What is the most common cause of TBI's?
Falls
What are the types of primary SCI?
Cord Contusion
Cord transection
Incomplete cord transection
What does ICP stand for?
Intracranial Pressure
What causes herniation?
Swelling, bleeding, tumors
What are your indicators for calling a referral to KODA?
Loss of two brain stem reflexes
Cardiac Arrest with ROSC
Initiation of TTM
Goals of Care meeting
GCS is no longer an indication
What does DAI stand for?
diffused axonal injury
MVA/MCC
What is the normal ICP readings?
0-20
What are signs and symptoms of a patient herniating?
Cushing triad
blow pupils
large blood output from EVD
High ICPs
What are your brain stem reflexes
cough reflex
gag reflex
corneal reflex
Pupillary light reflex
How do you test for a CSF leak?
If blood is present you do the halo test
If no blood present you do the glucose test
What is considered the hangman fracture?
C1 fracture
What are some things you as the nurse can do to reduce ICP?
Raise the HOB
Decrease stimulation
C-Collar is not too tight
Patient alignment
Pain reduction
Sedation
What is Uncal Transtentorial Herniation?
Compression of the midbrain, lateral displacement (changes in LOC and unilateral pupil dilation)
Is brain death legal death?
Yes, in the State of Kentucky brain death is considered legal death.
Your patient presents after being hit with a baseball bat on the side of the head. Patient lost consciousness, but regained consciousness. Shortly after arrival to hospital, patient loss consciousness again and decompensated quickly. What type of bleed may the patient have?
Epidural bleed
At what level of injury would you be concerned for insufficient ventilation?
T1-T11
injury may result in the loss of intercostal muscles and decreased respiratory effect
What are some medications that can be used for high ICP management?
Mannitol
3% Saline
23.4 % Saline
Paralytics
What do you do if you think your patient is herniating
Call the physician
Attempt to lower ICPs
May end up going to OR
Can we approach family about KODA?
The initial family contact has to be done by the KODA family coordinator.
What is storming?
What medications are used to prevent storming?
Paroxysmal Sympathetic Hyperactivity- symptoms include HTN, tachycardia, tachypnea, fever, diaphoresis, dystonic posturing
Propranolol
Gabapentin (pain medications in general)
What is the difference between a complete SCI and an incomplete SCI
With a complete cord transection- complete disruption; all cord-mediated functions below the level of injury are permanently lost
With incomplete cord transection- interruption in the vascular perfusion to the spinal cord. This can cause ischemia or necrosis if not treated quickly. Usually only causes temporary deficits.
What are your types of ICP monitors?
Bolt and EVD
What is Central / Transtentorial Herniation?
The cerebral hemispheres are pushed downward through the tensorial notch, directly compressing the brain stem
You are taking care of a patient who was diagnosed Brain Dead on dayshift. Family consented for organ donation and KODA orders Narcan. After administering the Narcan you patient begins to move. Are they really brain dead?
Yes, the narcan decreases swelling at the spinal cord level causing spinal reflex or the Lazarus sign.
Where is the most common location for epidural hematoma?
Temporal region or parietal region of the brain.
What level of injury can cause respiratory arrest
C3-C5
results in a paralyzed diaphragm
What all supplies are needed for an EVD and a Bolt
Bolt -Bolt box in Brittany's office- make sure to take a pink sheet or green sheet and place patient label and what supplies were taken
EVD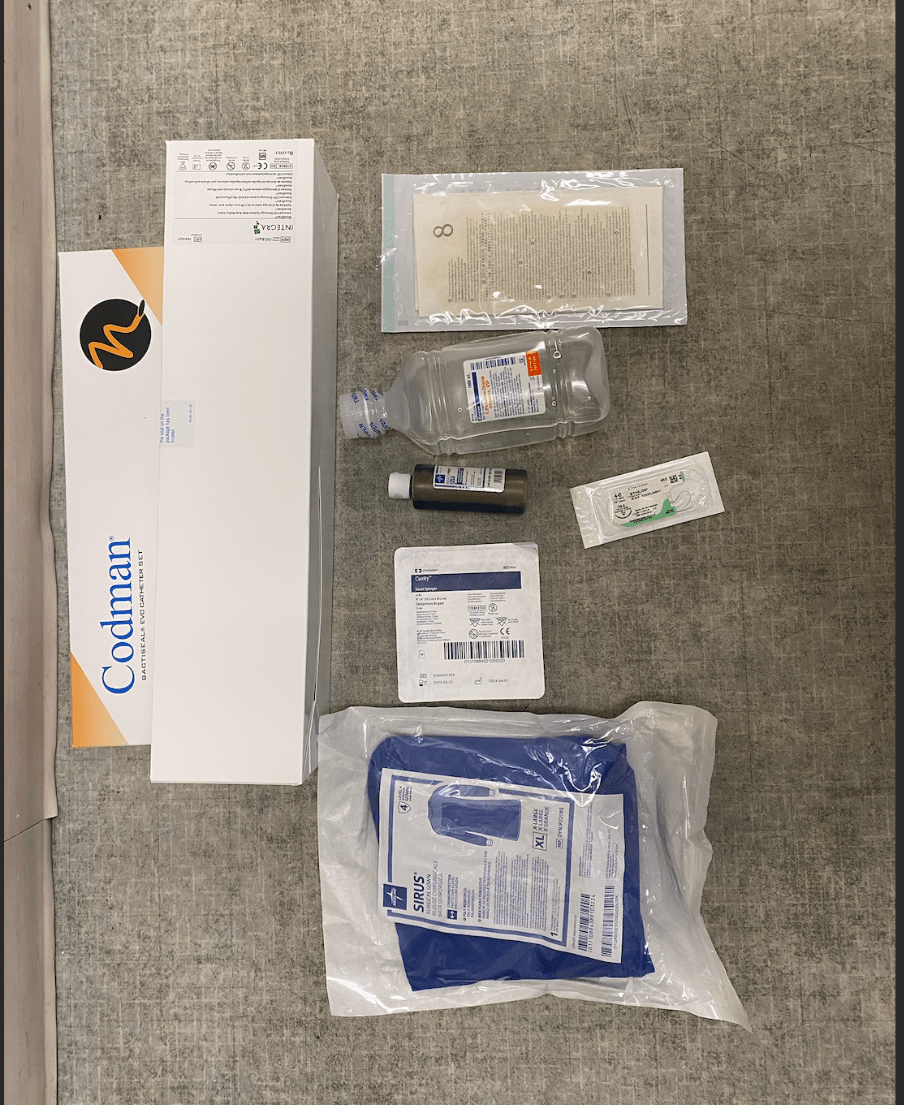 And the cranial access kit
And the cranial access kit
- possible places to find cranial access kit - House supervisor office, 5W, OR
What is a spinal reflex?
