What structure passes through the foramen magnum?
Spinal cord
(along with some other arteries and veins supplying the brain and cranial nerve X1 (accessory))
What is the difference between gyri and sulci?
gyri= Ridges (mountains)
sulci= Grooves
What is the layer in the meninges that is named because of its resemblance to a “spider web”
Arachnoid Layer
What is the layer that was pre-removed in the image during your dissection?
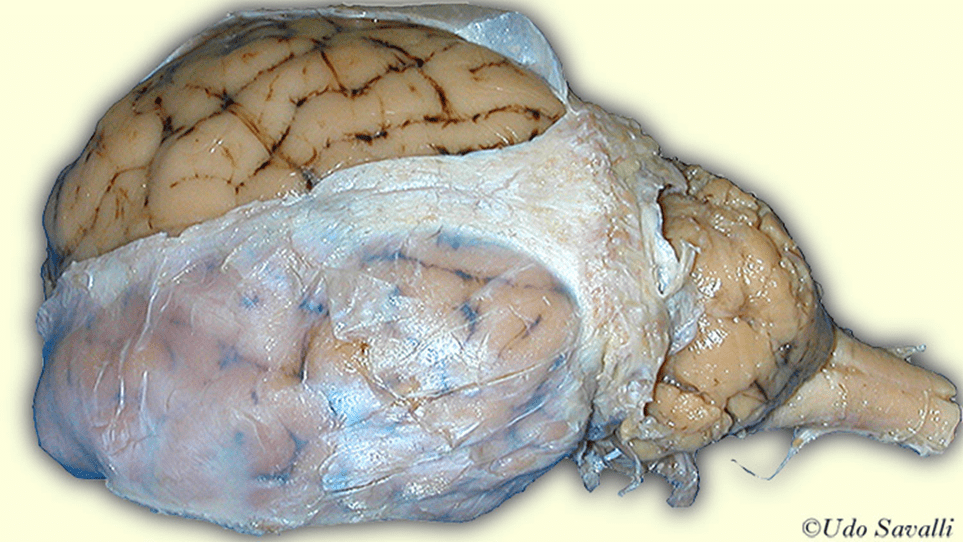
Dura mater
What bones make up the oral cavity?
Mandible, maxilla, and palatine bones
What is the branching tree-like structure called, and what part of the brain is it associated with?
arbor vitae; cerebellum
What sinus is being pointed to by the black arrow?
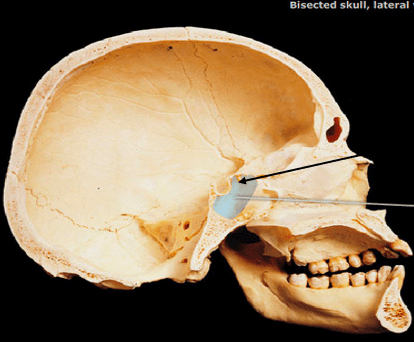
Right Sphenoidal Sinus
Name all three structures labelled A,B and C.
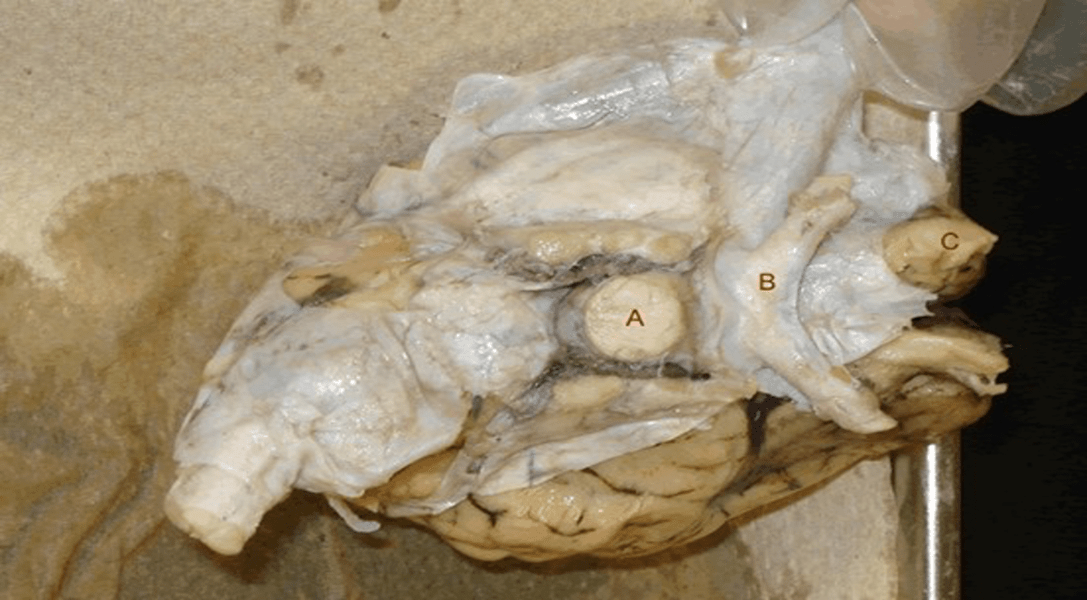
A = pituitary gland
B = Optic Chiasm
C = Olfactory Bulb
What bone is shown with an arrow?
