The part of the brain/spinal cord that contains cell bodies
What is the grey matter?
This UMN system controls involuntary movement and is related to posture, balance and gait
What is the extrapyramidal system?
Unconscious proprioceptive input from the body is processed primarily in this part of the brain.
What is the cerebellum?
Nociception signals travel on this side of the spinal cord
What is the contralateral side?
Location where the decision to contract skeletal muscle is made
What is the spinal cord?
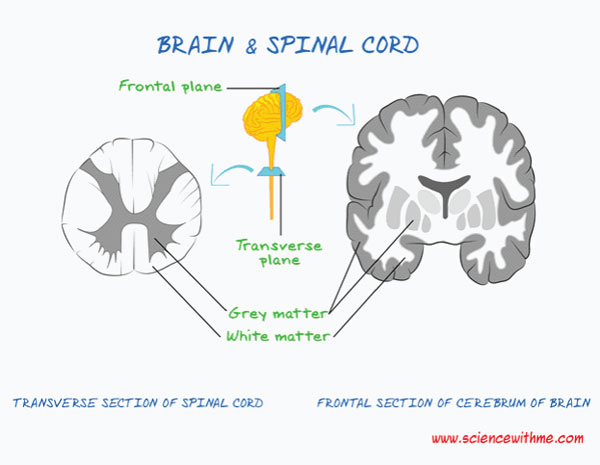
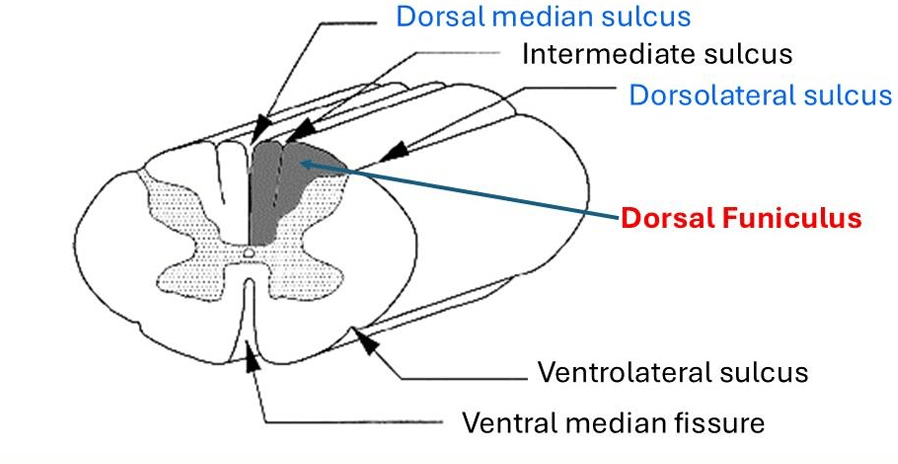
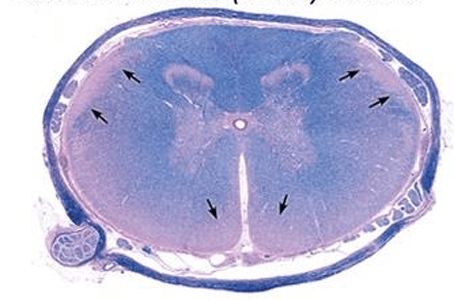
The part of the spinal cord that primarily contains ASCENDING tracts
What is the dorsal funiculus?
