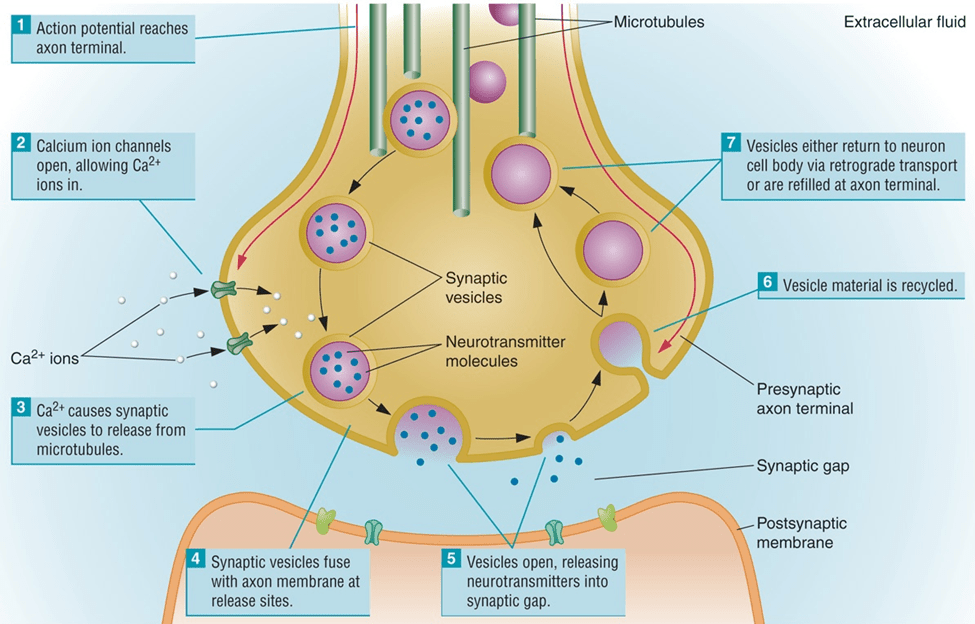
What ion enters the presynaptic neuron to trigger neurotransmitter release?
Calcium (Ca²⁺)
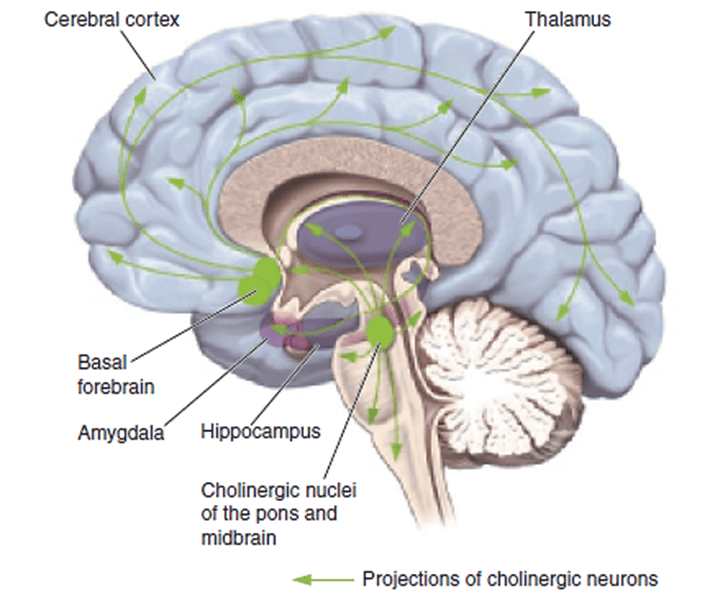
Which neurotransmitter is essential for muscle contraction?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Also involved in autonomic functioning, REM sleep, and learning/memory.
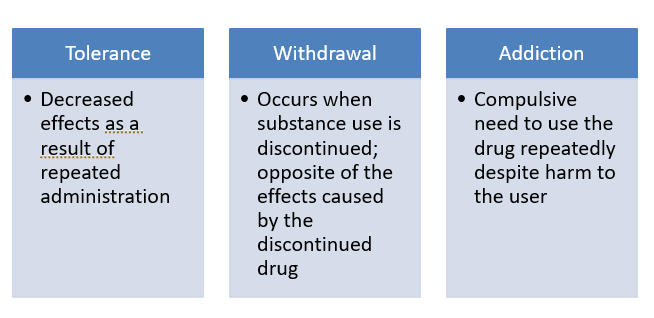
This is a reduced effect of a drug after repeated use.
