A. HIV testing
B.Wait for culture results
C. Enforce Respiratory Isolation
D. Respiratory isolation and prescribe Rifampin for close contacts
E. Make way to your emergency bunker, the zombie outbreak has started
Also there is no known cure for the solanum virus so just accept the pending zombie apocalypse.
A. Work safety
B. Ca and Vit D supplementation
C. Driving
D. Alcohol consumption
E. Epilepsy Surgery
Epilepsy Surgery is reserved for patients who are intractable to medical management and have failed at least 2 AEDs.
Calcium and Vitamin D supplementation should be initiated with AEDs due to increased risk of osteoporosis. Safety issues should be addressed including work and driving safety. Alcohol should be avoided with AEDs.
The father of an 18-month old girl expresses concern that she has always had trouble falling asleep, even when at home, but most notably when removed from her unusual environment. The girl is otherwise doing well. She can run, stack four cubes, draw a vertical line, and undress herself. Her vocabulary is limited to mama, dada, baba. She does not point to things, but she does pull her parents toward desired objects. She does not yet show interest in pretend play with dolls, tea sets, stuffed animals, or other objects. She spends most of her playtime watching a ceiling fan spin. When her parents try to redirect her, she becomes agitated and resists changing activities. Physical exam is normal.
Which one of the following diagnosis is most likely?
A. Social Communications disorder
B. Developmental language delay
C. Rett Syndrome
D. Hearing impairment
E. Autism Spectrum Disorder
E. Autism Spectrum Disorder
According to the AAP, all children should be screened for autism spectrum disorder at ages 18 and 24 months
A 22-year-old college student reports having several unpredictable episodes of intense fear accompanied by dyspnea, diaphoresis, palpitations, chest pain, and tremor. The episodes which have occurred a few times a week for the past 2 months, begin abruptly and reach a peak within 10 minutes. They occur unpredictably and can happen anywhere. When they occur in public, such as in class or when driving, he feels uncomfortable and embarrassed. The fear of these episodes has caused him to curtail his activities. These features are most consistent with which diagnoses
A. Somatic Symptom Disorder
B. Generalized anxiety disorder
C. Social Anxiety Disorder or Phobia
D. Panic Disorder
E. Specific Phobia
D. Panic Disorder
Recurrent episodes of intense fear accompanied by somatic symptoms that begin abruptly and peak with 10 minutes are most consistent with a diagnosis of panic disorder.
A. C-3 disk lesion
B. Ulnar nerve compression
C. C-4 Disk lesion
D. Median Nerve Compression
E. Radial Nerve compression (i.e. Saturday Night Palsy.)
F. Saturday Night Fever

What is the most common infectious cause of peripheral neuropathy in the world (not just the US)?
A. HIV
B. Lyme
C. Leprosy
D. Hepatitis C
E. Tuberculosis
C. Leprosy, caused by Mycobacterium leprae. Usually presents with hypopigmented anesthetic patch. The sensory deficits start with loss of temperature, followed by loss of pain then tactile sensations.
A 33 year old recently married woman with a history of focal seizures has been seizure-free while taking valproic acid for the past 2.5 years. She asks for advice about becoming pregnant safely within the next 12 months. Her epilepsy was diagnosed at age 10, she is otherwise healthy and takes no other medications. She has never been pregnant.
If this woman still needs an antiepileptic medication, which one of the following agents is most appropiate?
A. Levetiracetam
B. Phenytoin
C. Phenobarbital
D. Topiramate
E. Carbamazepine
A. Levetiracetam (keppra)
The newest anti-epileptic drugs Lamictal, levetiracetam, Trileptal, and Gabitril, are all class C drugs for pregnancy.
Valproic acid, phenytoin, phenobarbital, primidone and carbamezapine are all Class C drugs. Valproic acid in particular interferes with Neural tube defects and should be avoided. Additionally it is recommended to attempt Monotherapy while pregnant and take the lowest effective dosage.
Which one of the following motor milestones would you expect a 24-month old boy to exhibit?
A. Pedal a Tricycle
B. Balance on one foot for 3 seconds
C. Kick a ball
D. Walk up stairs while alternating feet
C. Kick a ball
Motor milestones at 24 months of age include throwing overhand, kicking a ball, walking down stairs with both feet on each stair, and jumping in place
Which one of the following diagnoses is most likely in a patient with Weakness of the right biceps, pronator teres, and brachioradialis; numbness in the thumb and forefinger; an absent biceps reflex; and a negative Tinel sign?
A. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
B. Thoracic Spinal cord radiculopathy
C. C6 Cervical radiculopathy
D. Cervical Spinal cord injury/myelopathy from a C1 lesion
E: C8 cervical radiculopathy
C. C6 Cervical Radiculopathy is the most likely diagnosis in a patient with hand numbness, biceps weakness, and an absent bicep jerk who does not have a Tinel Sign
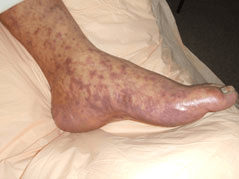
What is Paralysis, usually of the lower extremities (I'll also accept hearing loss although it is less common.) The patient is suffering from Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever as noted by the peripheral rash that moves inward. Of Note only 60% of patients remember a tick bite.
