Patient was involved in a car accident and is lethargic. Opens eyes to pain, doesn't vocalize, and withdraws to pain? What's the GCS? Should you intubate?
Eyes: 2
Vocal: 1
Motor: 4
Total: 7
Yes
Patient comes in with left facial droop and left arm weakness. MRI is shown below. What additional workup should you do? 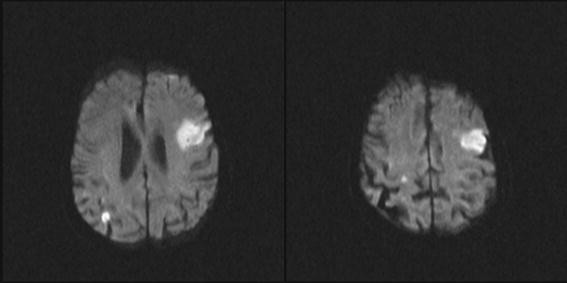
Cardioembolic stroke - should get EKG and echo
Patient has a new headache. Name three red flags for secondary headache
New headache, worsening, thunderclap, seizure, focal deficit, systemic signs, presence of a shunt, cancer history, waking up from sleep, vomiting
Name three medications that can be used in status epilepticus
Ativan, Versed, fosphenytoin, Keppra, VPA, pentobarbital, ketamine
Patient comes in after an intentional overdose of an unknown substance. They have dilated pupils and are tachycardic and hypertensive. Skin is dry and flushed. What kind of substance did they take?
Anticholinergic
Would have sweating in sympathomimetic overdose
What's the equation for CPP?
What are ways you can measure this in real life?
MAP - ICP
Bolt or external ventricular drain
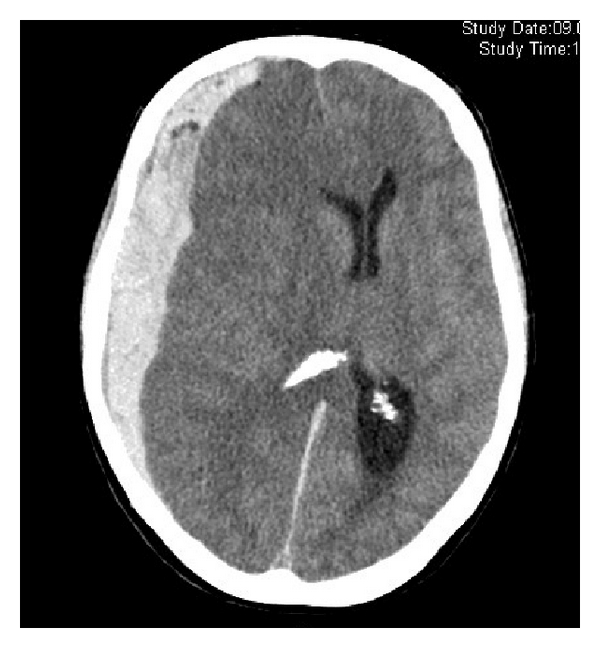
What is this?

Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Patient comes in after a fall. Lost consciousness but now feels fine. Later on becomes increasingly lethargic. You notice that the right pupil is fixed and dilated. What condition is this? What kind of vitals would you expect?
Epidural hematoma
Cushing triad - hypertension, bradycardia and irregular respirations
What seizure medication should be started prophylactically after someone has a TBI?
Trick question
What cranial nerves are tested in the corneal reflex?
5 and 7
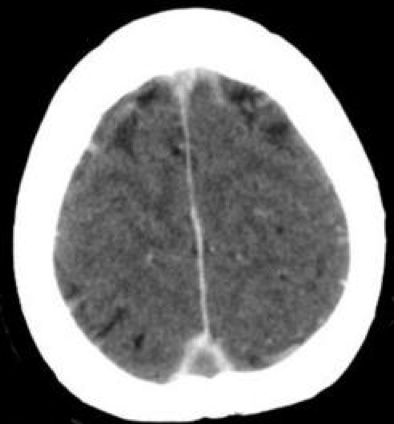
What is this? Acute or not? What if you saw this in a baby?
Subdural hematoma, acute
Abusive head trauma
This is a complication following subarachnoid hemorrhage that can cause ischemia. Bonus points if you can name the medications that helps to prevent this
Nimodipine (calcium channel blocker)
Name two temporizing measures you can do to acutely lower someone's ICP
Mannitol
Hypertonic saline
Hyperventilation
Patient has a cardiac arrest but ROSC is achieved within 10 minutes. Not responsive afterwards. What therapy should be considered for this patient? What is a common complication during this treatment?
Therapeutic hypothermia
High risk for seizures with rewarming
What must be done generally speaking before a brain death exam can occur
Name 3 classic exam findings seen in a basilar skull fracture
raccoon eyes, Battle sign, CSF rhinorrhea or otorrhea
Patient with cancer is admitted for encephalopathy and intubated. CT head with contrast shows the following. What is this, and what should you start?
Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis
Heparin
Patient comes in with diabetic ketoacidosis and glucose is aggressively lowered. Later on you notice the patient is becoming increasingly lethargic and eventually herniates. What happened?
Cerebral edema from rapid lowering of serum osmolality
Patient with hypertension begins complaining of a headache and blurry vision. Later on has a generalized tonic clonic seizure. What condition is this? What should you do?
PRES
Control blood pressure and administer anti-seizure meds
Patient is admitted after TBI and aggressively treated with hypertonic saline. After apparently stabilizing, you notice the patient is unable to move all extremities or their head although is still blinking. What happened?
Central pontine myelinolysis
Patient has a cervical spine injury from an MVA. Subsequently develops becomes very hypotensive. What kind of shock is this? What would the heart rate be? Would fluids help?
Neurogenic shock
Bradycardia
Nope need vasopressors
Patient suffers a cervical cord stroke. After several days you notice she is extremely hypertensive and bradycardic but doesn't say she's in any pain. What condition is this and what should you do?
Autonomic dysreflexia
check bladder and bowel retention
Patient has a large cerebellar stroke and develops ataxia. Later on in hospitalization they become increasingly obtunded. What life-saving measure should be considered (besides the temporizing measures previously mentioned)?
Hemicraniectomy
Patient is admitted to NCCU in refractory status and started on a pentobarbital drip. You go in the room and see this on EEG. Is this good or bad?

Burst suppression
Technically good assuming you're doing it on purpose
Patient has a stroke and is intubated. You notice the patient has pinpoint pupils and is unresponsive. What should you check first?
What type of sedation they're on