The signs you would see with a lesion at L4-S3
What is:
LMN signs in the pelvic limb
Normal thoracic limb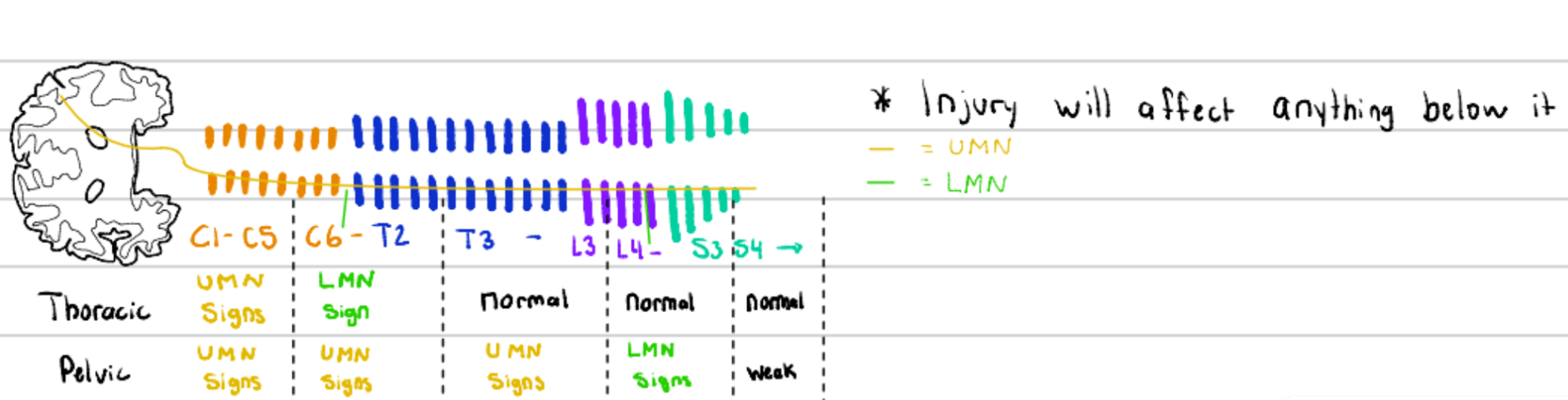
These two receptors detect stretch in muscles and tension in tendons to provide information about body position (proprioception).
Muscle spindle and golgi-tendons
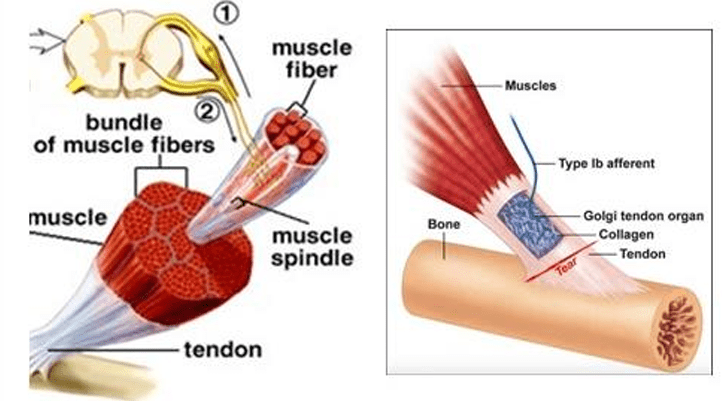
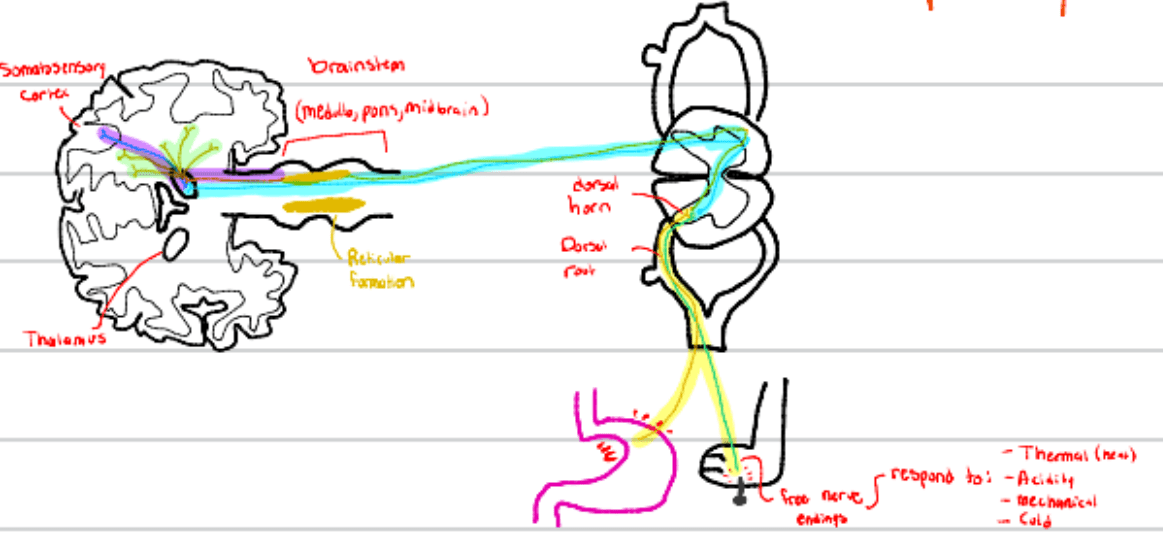
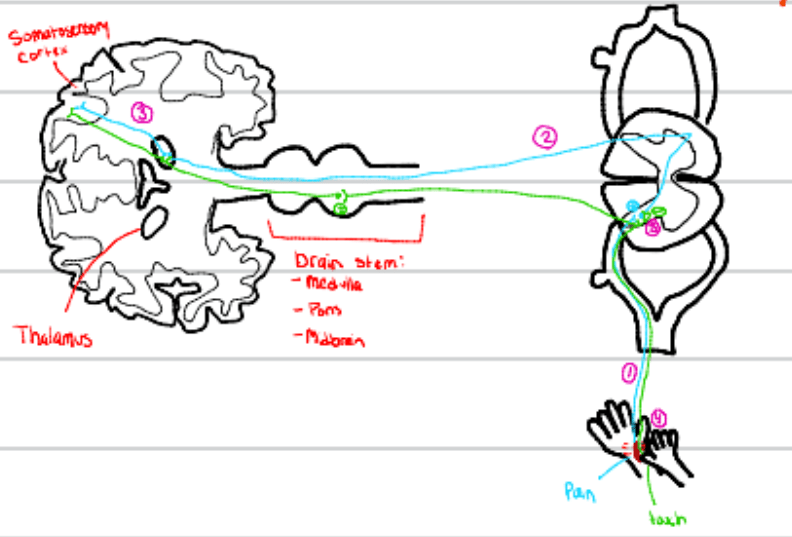
Third order nociceptive neurons synapse on this part of the cortex.
What is the somatosensory cortex?
This type of fiber is innervated by a-motor neurons and controls main contractile function