Lyme disease is an incorrect answer because it typically does not cause nausea vomiting. Additionally it is characterized by a very different Bulls eye rash.
All of the following are indicated in the treatment of petit mal seizures (aka absence seizures) Except:
A. Ethosuximide
B. Acetazolamide
C. Valproic acid
D. Clonazepam
E. Phenytoin
E. Phenytoin is not indicated in the treatment of petit mal seizures. The other options are indicated.
Which one of the following management approaches is most appropriate for a 7-year-old boy diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder after presenting with echolalia, avoidance of eye contat, and repetitive actions?
A. Applied Behavioral analysis
B. gluten-free diet
C. Treatment with Olanzapine
D. Treatment with Methylphenidate
E. Treatment with naltrexone
The Mainstay of treatment for children with autism spectrum disorder is applied behavioral analysis
A. Diazepam
B. Fluoxetine
C. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
D. Haloperidol
C. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) seeks to change the way a trauma victim feels and acts by changing patterns of thinking or behavior, or both, responsible for negative emotions.
Which one of the following historical features or physical examination findings is most consistent with a Central, rather than a peripheral, cause of vertigo?
A. Tinnitus
B. Nystagmus that changes direction and does not suppress with visual fixation
C. Hearing impairment
D. Recurrent episodes of vertigo lasting less than one minute each
E. A 30 second episode of nystagmus on Dix-Hallpike Maneuver
B. Nystagmus that changes direction and does not suppress with visual fixation is a feature suggestive of central vertigo.
An Afebrile 39 year old woman presents to the emergency department after experiencing an episode of new-onset left-hand jerking that, within seconds, progressed proximally to the elbow and then to the entire left limb before culminating in a fall with loss of awareness. Her physical and neurologic examinations are normal, as is a comprehensive metabolic panel. Which one of the following diagnostic tests is most appropriate?
A. MRI of the head
B. Electrocephalogram
C. EKG and Echo
D. Blood and Urine testing for drug and alcohol
E. Cerebrospinal fluid testing for infection or inflammation
A. The most useful investigation in a patient with an initial unprovoked focal seizure is cerebral imaging preferably with MRI. It can visualize the cerebral abnormalities and structural lesions that are typically associated with such seizures. CT is allowable in emergency when MRI is not available or contraindicated.
A. In delirium it is rare to find an underlying medical cause.
B. A primary feature of delirium is inattention
C. Dementia is characterized by an acutely fluctuating course
D. Delirium only occurs in patients with dementia
D. They are the same. After all memories are just a construct of the matrix.
A diagnosis of delirium requires the following: disturbance of conscious, with reduced ability to focus attention, disorientation, or other change in cognition that cannot be accounted for by a preexisting dementia, acute onset with fluctuating course and evidence that the disturbance is caused by an underlying medical condition or drug. Dementia is chronic and usually has an insidious onset. Dementia can not be reversed. Patients with dementia usually have intact attention.
Which one of the following diagnoses is most likely in a 19 year old female college student with persistent somatic complaints in multiple organ systems that result in academic and social impairment, but are not fully explained by a medical condition?
A. Conversion disorder
B. Malingering
C. Illness anxiety disorder
D. Factitious disorder
E. Somatic symptom disorder
The most likely diagnosis in a young woman who has persistent physical complaints that involve multiple organ systems, that result in functional impairment, and that may or may not be fully explained by a medical condition is somatic symptom disorder.
A 64 year old man with hypertension and type II DM reports worsening back discomfort and bilateral leg pain when walking his dog each day. He denies recent trauma, sensory symptoms, or bowel/bladder incontinence. He has noticed that the leg pain has worsened during the past few weeks. The pain not occurs after he walks only a few blocks, but it improves if he sits to rest or if he bends forward at the waist to walk uphill.
On physical examination, his pedal pulses cannot be appreciated, but his extremities are warm and well perfused. He is currently asymptomatic with intact strength, sensation, and reflexes. In all four limbs. Vibration and proprioception are intact at the great toe. When he walks down the office hallway he reports no pain and has a normal, narrow-based gait.
Which one of the following conditions is most likely to explain this patients pain?
A. Neurogenic claudication related to spinal stenosis
B. Myelopathy related to bulging disk
C. Peripheral Neuropathy related to diabetes
D. Impaired muscular blood supply related to peripheral vascular disease
E. Radiculopathy related to a growing tumor
A. The most likely cause of worsening bilateral leg pain that occurs while the patient is walking and improves with sitting down or bending forward at the waist is neurogenic claudication related to spinal stenosis. Narrowing of the spinal column can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots, resulting in pain, numbness and weakness. The most common cause is degeneratvie disease.
