The incomplete closure of the embryonic neural tube.
Spina Bifida
Part of the brain that synthesizes hormones and releasing factors that regulate secretion of hormones.
Hypothalamus
The ability to hear is controlled by what type of sensory receptor?
Mechanoreceptors
The process by which threshold is reached from all excitatory and inhibitory synapses in a neuron is called...
Summation
Contrast innate and learned behavior.
Innate behavior: Heritable – encoded in DNA and passed down, Intrinsic – present even in isolation, Stereotypic- performed in the same way, Inflexible- not modified by development, Consummate- fully expressed the first time
Learned behavior: Non-inheritable- acquired either through observation or experiment , Extrinsic- absent even in isolation, Permutable- pattern/ sequence can change over time, Adaptable- modified to suit changing conditions, Progressive- subject to improvement with practice.
Name the three embryonic germ layers. Indicate which one becomes the neural tube.
Ectoderm: Skin and nervous system
Endoderm: digestive, hormone, and respiration
Mesoderm: bone, blood, muscle, and kidney
Desribe the regulation of breathing by the medulla
Medulla contains two control centers for breathing (timing control of inspiration and force of inspiration. active voluntary expiration).
Regulation occurs via chemoreceptors in the medulla that monitor blood pH. When CO2 increases in blood, the pH lowers. The medulla then causes breathing to become deeper and/ or more frequent to expel the excess CO2
Describe our sense of smell.
The nose contains cells that have cilia projections into the air of the top part of the nose. These cells detect chemicals in the air, they create an action potential that travels to the brain and is decoded.
The exact mechanisms of smell are still unclear.
Neurotransmitters and drugs can be excitatory and inhibitory- explain the difference.
Excitatory neurotransmitters/ drug cause an action potential to continue by depolarizing the post- synaptic neuron.
Inhibitory neurotransmitters/ drugs cause hyperpolarization of the post-synaptic neuron causing no action potential to continue.
Difference between operant and conditional conditioning, give an example of each
Operant conditioning: learning that requires trial and error. Example: foxes learning where to find the best rabbits or how best to catch them. (answers vary)
Classical Conditioning: An innate behavior is connected to a neutral task or stimulus. Example: salivation when seeing the golden arches of McDonalds (answers will vary)
Describe the migration and growth of axons.
Axons use two different methods as they grow. Somal Translocation occurs by them migrating by extensions along their perimeter or by Glial cells which provide a scaffolding for them to migrate.

Chemical responses also help to navigate the young neurons toward their destination. (chemostimulant and chemorepellant)
Describe two ways to research the brain.
Lesions/ Tumors/ strokes/ autoposy etc in brains of patients- observation of areas affected and symptoms that had.
Functional MRIs- activated parts of brain glow on a image due to dyes in the system.
Animal Experiments-open brain to see what happens when electrodes or stimulis is given to areas of the brain.
Pupil eye dilation reflexes- can be indications of brain damage.
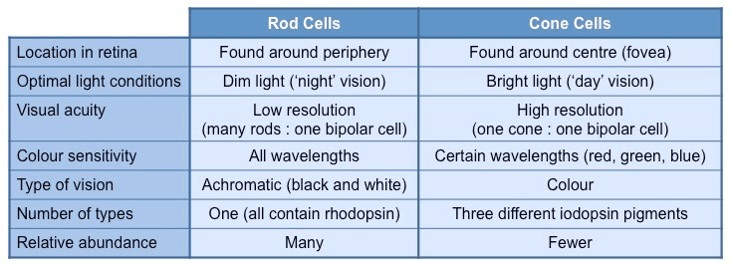
Differences between rods and cones.
Name one example of an excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitter. AND two examples of an excitatory and inhibitory drugs
Excitatory Neurotransmitters: acetylcholine, epinephrine
Excitatory Drugs: Cocaine, Paramipeole, nicotine, amphetamines
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters: GABA, Serotonin,
Inhibitory Drugs: Diazapam, THC, alcohol
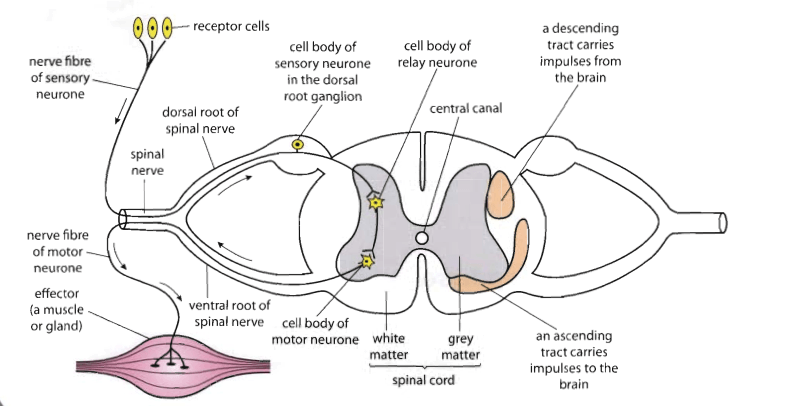
Draw and Label a diagram of a reflex arc.