What are extrafusal fibers
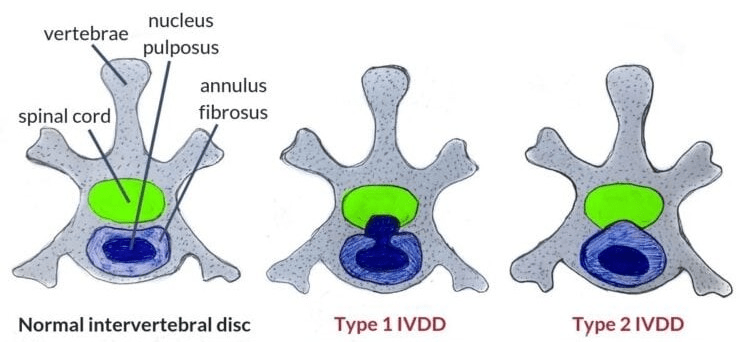
This disease involves the nucleus pulposus degenerating and being replaced with fibrocartilage
What is intervertebral disk disease type II? (PROTRUSION)
Locate the lesion:
A dog presents with decreased muscle tone, weakness, and reduced reflexes in the thoracic limbs, along with spastic gait and exaggerated reflexes in the pelvic limbs.
Where is C6-T2?

In this test, the dorsal surface of the paw is placed on the ground; failure to correct indicates a proprioceptive deficit.
What is the knuckling test?

