If you can't smell, then this CN is affected.

What is CN 1? or What is the Olfactory CN?
These two systems make up the neurologic system.
What are the CNS and PNS?
When testing this reflex, the nurse can expect to find an involuntary extension of the lower leg.

What is the patellar reflex? Or What is the Quadriceps reflex?
This is apparent when a person's response is much greater than the expected reaction to a traumatic life event.
What is a mental disorder?
This word describes an unsteady gait.
What is ataxia?
This vocabulary term is used to describe an exaggerated reflex.
What is hyperreflexia?
If you eat something gross and you gag, then cranial nerve is affected.
What is cranial nerve IX? or What is the Glossopharyngeal CN?
What is 12 pairs?
When inspecting and palpating the motor system, this term is used to describe abnormally small muscles with a wasted appearance.
What is atrophy?
These are the 4 main headings of mental status assessment.
What are Appearance, Behavior, Cognition, and Thought Process?
One would describe this mood or affect as:

What is Rage?
This term describes "repeated muscular movements", and should be tested when a patient has hyperreflexia.
What is clonus?
When your teen daughter gives you attitude and shrugs her shoulders, this CN is being activated.
What is cranial nerve XI? or What is the Spinal Accessory CN?
Humans have spinal nerves divided into these 5 categories.
What are cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal nerves.
This word describes the back and forth oscillation of the eyes when performing an eye exam and testing the cardinal positions of gaze.
What is nystagmus?
The Glasgow Coma scale tests consciousness by looking at these three categories.
What are eye opening, verbal response, motor response?
This area of the nervous system controls the coordination, equilibrium and balance.
What is the cerebellum?
When checking reflexes, the babinski sign is considered positive in adults when these 2 things happen.
What is dorsiflexion of big toe and fanning of all toes?
This CN is activated when you listen to and hear your professor explain the rules and expectations for class.
What is cranial nerve VIII? or What is the Acoustic CN?
This disease or illness occurs when there is an interruption of blood supply to the brain, and is the 5th leading common cause of death in the US.
What is a stroke? Or what is ischemia?
Asymmetric pupils can be caused when this process occurs inside the skull.
What is increased intracranial pressure (ICP)?
This mood or affect is described as "excessive-wellbeing; elated".
What is euphoria?
This test is done by asking a person to stand, feet together, arms by their side, with eyes closed, assessing balance.

What is The Romberg Test?
This reflex is seen in infants when startled, such as when jarring the crib or making a loud noise, is called this reflex.

What is the moro reflex?

What are CN III, IV, and VI? or What are the Oculomotor, Trochlear, and Abducens CN?
This is a term to describe an area of skin that is supplied mainly by one spinal cord segment.
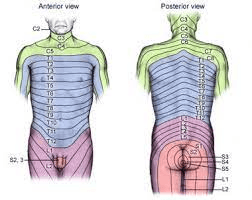
What is a dermatome?
This term is used to describe "the ability to read a number by having it traced on the skin".
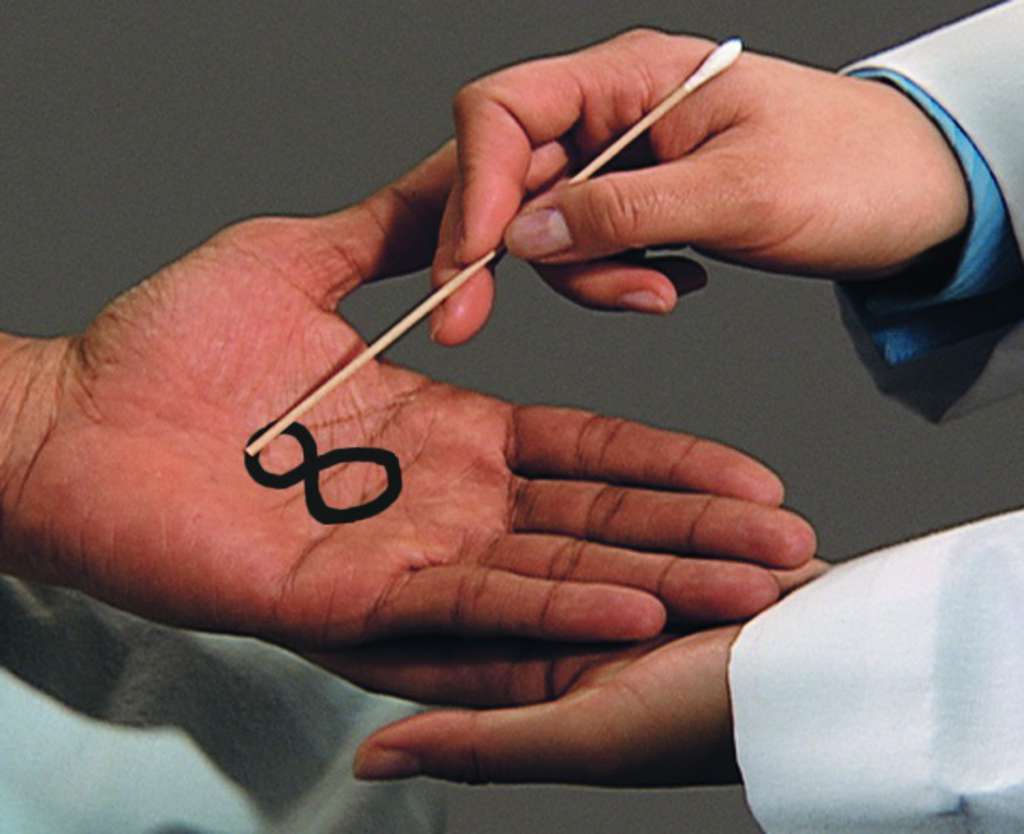
What is graphesthesia?
This condition is an acute confusional change and perceptive distrubance.
What is delirium?
This word describes a distorted speech sounds and may sound unintelligible.
What is dysarthria?
This term means a constant state of resistance; also known as dystonia.
What is rigidity?
This cranial nerve is responsible for the rooting reflex.
What is cranial nerve V?
This is the insulation on the axon that increases the conduction velocity of nerve impulses.
What is Myelin?
These are the three categories that you look at when inspecting and palpating the motor system.
What are Size, Strength, and Tone?
A nurse will test for this kind of memory when asking questions about their first job, their anniversary, or other historical events.
What is Remote Memory?
This term means an extreme resistance to any direction of head movement, and may occur with inflammation of the meninges.
What is nuchal rigidity?
This posture can be seen after injury occurs in the cerebral cortex.
What is decorticate rigidity?