Tolerance
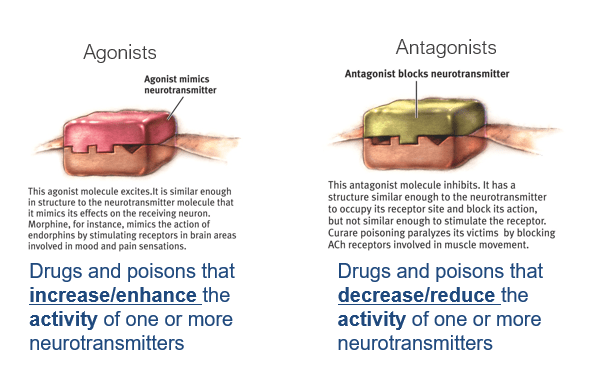
What term describes a substance that enhances neurotransmitter action?
Agonist
The key difference between neurotransmitters and hormones is where they are released. Neurotransmitters are released in the nervous system at the synapse while hormones are released here.
In the blood or endocrine system
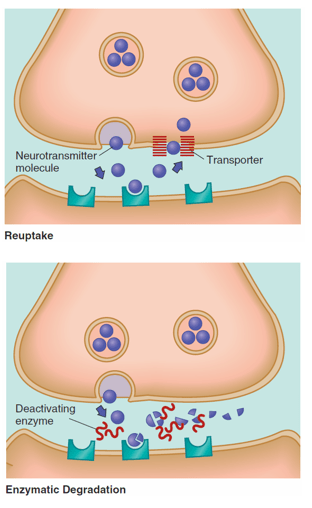
Name one way neurotransmitters are cleared from the synapse.
Reuptake, enzymatic degradation, or diffusion
Which neurotransmitter is the brain’s main inhibitory neurotransmitter and is the primary target of alcohol?
GABA
•Approx. 1/3 of brain synapses
•Receptors both ionotropic and metabotropic
•Important in Mood and Seizure Threshold
•Removal: reuptake
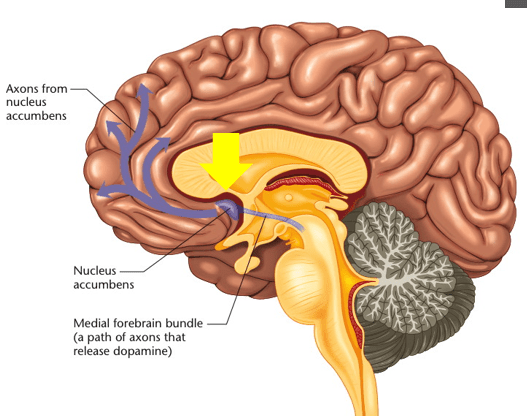
Dopamine is associated with feelings of pleasure/reward or wanting when released in this area of the brain.
Nucleus Accumbens
Dopamine can be excitatory or inhibitory.
It is also involved in Motor control/Movement and planning
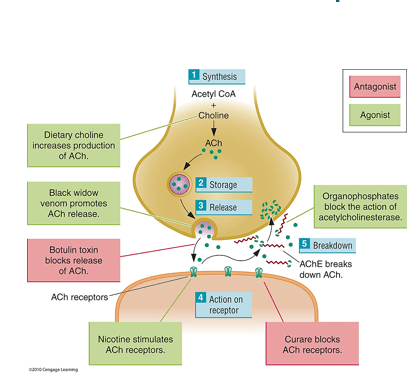
Black widow spider venom acts on which neurotransmitter system?
Acetylcholine
Inland taipan of Australia blocks the release of acetylcholine, producing death by muscular paralysis in as little as 35-40 minutes.
When binding to a receptor, neurotransmitters can have two primary types of effects, excitatory and inhibitory. This effect INCREASES the likelihood that the next neuron will fire.
Excitatory
This is compared to INHIBITORY effect which DECREASE the likelihood of firing.
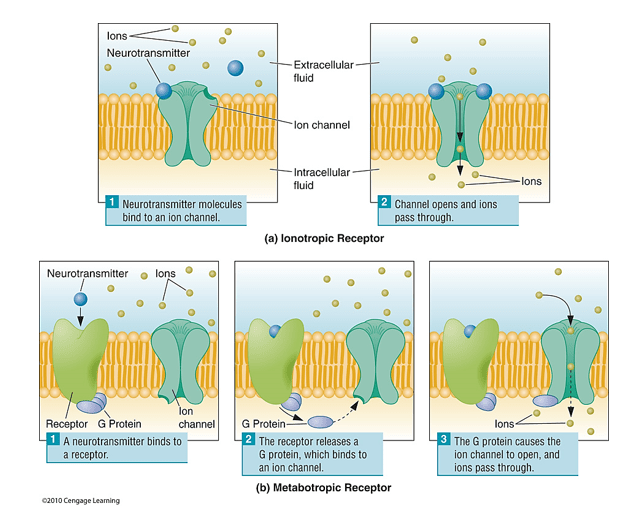
Which type of receptor produces a fast response: ionotropic or metabotropic?