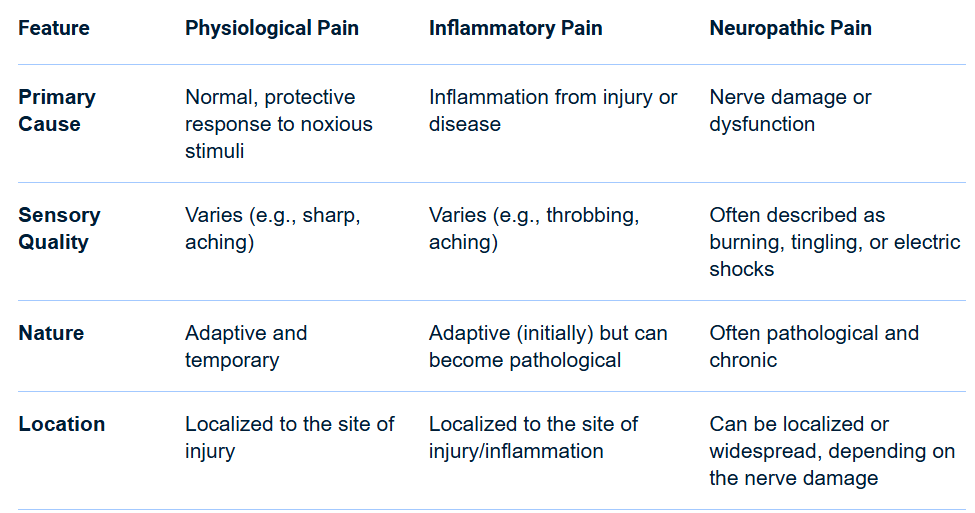
Name the three types of pain.
What is physiological, inflammatory, and neuropathic pain?
These three things maintain the negative charge in a neuron.
What is:
1. Negatively charged proteins (selectively permeable membrane)
2. Passive K+ channels
3. Na/K ATP pump
This disease involves the degeneration of spinal cord myelin and axons causing progressive ataxia, paresis, and several other neuro issues
What is degenerative myelopathy?
The signs of an UMN disease related to motor function, reflexes, atrophy, and muscle tone.
What is loss of voluntary movement (motor function), hyperreflexia, disuse atrophy, and increased muscle tone (spastic gait)

This system detects and responds to changes in head/eye movement and sends information to the cerebellum
