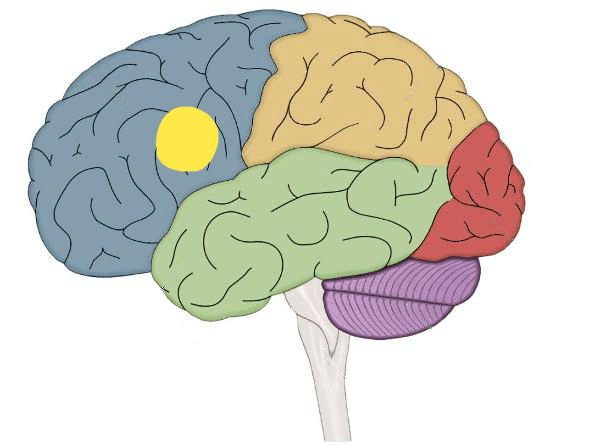
 This area of the brain controls language expression and syntax.
This area of the brain controls language expression and syntax.
Broca's Area
This structure is made up of many nuclei, and contains both the thalamus and hypothalamus.
The Diencephalon
During the resting potential, there is more of this element that sodium.
Potassium (K+)
This layer of the meninges is the most superficial.
The Dura Mater
This structure is the joining area for several arteries and is located at the bottom (inferior) side of the brain.
The Circle of Willis
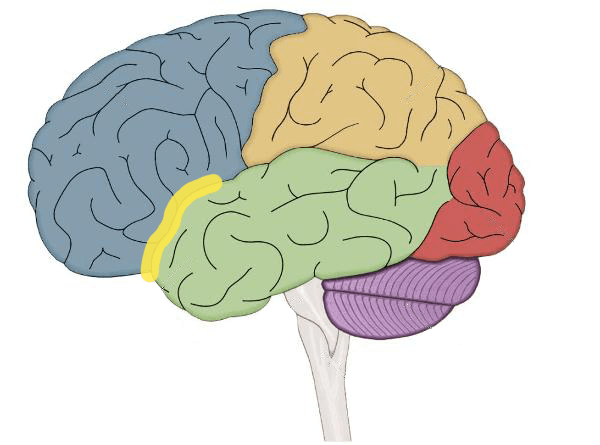 This area is the place where the frontal and temporal lobes meet.
This area is the place where the frontal and temporal lobes meet.
This structure's functions includes processing most sensory info, encoding information passed through it, and maintaining sleep and wake cycles.
The Thalamus
These nerves carries both motor and sensory info to and from areas below the neck.
The spinal nerves
The space below this layer contains CSF, cranial nerves, arteries, and veins.
The Arachnoid Mater
The ventricles of the brain contain this fluid.
Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF)
This lobe contains areas such as the hippocampus and Wernicke's Area
Temporal Lobe
This structure, that deals with hormone control, is associated with the hypothalamus.
The Pineal Gland
During the action potential, this is the primary cause of the rising phase.
The rapid entry of sodium (Na+) into the cell.
An epidural hemorrhage is the laceration of this artery.
The middle meningeal artery (and branches).
The anterior, posterior, and inferior horns are part of this system of ventricles.
The Lateral Ventricle System.
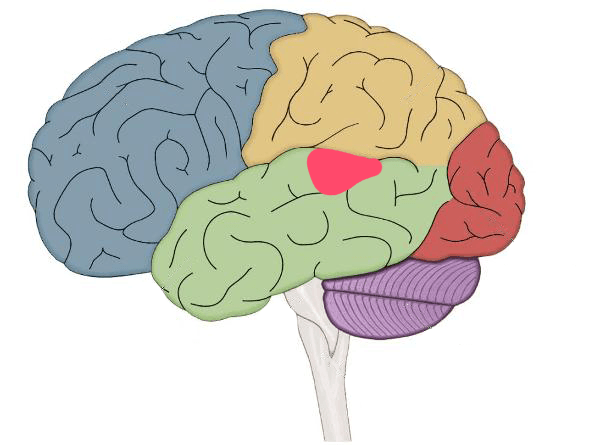 This area deals with language comprehension and lexical semantics.
This area deals with language comprehension and lexical semantics.
Wernicke's Area
This structure is made up of a set of 3 nuclei, including the caudate nucleus.
The Basal Ganglia
These nerves carry motor and sensory information to and from areas above the neck.
These bony frameworks help protect the brain, along with the meninges.
The spinal column and the cranium.
This artery passes laterally and superiorally between the temporal lobe and the insula to cortex.
The Middle Cerebral Artery
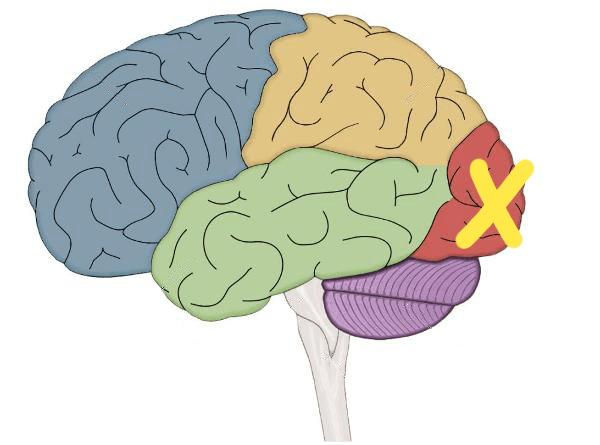
This lobe deals with visual processing.
The Occipital Lobe
This type of ion channel works consistently without regard to changes in the membrane.
Non-Gating Ion Channels
These are the names of the two potential spaces inside the meninges.
The epidural and subdural spaces.
This artery supplies blood to the occipital lobes, the inferior lobes, and the thalamus, to name a few.
The Posterior Cerebral Artery