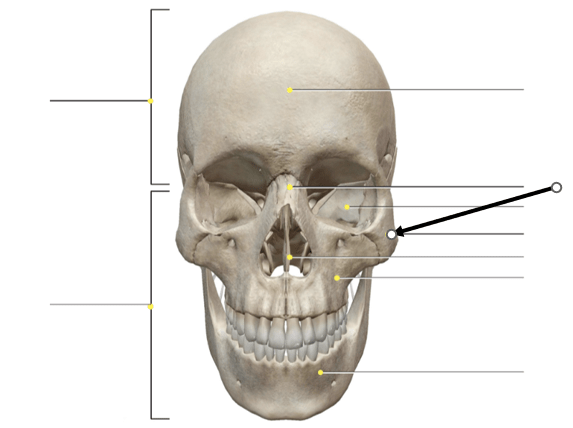
Zygomatic
Name the structures #1, #2, and #3.
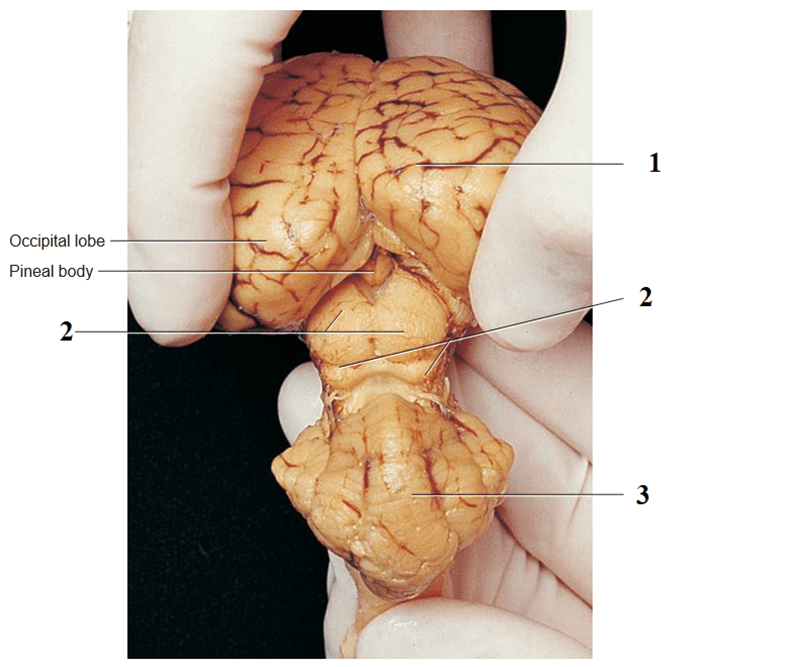
1) Cerebrum, 2) superior and inferior colliculi, 3) Cerebellum
What is the largest sinus(es) most prone to infection, and where are they located in the skull?
Right and Left Maxillary Sinuses
Located posterior to the nasal cavity
What Cranial Nerve is being pointed to by the yellow arrows, and what number is this cranial nerve?