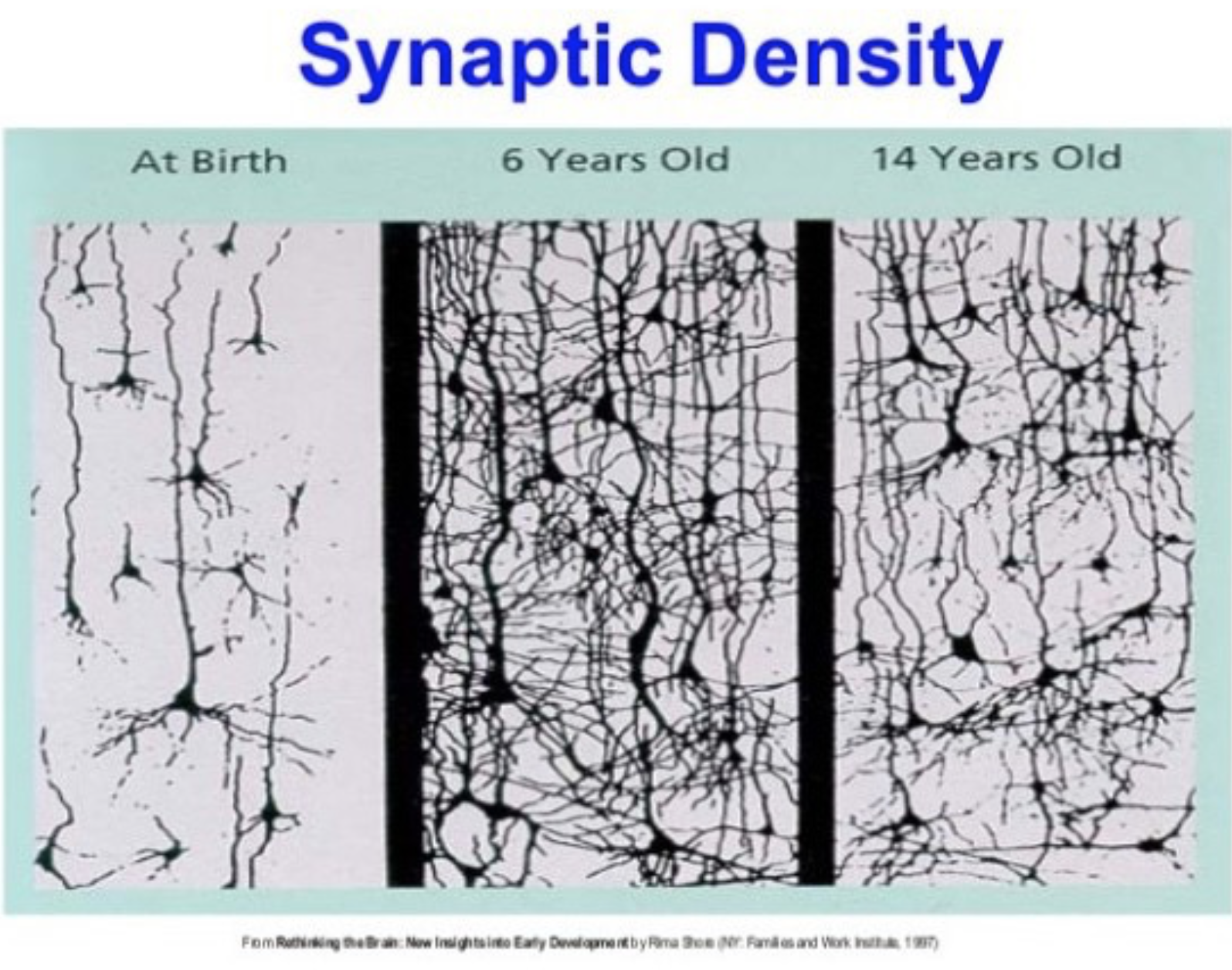
Process occurs when neurons are no longer used.
Neural Pruning.