Ionotropic
Which neurotransmitter is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain?
Glutamate
•Receptors both ionotropic (e.g. NMDA, AMPA) and metabotropic
•Important in Long-Term Memory
•Removed from synapse by transporters
What class of neurotransmitters like endorphins?
Neuropeptides
•Large molecules
•~100 have been isolated and characterized
•Often act as neuromodulators
•Example – endorphins
–“Endogenous opioids”
–Produce analgesia (pain suppression)
Nicotine is an agonist for which neurotransmitter?
Acetylcholine (nicotinic receptors)
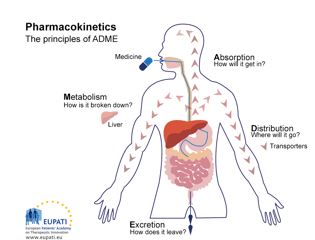
Name 3 ways a drug can be administered.
Injection, oral, sublingual, intrarectal, inhalation, topical, brain administration.
Injection
•Intravenous (IV)-into vein
•Intraperitoneal (IP)-into abdominal wall
•Intramuscular (IM)-into muscle
•Subcutaneous (SC)-under skin
–Brain
•Intracerebral
•Intracerebroventricular
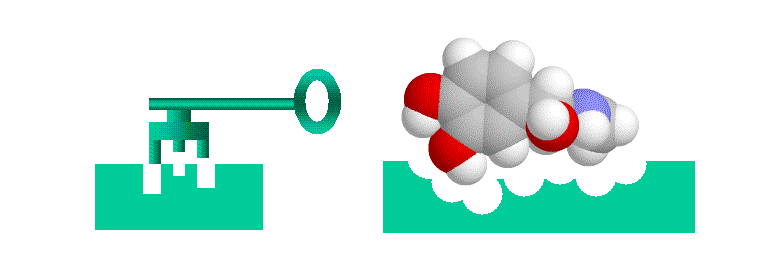
What term describes molecules that bind to receptors?
Ligands
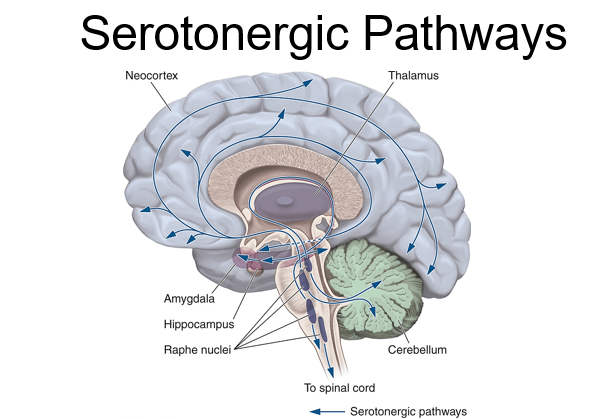
Concentrated in the raphe nuclei and sometimes called the happy chemical, this neurotransmitter is involved in regulating mood, appetite, and sleep.
Serotonin
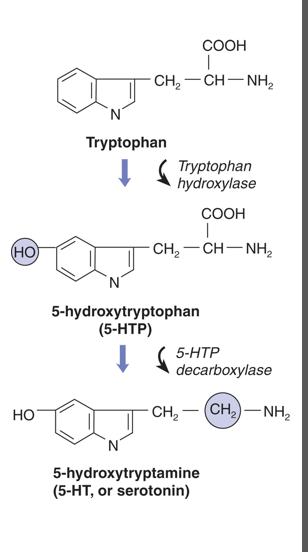
What disease is caused by the breakdown of dopamine neurons in the basal ganglia?
Parkinson’s Disease

PCP acts as an antagonist of which neurotransmitter receptor?
Glutamate (NMDA receptor)
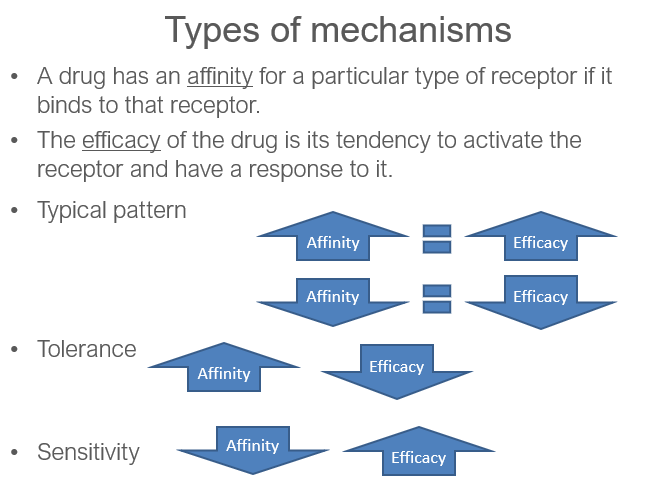
What term describes how strongly a drug binds to a receptor?
