These are the 3 primary vesicles that eventually form the central nervous system.
What are the Forebrain, Midbrain, and Hindbrain?
This portion of the nervous system is responsible for maintaining homeostasis, also known as “rest and digest”.
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
This part of the neuron receives information.
What are dendrites?
While present in the same quantity as neurons, this type of cell provides physical and functional support to the neurons.
What are glia/glial cells?
As the electrical impulse travels down the axon and from one neuron to another, it is known as:
What is the action potential?
Highly myelinated, the corpus callosum is composed of mostly this.
What is white matter?
The brain region (lobe) colored in blue, contains Broca’s area which is largely associated with speech production.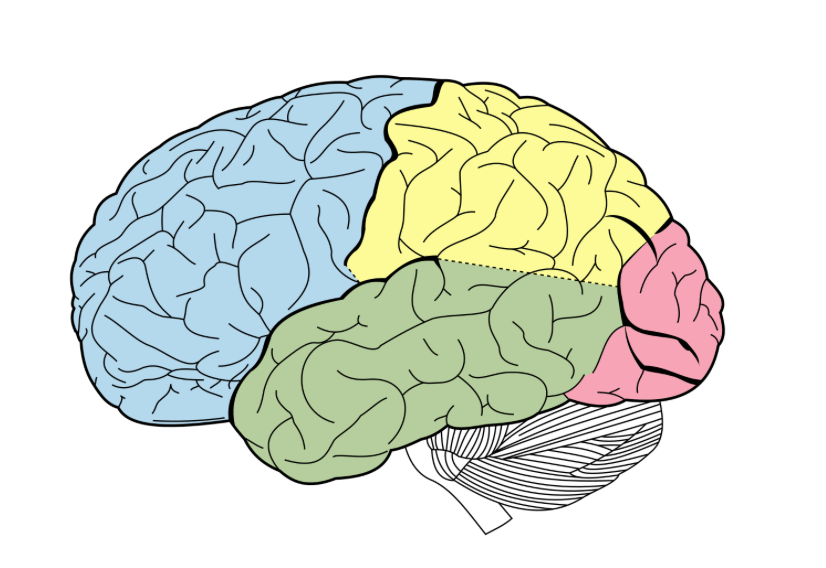
What is the frontal lobe?
Because action potentials are “all or nothing” and not graded, this allows signals to vary in strength.
What is frequency of firing?
These cells secrete cerebrospinal fluid which serves to cushion the brain.
What are ependymal cells?
The action potential jumps from one unmyelinated section of the axon to another landing at these specific locations (red squares).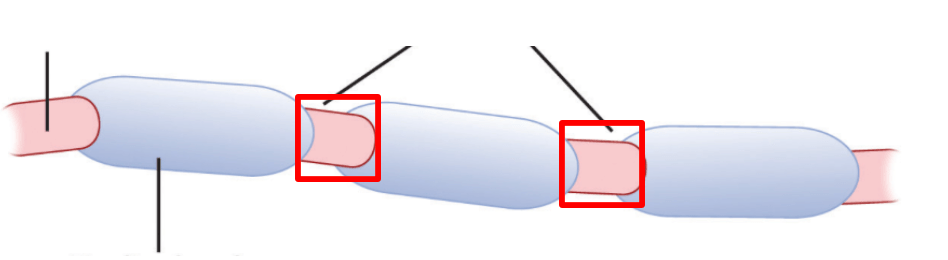
What are the nodes of ranvier?
The ridges and folds of the cerebral cortex are known as what, respectively.
What are gyri and sulci?
Arguably the most important part of the brain, this structure maintains heartbeat, breath control, and swallowing.
What is the medulla/medulla oblongata?
Myelin helps with signal transduction within the nervous system in these ways.
What is speed, preventing signal dropoff, and avoiding crosstalk from other cells?
These support cells are responsible for maintaining the blood-brain barrier and assist with synaptic function.
What are astrocytes?
Known as the main excitatory neurotransmitter, this plays an important role in learning and memory and is found in every organism with a nervous system.
What is Glutamate?