Which numbers correspond to the following parts: medulla oblongata, cerebellum, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and cerebral hemispheres.
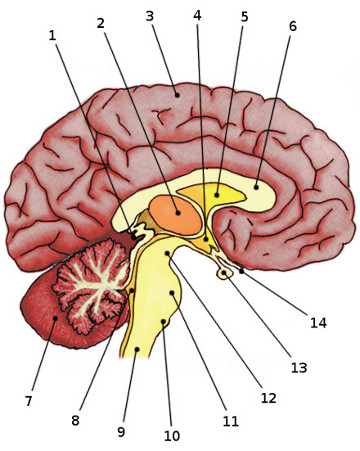
medulla oblongata: 10, cerebellum: 7, hypothalamus: 4, pituitary gland: 13, and cerebral hemispheres: 3.
Explain how the cochlea causes you to hear.
The sound waves vibrate the malleus, incus, and stapes to amplify the sound 20x and hit the oval window. This causes the sound waves to travel through the fiuld filled cochlea. Within the cochlea are hair cells that all vibrate at different frequencies. The vibrations trigger an action potential that is translated by the brain.
Describe three factors that influence addictive behavior.
Genetic predisposition- you inherit the genes that make you more susceptible to these drugs. (usually a history of drug abuse).
Social environment- poverty, peer pressure, social deprivation, traumatic life experiences, and mental health all contribute to addictive behavior.
Dopamine secretion- most addictive drugs affect or influence dopamine secretion (pleasure center) of the brain
Explain if the following are innate or learned and why:
Imprinting
Kinesis
Classical Conditioning
Imprinting- innate: birds do not change their behavior regardless if they are dying. Heritable & intrinsic as well as stereotypic. Because it is never modified it is also Inflexible, and it never changes therefore being Consummate
Kinesis- Innate or learned depending on species. Innate if they move more in it's presence regardless, learned if it is done over time or lifetime as it is learned.
Classical Conditioning- learned. the initial action is an innate response, but responding to the neutral stimulus with the innate response is learned. They have to learn to tie the stimulus with the behavior and it does not exist naturally; you can also unlearn it so it is adaptable and modifiable.
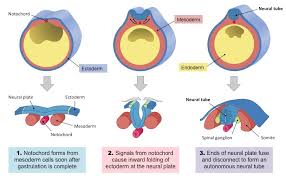
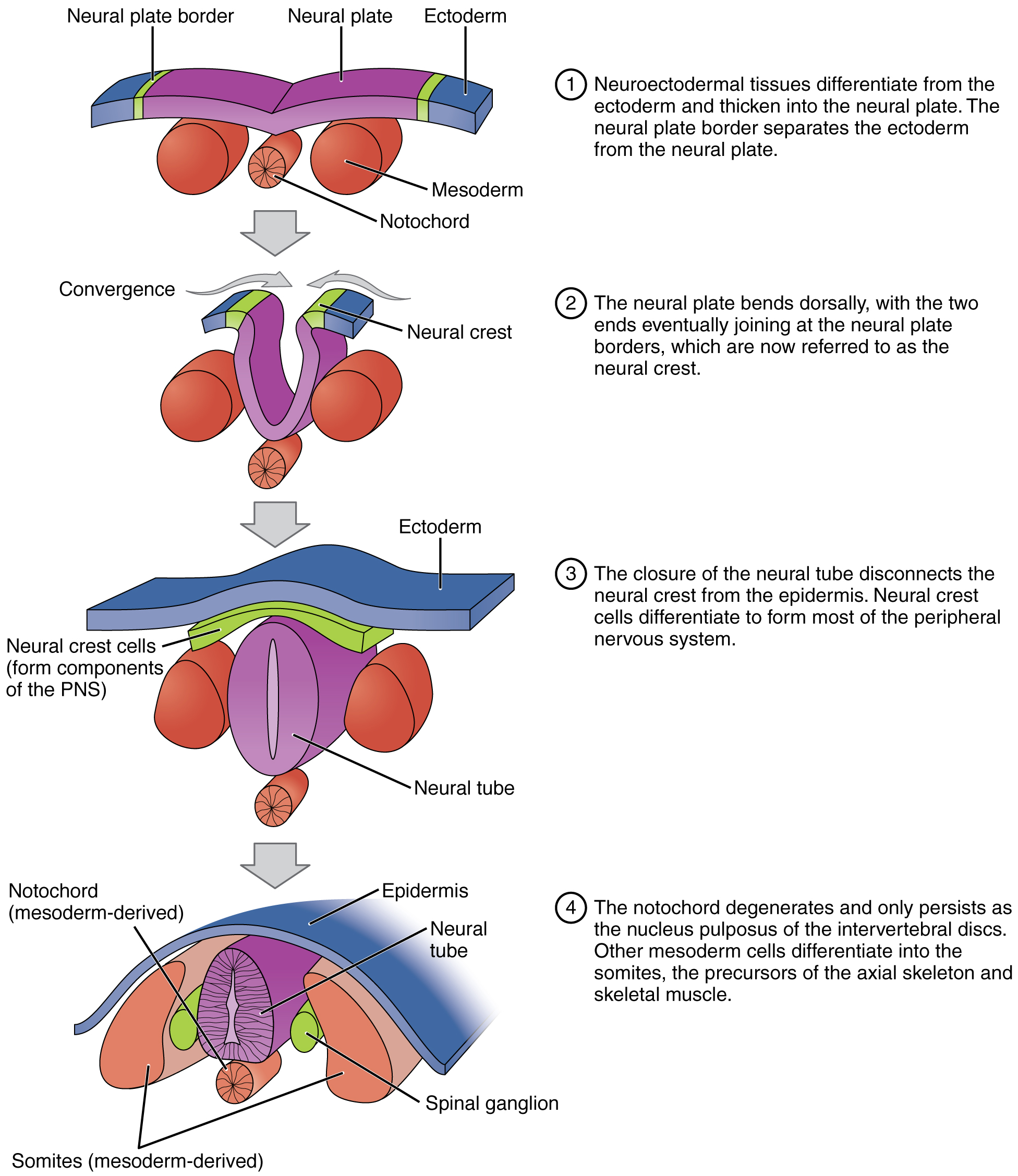
Annotate the following picture of neurulation:
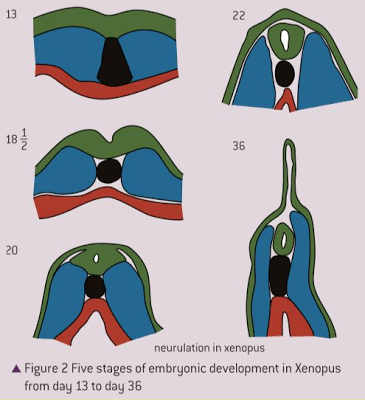
labels should include: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm, neural groove, neural tube, notochord, dorsal fin, gut cavity.
Annotation sample:
13) ectoderm germ layer differentiated for neurons
18.5) Neural Groove begins to form by folding inward because the notochord releases stimulants to cause it's differentiation