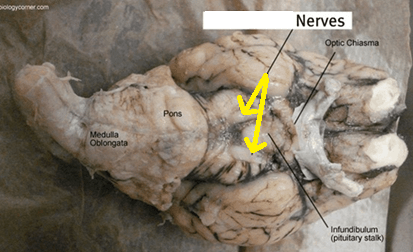
CN III - Occulumotor
The sphenoid bone is responsible for holding a “master gland” of the body, producing many hormones. What is this gland, and what part of the sphenoid bone is it located?
pituitary gland; sella turica
What are the structures that make up the brainstem? Name one function for each.
medulla oblongata: It relays messages between the brain and the spinal cord; controls involuntary functions of the respiratory and digestive and contributes to sensory functions. The respiratory center controls the rate and depth of breathing, and the cardiovascular center is responsible for the rate and force of the heartbeat and blood pressure reflexes. Other reflex centers in the medulla are for coughing, vomiting, and sneezing.
pons: It acts as a relay center between the higher brain centers and the spinal cord and contains nuclei responsible for breathing rhythms.
midbrain: It regulates vision, hearing, motor control, alertness, and thermoregulation. The superior part has reflex centers involved in eye, head, and neck movements with visual stimulation, whereas the inferior part has reflex centers involved in auditory stimuli that result in head and trunk movements.
Identify the following structures (on the parietal bone of the skull): #6, #7, #8, and #9
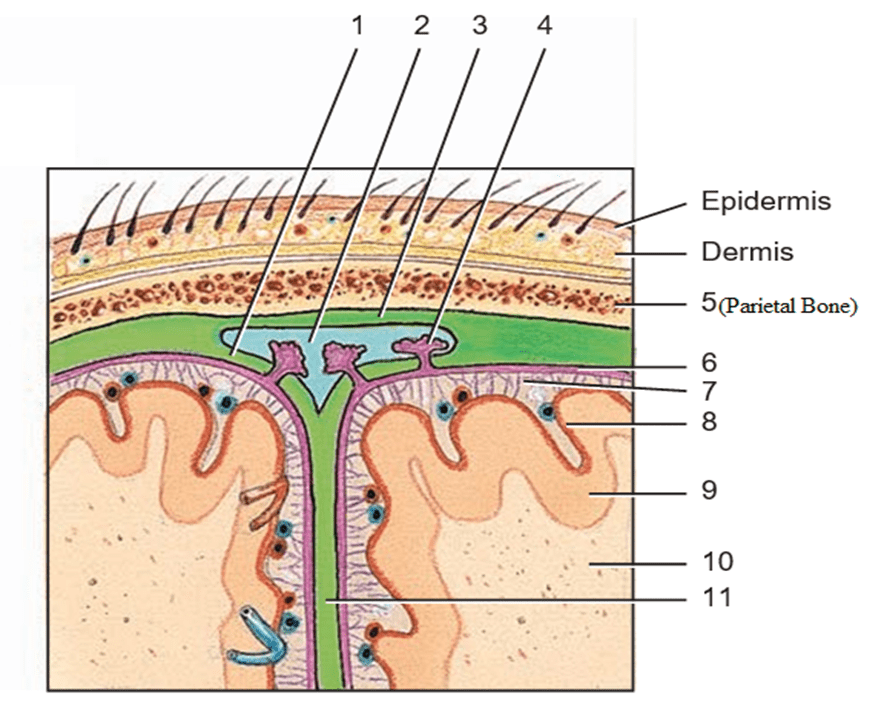
1) meningeal layer of dura mater
2) superior sagittal sinus
3) periosteal layer of dura mater
4) arachnoid villus
5) parietal bone
6) arachnoid mater
7) subarachnoid space
8) Pia mater
9) cerebral cortex
10) White matter
11) Flax cerebri
What is this structure (white matter) called, and what is its English translation?