Identify the feature indicated by #1.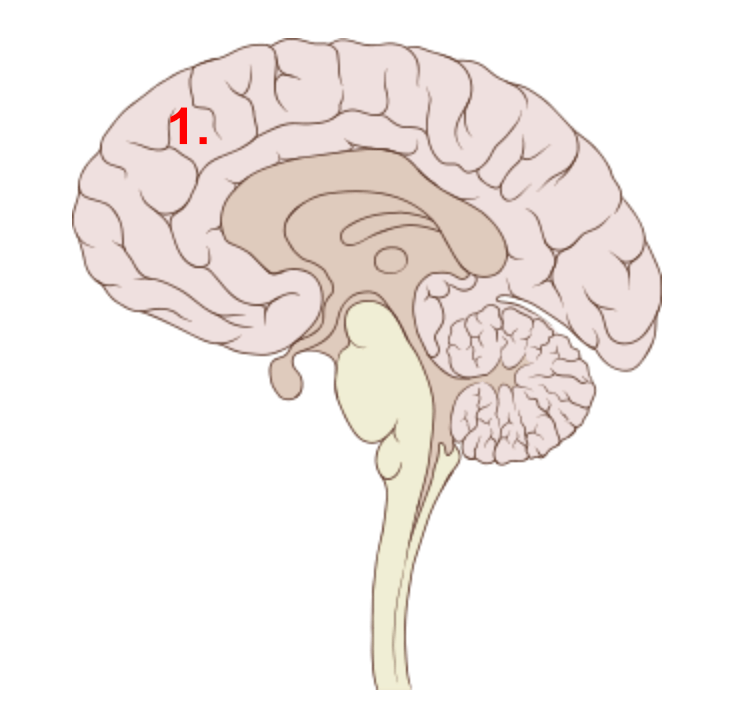
What is the cerebrum/cerebral cortex?
The following labeled region (#1), is responsible for coordination of movement and balance.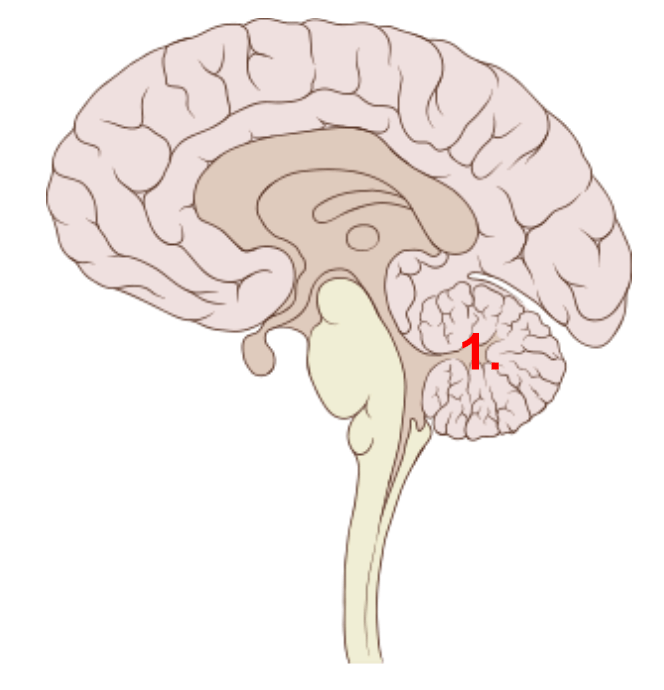
What is the cerebellum?
The gap between neurons that signals cross that was discovered in the 1950’s is known as:
What is the synaptic cleft?
Small but abundant, these cells respond to inflammation and clean up waste within the nervous system.
What are microglia?
This neurotransmitter is associated with reward and motivation behavior and is released when you scroll on your phone or get “likes” on social media.
What is dopamine?
These structures, colored in green, are located below the thalamus and above the pons.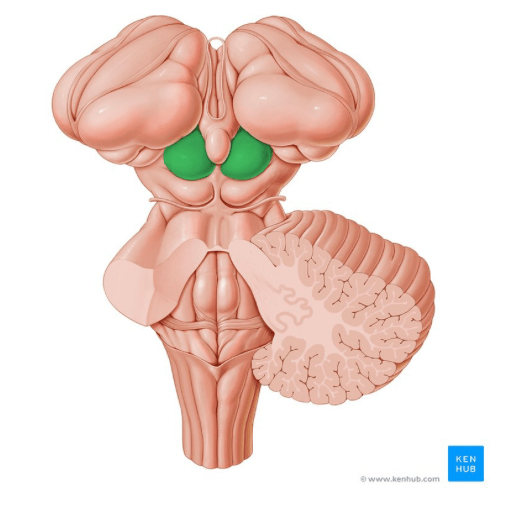
What are the superior colliculi?
This structure takes in sensory information from the environment, except smell, and is located deep within the brain.
What is the thalamus?
The arrangement of neurons that varies between brains regions is known as:
What is cytoarchitecture?
Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes are located in which regions of the nervous system, respectively.
What are the PNS and CNS?
When a neurotransmitter binds to this type receptor, it initiates a secondary cascade pathway instead of opening the receptor channel right away.
What are metabotropic receptors?