20) Almost fully formed neural tube is formed, with ectoderm layer on top of it.
Endoderm and mesoderm have moved into proper places for development. Endoderm forming gut cativty, and mesoderm forming middle layers including muscle.
22) Separation of neural tube from ectoderm, formation of neural crest (not shown)
36) development of "dorsal fin"
Describe the reasons for the folds in the cerebral cortex.
The cerebral cortex is greatly enlarged and in order to fit inside the skull, it contains extensive folding to accommodate it. This increases it's surface area and allows for more neural capacity in a relatively small space.
Discuss the connection of rods, cones, biopolar, and ganglion cells in the creation of an Action Potential.
Rods and cone cells synapse with neurons called bipolar cells . Groups of rods send signals via 1 bipolar nerve. Each individual cones sends a signal via 1 bipolar nerve. If a rod or cone is NOT stimulated, the neuron sends an inhibitory neurotransmitter into the cleft causing the neuron to become hyperpolarized. When a rod or cone absorbs light it becomes hyperpolarized and stops sending the inhibitory neurotransmitter. The bipolar cell then depolarizes sending signal to the ganglion cells in the retina. Ganglion cells give a constant impulse at low frequency to the brain. But when stimulated by the bipolar cells the frequency of the action potential increases sending a signal to the visual cortex of the brain.
Explain the effects of anesthetics on awareness.
General anesthetics cause a person to have no awareness of procedures as they are unconscious. Local anesthetics inhibit action potentials from reaching the end of their axons by blocking Na+ pathways in a specific location (causing the numbing sensation)
Explain the development of different mating behavior in salmon using the four aspects of natural selection to discussion if it is innate or learned behavior.
Salmon have two mating styles: Jack (sneaky) and Hooknose (fighting). Jacks are males which are small in size and hooknose males tend to be larger. The genetic variation of the males in the fish have lead to survival of specific sizes due to the development of the two types of mating techniques. Hence reproduction of all sizes continues. Seems to be more innate as offspring of each type will stick to the same mating type generally.