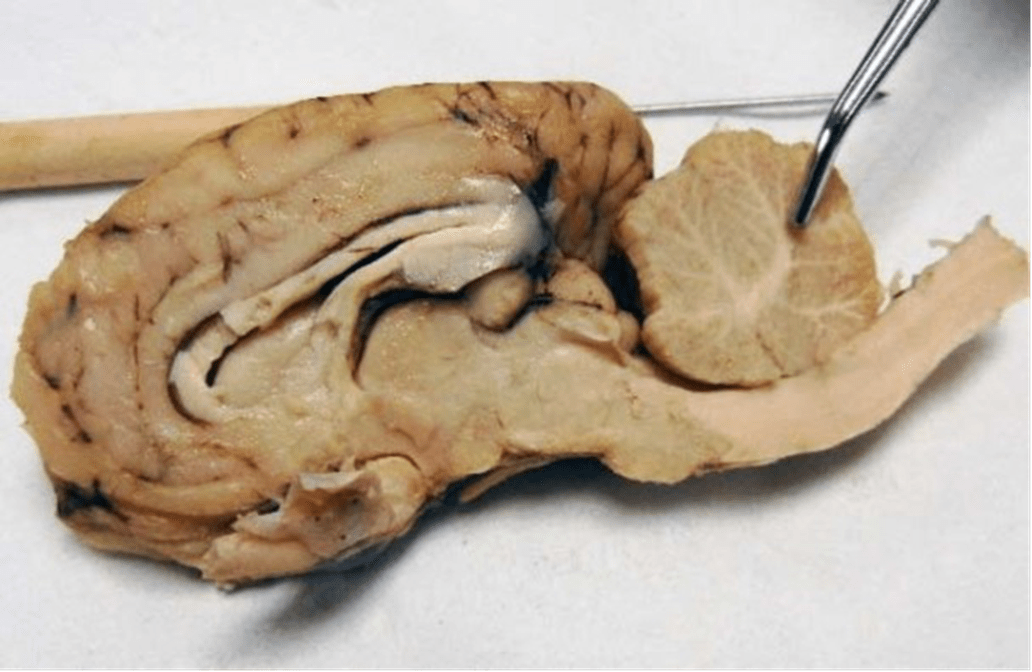
Arbor Vitae (“tree of life”)
What is the name of this bone and the bony landmark indicated with an arrow?
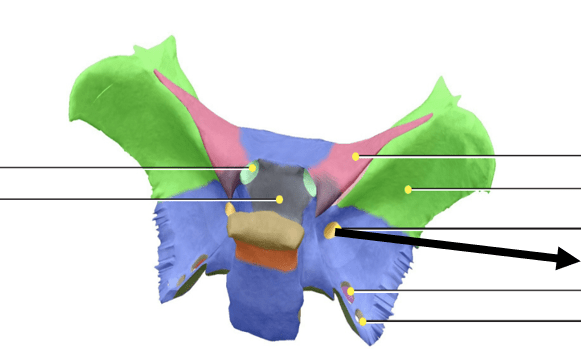
sphenoid bone; foramen rotundum
FYI: Maxillary nerve, the second division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) passes through this foramen.
Name the structures #1 through#5. What is the function of #2?
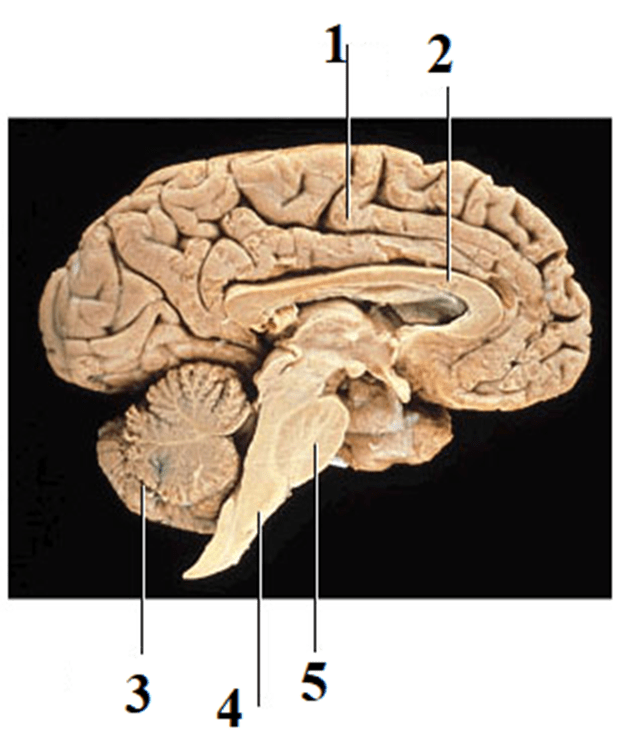
1) Cerebrum
2) Corpus callosum; connects gray matter of two cerebral hemispheres and allows for communication between both sides of the brain as well as integrated function
3) Cerebellum
4) Medulla
5) Pons
Choose one number and give the type of hemorrhage it represents and why it is that type.