And what does it look like?
Simple behaviors produced by central nervous system (CNS) pathways that lie entirely within the spinal cord
Applying pressure and while you continue to hold pressure the limb relaxes. Where as with a withdraw as long as you are holding pressure they are trying to move away from the pressure.
Why do we give T4 to Brain Death KODA patients?
To improve their hemodynamic stability, particularly cardiac function, by potentially preventing cardiovascular collapse, thereby increasing the chances of successful harvesting organs for transplantation by making them more viable for donation.
How do you treat a CSF leak?
If there is no need for ICP monitoring then they will do a lumbar drain but if there is a need for ICP monitoring they will do an EVD
What MAP goals are normal for a SCI?
>85 for 7 days
How do you calculate CPP?
MAP-ICP=CPP
How do you assess the oculocephalic reflex (doll's eyes reflex)?
You have eyes open and turn the patients head side to side
You want to see the patient keep their eyes towards the ceiling with the movement
You don't want the patient to have there eyes stay fixed
used for neurologic examination of cranial nerves 3, 6, and 8, the reflex arc including brainstem nuclei, and overall gross brainstem function.
At what age do they stop taking the pancreas for transplant?
35 yo- they will still take it but for research.
Name the types of posturing shown.
1)
 2)
2)
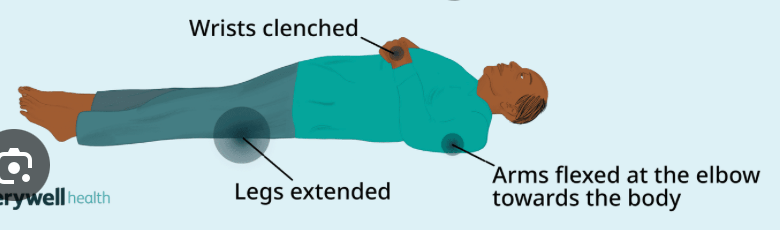
Which one's worse?
1) Decerebrate
2) Decorticate
Decerebrate
What is neurogenic shock?
A distributive shock classified as occurring with spinal cord injury that results in the loss of sympathetic nervous system control of vascular tone, leading to venous and arterial dilation
Typical occurs with high thoracic and cervical cord injury
Temporary (lasting less than 72 hrs)
S/S - bradycardia, hypotension, loss of ability to sweat below level of injury
Why would NES not take a patient to the OR for a DECRA with an opening pressure of 64?
When you release that much pressure all at once it causes the entire body to crash. Instead they will attempt to lower ICPs with pharmacological means prior to going to the OR.
What is the babinski reflex?
the upward movement of the big toe and fanning out of the other toes when the bottom of the foot is stroked
In adults it's an abnormal reflex that may indicate a brain or spinal cord issue
Who do you place the KODA orders under?
KODA DONATION
MRI
What is spinal shock?
occurs when normal activity in the spinal cord at and below the level of injury ceases because of a disruption or inhibition of impulses in the spinal cord
Duration is variable
S/S- flaccidity, loss or reflexes, bowel and bladder dysfunction
What medications can be used to lower ICPs, but have to be administered through a central line?
Salt bomb
3% running at rate greater than 50ml/hr
What is the Oculovestibular reflex?
The eyes should move when cold water is placed in the ear. If no eye movement it's a sign of brain death.
What's the difference between DCD and Brain Death
Brain death: pt is considered legally brain dead (KODA takes over care at this time and they coordinate care of the pt)
DCD: pt is not considered brain dead, but has poor prognosis, indicating it is appropriate for organ donation. (Physician will still be coordinating care of pt)
What is the highest GCS you can rate a patient that's intubated?
What is the lowest GCS a person can be rated?
What GCS would you rate an intubated, sedated, paralyzed patient?
11t
3
3t
Criteria for cervical spine clearance (removing c-collar)
- No posterior midline cervical tenderness present
- No evidence of intoxication
- Pt is A&O X 4, GCS 15
- No focal neurological deficits are present
What is CO2 and its relationship to ICP? And what levels do most providers want CO2 between for patients with ICP issues?
Hypercapnia causes a significant dilation of cerebral arteries and increases blood flow to the brain. Physicians typically want CO2 between 35 and 40, on the lower end. Lower CO2 reduces cerebral blood flow.
Why is a gag not a good indicator of brain stem function?
Only 70% of the population have a gag.
What is the apnea test for brain death testing?
Observing no spontaneous breaths after removing ventilator support while monitoring a significant rise in blood CO2 by at least 20mmHg above baseline- off the ventilator for 8-10min.