What is the vestibular system?
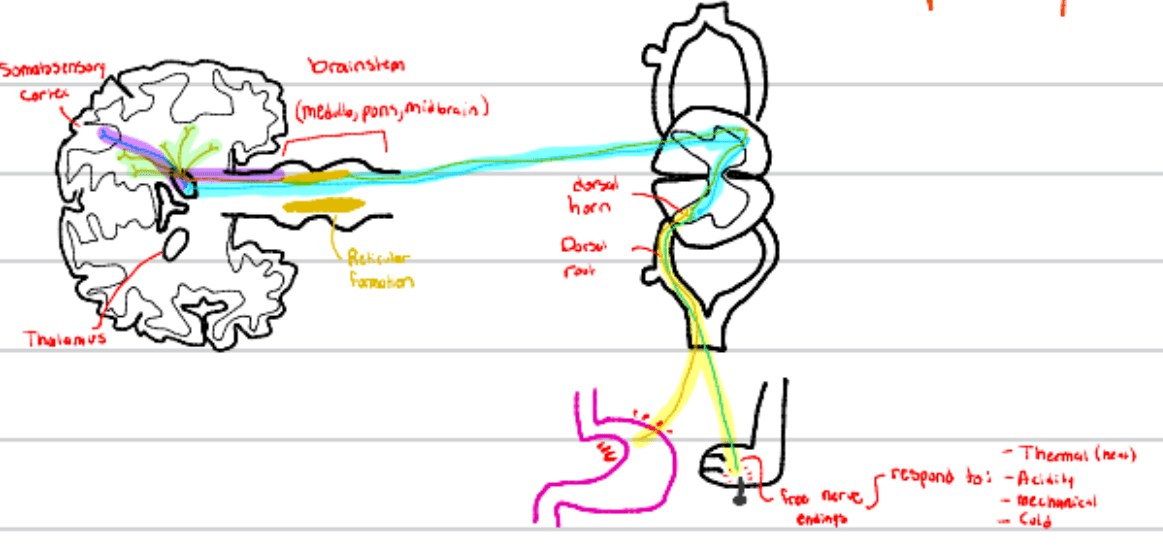
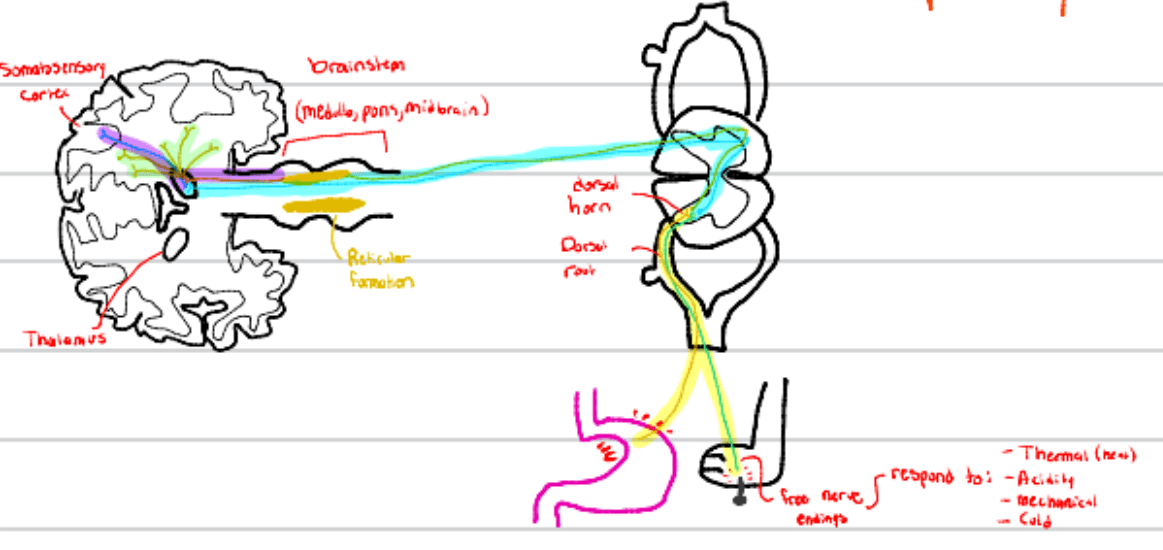
This tract transmits deep or visceral pain and is transmitted through these fibers (TWO ANSWERS!)
What is the spinoreticular tract? What are C fibers?
Four things that occur in response to neural damage.
What is:
1. Reorganization (primarily CNS)
2. Regeneration (primarily PNS)
3. Survival (primarily CNS)
4. Neurogenesis (RARE)
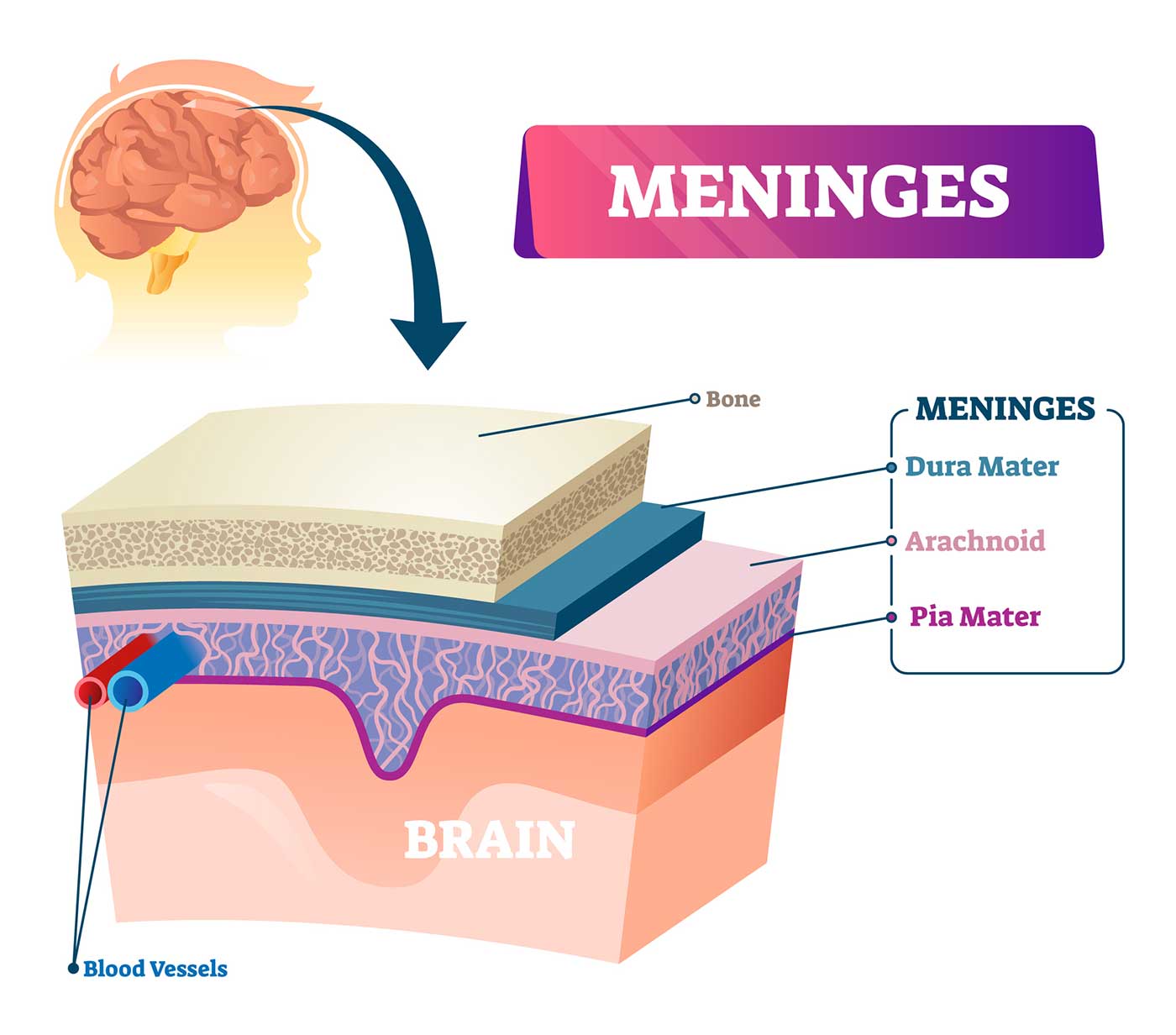
The three meningeal layers that protect the spinal cord and brain from innermost layer to outer
What is the pia mater, arachnoid membrane, and dura mater?
The four functions of upper motor neurons
What is:
1. Control (inhibit/facilitate) LMN function
2. Initiate and maintain normal voluntary movement
