than adults

Palmar- The palmar grasp reflex allows a newborn to clench an object when pressure and touch are applied to the palm; however, this is not volitional in nature. The first readily recognizable fine motor skill that is crucial to normal development is unfisting.
Moro - Startle reflex
Babinski Positive until about 2 years of age then negative with normal assessment
- Widened pulse pressure: A large difference between systolic blood pressure (when the heart contracts) and diastolic blood pressure (when the heart relaxes)
- Bradycardia: A slow pulse rate, also known as a low heart rate
- Irregular respirations: Abnormal breathing
What is Cushing triad , a set of three signs that indicate increased intracranial pressure (ICP), or increased pressure in the brain
Describe the cerebellum.
What is the center for voluntary muscle movements, muscle tone, and balance /equilibrium?
CN XI may be compromised for your client. What symptoms may they show and how do you test this CN?
Clients with an injury to the Spinal Accessory Nerve CN XI may present with neck pain, asymmetrical shoulders, inability to shrug the shoulder, or weakness in the neck area.
CN 11 is tested by asking the patient to shrug their shoulders (trapezius muscles) and turn their head (sternocleidomastoid muscles) against resistance.
A nurse is asked to test the CN II nerve for a client regarding changes with her eyes. What does this CN test for and how would you test it?
Cranial Nerve II - Optic Nerve_ Visual Acuity Test
The visual acuity test is used to determine the smallest letters you can read on a standardized chart (Snellen chart) or a card held 20 feet (6 meters) away.
Even small changes in the assessment of wakefulness, alertness and awareness can be big problems and are a high priority if changes are noted.
What is the Level of Consciousness in the Mental Status assessment?
https://www.osmosis.org/learn/Altered_level_of_consciousness_(LOC):_Nursing
https://quizlet.com/458133075/assessment-jarvis-chapter-5-mental-status-assessment-flash-cards/
Triple Jeopardy!!!!
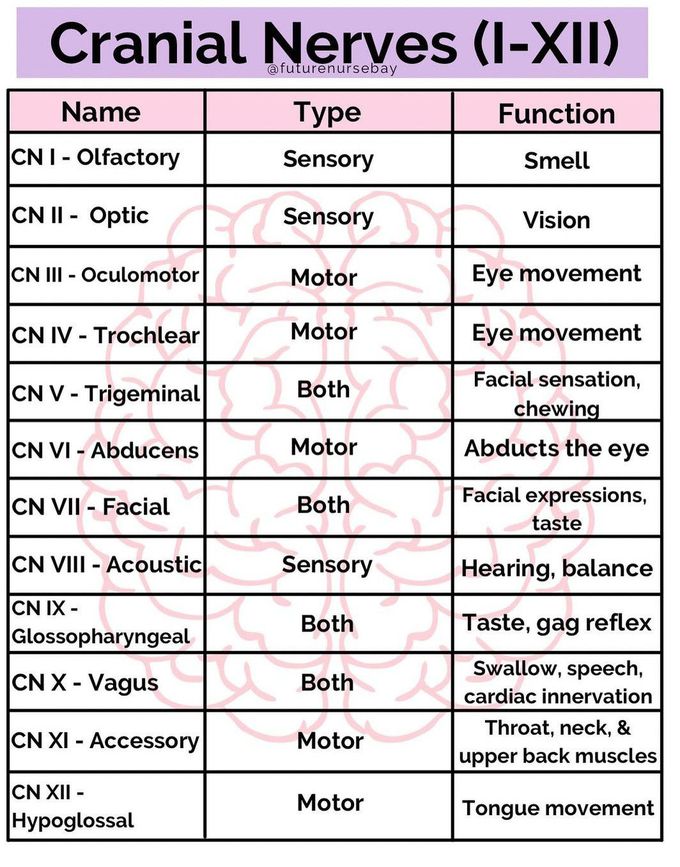
Name the 12 Cranial Nerves, their type and function!
What is Page 634 of Jarvis and Eckhart? :) Look it up or use this chart. Know it!!