An 18 year old female with a history multiple sexual partners presents through the ED with new onset Bizarre behavior, unusual speech, and hallucinations. CSF shows lymphocytic pleocytosis, increased number of erythrocytes, and elevated protein. MRI shows bilateral temporal lobe abnormalities. HSV PCR tests of CSF are positive. What treatment should be started?
IV acyclovir
This patient has HSV encephalitis. Nearly 2/3rds of patients who survive HSV encephalopathy have Significant long term neurologic deficits. Because of this IV acyclovir must be started when suspected. Studies have shown IV acyclovir is most effective when given early.
A 29 year old man with history is brought to the ED for treatment of traumatic injuries after driving while inebriated. His vital signs are normal but he is too sedated to provide a history. He is hospitalized and becomes intermittenly agitated and tremulolus. Vital signs include a HR of 116, BP 190/100 and a temp of 39.2.
On the second day of hospitalization, the patient experiences a tonic clonic seizure that is witnessed by nursing. Lab testing follows.
AST: 368 (0-35)
ALT: 174 (0-35)
Alk Phos: 206 ( 30-120)
Platelet: 78,000 (150,000-350,000)
PT: 20.0s (11.1-13.1s)
Which of the following medications is the most appropriate for this patient?
A. Lorazepam
B. Alprazolam
C. Clonazepam
D. Chlordiazepoxide
E. Haldol
F. Soylent Green
A. The two benzodiazepines that are most appropriate for treating alcohol withdrawal in patients with hepatic dysfunction are lorazepam and oxazepam
A 64 year old woman with mild Alzheimer disease presents to discuss whether she should begin taking a cholinesterase inhibitor. Both she and her husband are quite anxious about it. They want to know what they can expect in terms of symptom improvement and her long term prognosis if she starts taking the medication.
Which of the following is the best way to explain the benefits of treatment with a cholinesterase inhibitor?
A. Although improvement in cognition is variable the medications prevents or delays nursing home placement
B. Most patients have a noticeable improvement in cognition but depression is a common side effect
C. Some patients have a noticeable improvment in cognitions but many do not
D. Most patients have a substantial, noticeable improvement in cognition and quality of life
E. Although improvement in cognition is variable, the medication changes the long term underlying course of the disease
C. Some patients have a noticeable improvement but many do not
Clinical trials for Cholinesterase inhibitors (donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine) for mild-to-moderate Alzheimer disease have shown statistically significant mean differences from placebo on standardized measures of cognition. However, the differences have been small, and their clinical importance for many patients is unclear. It is reasonable to offer patients a therapeutic trial, but the limitations of cholinesterase inhibitors should be acknowledged.
A 20-year old woman with a history of anorexia nervosa reports that she has been feeling increasingly depressed since breaking up with her boyfriend 2 months ago. She reports that she has been a "little depressed" for the past 2 years and, during that time, began to engage in some bad habits, including restricting her food intake to about 700 calories daily and excercising excessively.
A Brief interview reveals that she has a preoccupation with her body image and fears that she is "too fat for anyone to love." When asked, she admits to rare bingeing followed by vomiting. Physically, she feels "tired, weak, and dizzy."
She has a temperature of 37.0C a heart rate of 48 beats per minute, and a blood pressure of 84/56. Her height is 170 cm (5'7") and her weight is 46 kg (101 lbs) her BMI is 15.9. Physical examination reveals dry mucous membranes and prolonger capillary refill time.
Which one of the following management approaches is most appropriate.
A. Prescribe and atypical antipsychotic
B. Refer for acute inpatient hospitalization
C. Prescribe SSRI
D. Refer for outpatient nutritional counseling
E. Refer for outpiatent psychiatric evaluation
In a patient with anorexia nervosa who presents with clinically unstable vital signs, the appropriate next step in management is urgent care in an inpatient setting
A 64 year old man presents following two unexplained falls. Each fall occurred while he was walking; he did not trip, did not notice any palpitations or aura, and did not lose consciousness. He reports no chest pain, dizziness, visual or memory impairment, numbness or weakness of the extremities. He has a history of hypertension treated with HCTZ and Amlodipine. He is not taking any other medications.
Vital signs are normal without postural hypotension and a comprehensive physical examination is normal. Mental status is within normal limits. Cranial Nerves II through XII are tested and found normal. The patients eye movements are normal, but his affect appears muted.
Motor examination shows normal power in all limbs but an increase in muscle tone, and movements are slow. A tremor is present at rest (right greater than left) and when the patient attempts to hold arm position. Sensory examination and reflexes are normal. ON gait testing there is no ataxia. The patient uses short shuffling steps with decreased arm swinging bilaterally.
What is the diagnosis?
Parkinson's Disease.
The combinations of resting tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia is consistent with a diagnosis of Parkinson Disease. Significant cognitive impairment early in the course of the disease would suggest dementia with Lewy bodies, and medications lists should be reviewed carefully to exclude extra-pyramidal syndromes.