Affinity
What is the process by which synaptic vesicles fuse with the membrane and release neurotransmitters?
Exocytosis
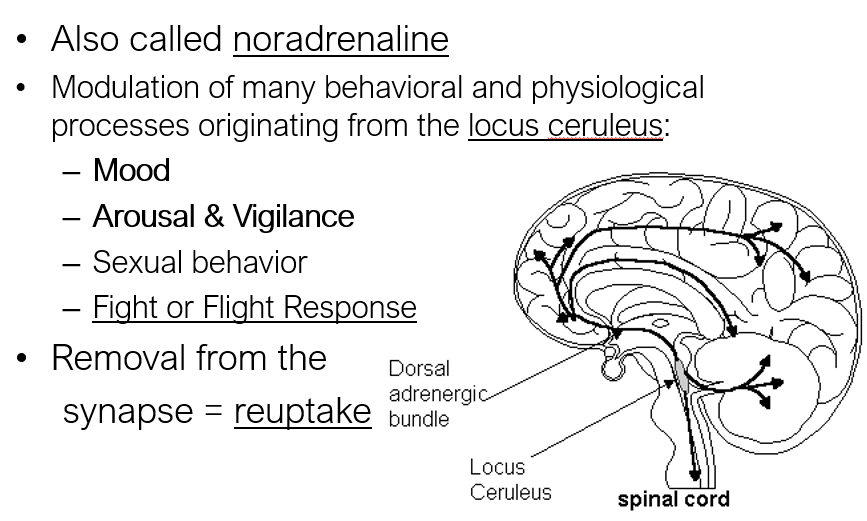
This neurotransmitter is involved in the modulation of many behavioral and physiological processes including the fight or flight response.
Norepinephrine
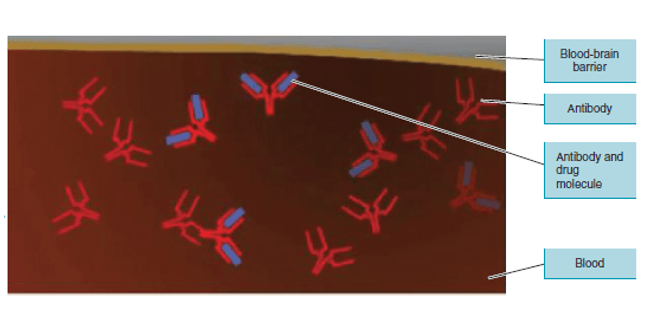
What novel treatment approach is being researched to fight drug addiction, involving the immune system?
Vaccines or immunotherapy

What type of drug interaction blocks reuptake of neurotransmitters like serotonin?
Reuptake inhibition (e.g., SSRIs)
What happens if neurotransmitter activity in the synapse is not terminated?
The signal remains active, leading to overstimulation of the postsynaptic neuron.
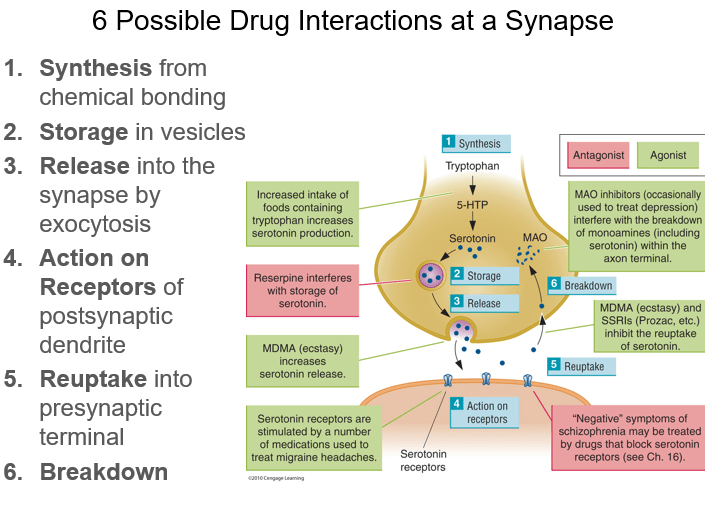
Drugs can impact the action of a neurotransmitter is many ways at the synapse. Name two of these possible interactions.
Synthesis, Storage, Release, Action on Receptors, Reuptake, Breakdown