3. Maintain posture and tone (involuntary)
4. Control visceral muscle activity
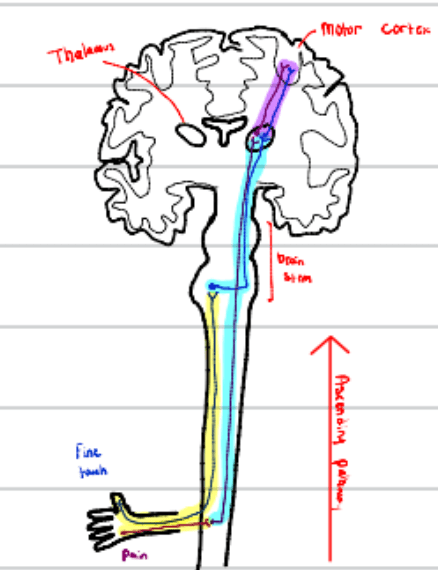
A dog with a lesion in the left thoracic spinal cord has a loss of conscious proprioception in the left pelvic limb, but pain perception remains intact. This indicates damage to this neuron in the sensory pathway.
What is the second-order neuron (UMN lesion)?
According to the gate control theory, activation of these fibers can inhibit nociceptive transmission in the spinal cord.
Aβ fibers (tactile stimulation)
A horse presents with possible nerve damage to his sciatic nerve. Name the reflex you would test, what stimulus this would incite, and the location of the spinal segment
What is the withdrawal reflex, nociception, and L6-S1