Main components of SSEP signal
Amplitude (size wave) and latency (time between waves) 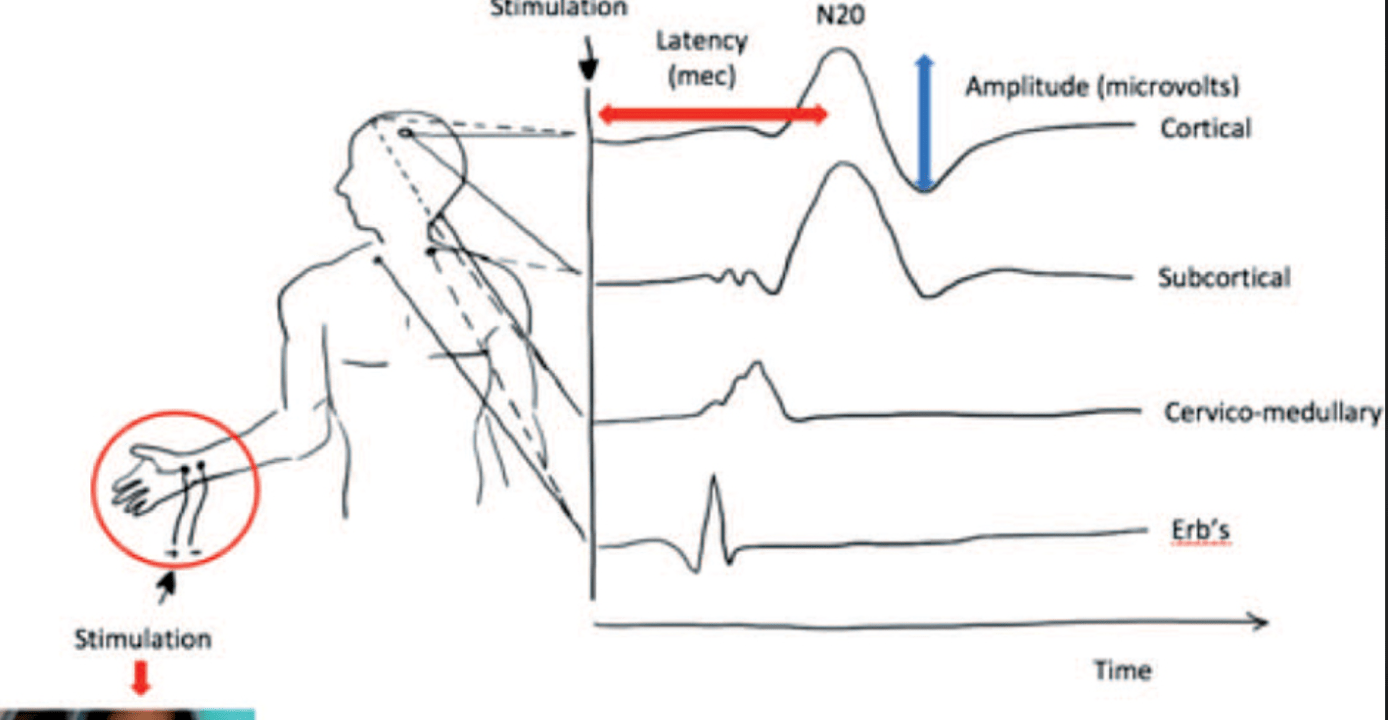
Why are TcMEPs monitored during a AAA
What is monitoring for compromise to artery of Adamkiewicz = decrease in flow = may cause ischemia and paralysis. This feed majority of anterior portion of spinal cord which is where motor signals travel down from the brain.
Myasthenia Gravis vs Lambert-Eaton
What is LE = deficient release of ACh at neuromuscular junction from antibody mediated destruction presynaptic voltage gated calcium channels= better with exercise
It is ok to use SUX with CP patients True or False?
What is true. Normal amount of K released despite evidence of proliferation of extrajunctional receptors acetylcholine
Children with mitochondrial disorders are at higher risk for complications when using volatile anesthetic :True or False.
What is False per the latest edition of Cote. All anesthetics whether propofol or VA must be carefully titrated. Other caveat: kiddos on ketogenic diets and with mitochondrial D/O may be more sensitive to propofol.
Bonus: Are these kids more susceptible to MH?
NO
How muscle relaxant affects SSEPs
What is signal can be improved due to elimination of background noise
What parts of the spinal cord do SSEP and TcMEPs monitor
What are SSEPs posterior columns and TcMEPs anterior horn.