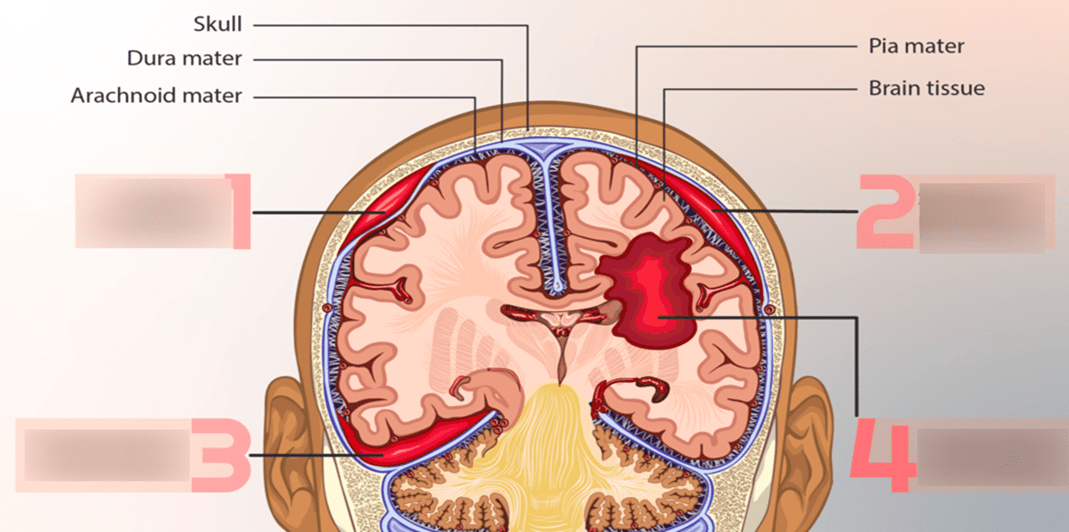
1) Epidural Hematoma - Hematoma located on top of the dura
2) Subdural Hematoma - a collection of blood under the dura mater
3) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage - bleeding between the subarachnoid space
4) Intracerebral Hemorrhage - describes bleeding into the brain due to sustained hypertension
What two structures is the yellow pin running through and bisecting respecively?
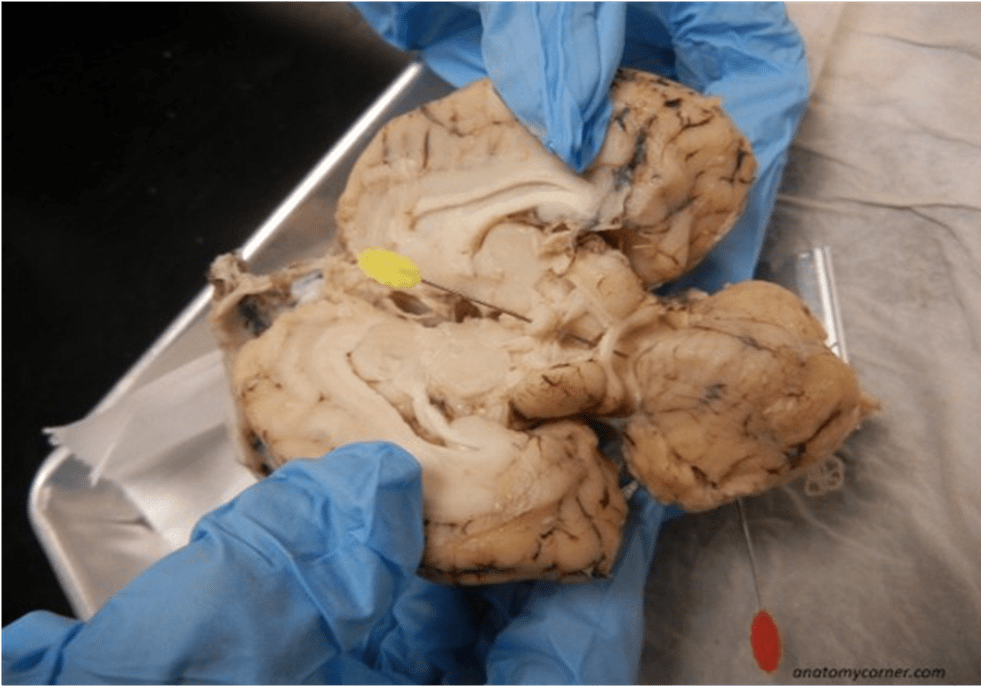
Running through the pineal gland and bisecting colliculi