On saturday night, a group of adventurous teenagers went on a rave and used the most "raved" drug--ecstasy, a substance that affects this neurotransmitter
1. dopamine
2. glycine
3. norepinerphrine
4. serotonin
5. glutamate
Serotonin.
electrocerebral silence is seen in this condition
brain death
agraphia without alexia, right–left disorientation, acalculia, and finger agnosia
Gerstmann's Syndrome
Conventional TMS usually targets this area of the brain
Left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
This imaging modality uses 99mTc-hexamethylpropyleneamine oxime as tracers
SPECT
On Saturday night, you went to trivia with some friends who had a bit too much to drink. In the spirit of trivia, you mentioned this cool fact about how alcohol can have this effect on sleep architecture (two possible answers)
1. decreased latency of sleep onset
2. increased latency of sleep onset
3. decreased stage 3-4 sleep
4. increased stage 3-4 sleep
1. decreased latency of sleep onset
2. decreased stage 3-4 sleep
Frontocentral beta activity on EEG is seen in this condition
normal adult drowsiness
Often develops as a nonparaneoplastic phenomenon in association with diabetes and polyendocrinopathy and, often, antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase.
Stiff Person Syndrome
(The GAD antibody you get on consults!)
This neuroanatomical structure, located in the frontal lobe, is particularly important for decision-making and self-regulation. Dysfunction here can lead to impulsive behavior and personality changes seen in personality disorders or frontal lobe damage.
What is...?
A) Anterior cingulate cortex
B) Prefrontal cortex
C) Basal ganglia
D) Temporal lobe
Prefrontal cortex

A patient with this type of dementia has the above FDG-PET scan.
FTD
Let's cerebrate on Saturday night with the cerebellum!
Jk, bad pun.
But on the topic of cerebellum, what kind of cells project out of them?
1. granule cells
2. golgi cells
3. basket cells
4. stellate cells
5. purkinje cells
Purkinje Cells
(all other cells do not project out of the cerebellum)
bilaterally synchronous triphasic slow waves is seen in this condition
hepatic encephalopathy
Painful facial palsy, vertigo, ipsilateral hearing loss, and vesicles in the external auditory canadal, caused by VZV
Ramsey Hunt Syndrome
Mammilary Bodies (From Wernicke's Korsakoff)
A patient who presented with loss of consciousness was found to have the image below--what imaging modality was utilized?
CT
Saturday night palsy involves what nerve?
1. Radial nerve
2. Ulnar nerve
3. Median nerve
4. Subscapular nerve
5. Suprascapular nerve
Radial nerve
increase in delta wave frequency on EEG is seen with use of this substance
Benzodiazepine use
neoteny, vestigia, atavisms, microgenia, mongoloid fold, simian crease, brushfield spots
Down's Syndrome
Neoteny: retention of juvenile features
Vestigia: incomplete morphogenesis
Atavisms: revision to ancestral traits
Microgenia: small chin
Mongoloid fold: skin fold that covers inner corner of eye
Simian Crease: single palmar crease
Brushfeld spots: white/grey spots in periphery of iris
The most common cause of temporal lobe epilepsy is
Hippocampal sclerosis
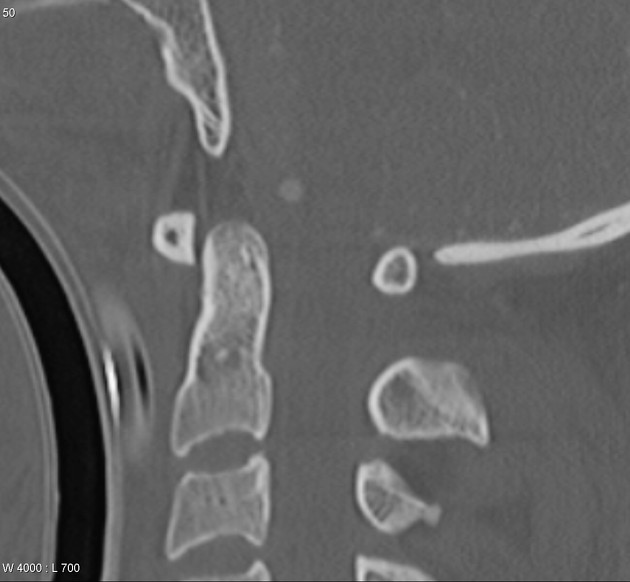
Which congenital condition would cause the following finding? (There are 3, name any 1 )
Down's
NF1
Marfan's
It's Saturday night and a group of teenagers decided to make bad choices and smoke nicotine, which acts on this receptor
1. nAch
2. mAch
3. NMDA
4. dopamine
5. norepinephrine
6. alpha 1 adrenergic
Nicotinic Ach
PLEDs (Periodic lateralized epileptiform discharges) is the characteristic EEG finding in this condition
herpes encephalitis (but it can be found in other conditions too)
infantile spasms, hypsarrhythmia, and psychomotor developmental arrest
West syndrome
The cortical– striatal–thalamic–cortical (CSTC) circuit is implicated in the following condition
1. Depression
2. Mania
3. Obsessions and compulsions
4. Psychosis
5. Trauma processing
3. Obsessions and Compulsions
The following image finding is seen in this condition.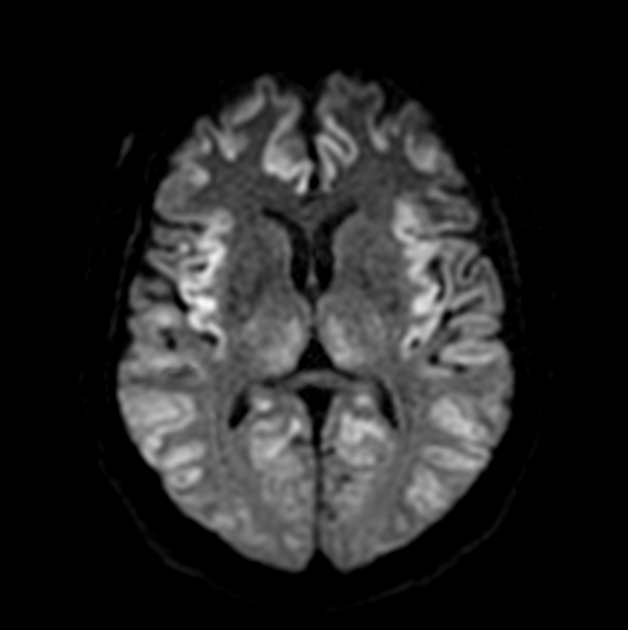
CJD