What organ is associated with myasthenia gravis
What is the thymus. 25% patients with thymomas have MG. Prophylactically removed in MG patients who do not have thymomas.
Perioperative risk factors for CP patients
What are mobility, severe neuro deficits, major cognitive dysfunction, scoliosis, malnutrition, aspiration risk, possible post operative pulmonary issues
Most commonly inherited neuromuscular disorder in the general population
What is myotonic dystrophy. ANES: prolonged recovery, more susceptible to SUX, weakness correlated to severity of molecular defect
Medications decrease SSEP amplitude and prolong latency?
What are VAs, Nitrous oxide, Propofol (attenuate with bolus)
What causes of EEG burst suppression intraoperatively
What are high dose propofol, 2 MAC iso, barbiturates, etomidate, severe hypoxia, profound hypothermia (20 deg C)
Tracheal intubations can be performed without neuromuscular blockade in MG patients True of False
What is True
True or False: neonatal MG is transient
True: placental transfer antibodies from Mom that will resolve with supportive care, anticholinesterase medications, risk of recurrence small
X linked inherited disorder that is sensitive to both SUX and VA
What is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.
ANES: Hyper K with VA and SUX. Watch cardiac, GI, resp. Worse as age. Always get echo pre op.
Bonus: Becker = later onset and less severe.
Lack of dystrophin which reinforces inner strength of myocyte and helps with signal conduction.
Order of sensitivity to signal attenuation with neuromonitoring
What is VEPs>MEP>EEG>SSEP>BAEP
What is cerebral metabolic uncoupling and how produced
What is by VAs. Decrease CMRO2 and cause vasodilation = increase CBF = luxury profusion = less nutrient delivery due to decreased neuronal activity.
What is normal: CBF normally increases to areas of increased metabolic rate and decreases to areas of decreased metabolic rate
True of False: MG patients are more resistant to non-depolarizing muscle relaxants and less resistant to depolarizing muscle relaxants
What is False. More resistance to depolarizing (SUX) to the extent of at times requiring 2-3 times the amount
What is an ascending paralysis that may require ventilatory support?
Guillain-Barre Syndrome or AIDP = acute demyelinating polyneuropathy. Flaccid paralysis with sensation preserved. Watch out for autonaumic issues hemodynamically.
After viral illness or vaccination
Vagal nerve stimulators need to be deactivated during surgical procedures in patients with epilepsy: True or False
False. Place all grounding pads as far away as possible from the VNS generator. 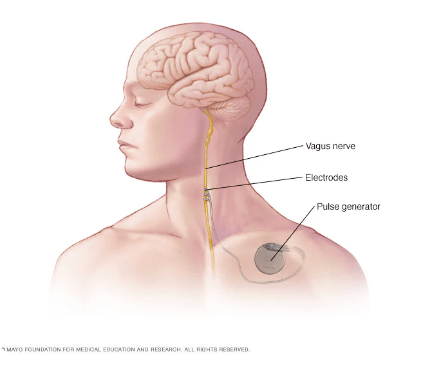
Differential for loss of signals during a case
What are Surgeon, Anesthesia, Neuromonitoring, Physiologic (positioning, hypotension, anemia, hypocarbia, acidosis, hypothermia)
What EEG rhythms correspond to various depths of anesthesia = alpha, beta, theta, delta
What are alpha = resting awake, beta = mental activity and possible light anesthesia, theta = moderately deep anesthesia, delta = deep anesthesia
What are 1) duration MG > 6yrs 2) hx other chronic respiratory disease 3) pyridostigmine dose >750 mg/day 4) pre operative vital capacity <2.9L
How many types of Spinal muscular atrophy are there and what is the most severe?
What are
0 (WORST) = prenatal/joints/facial diplegia/resp fail
1 (Werdnig-Hoffman)=onset before age 6 mo and die within 2 years of life resp failure, normal intelligence, no cardiac
2 (most prevalent) = onset age 6-12 mo, weakness, nutrition issues, may never walk (?), normal intelligence. Can live years with good management.
3 (Kugelberg-Welander)= onset after age 12 mo, ability to walk at least 25 mo, deteriorate around puberty, long term survival good with good management.
4 = adult onset, mild course, no nutrition issues, walkers
List 6 things important for perioperative management of children with epilepsy.
What are 1) Communication with parents about medication schedules...continue all anti-seizure medications 2) Avoid prolonged fasting 3) Schedule early in the day 4) Abortive medications benzodiazepines or propofol 5) Use IV formulations of anti epileptics as needed to keep dosing schedule during procedures 6) Check for ketogenic diet or VNS