What is the antidote for benzodiazepine overdose?
Flumazenil
Which of the following is NOT an example of a primary headache?
A. Tension headache
B. Cluster headache
C. Migraine
D. Medication overuse headache
E. Mixed-type headache
What is the most common new year's resolution?
Exercise more!
Michaela is a 54-year-old Greek woman who has recently had an NHS health check and has called her GP for the results. As part of this health check, she has had a blood pressure check, routine blood test and a urine dip. Her blood pressure is 125/78 mmHg and her urine dip is negative. Her blood test showed the following:
Hb 124 g/L (M:135-180, F: 115 - 160)
Platelets 300 * 109/L (150 - 400)
WBC 4.5 * 109/L (4.0 - 11.0)
Na+ 138 mmol/L (135 - 145)
K+ 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 - 5.0)
Urea 4.2 mmol/L (2.0 - 7.0)
Creatinine 82 µmol/L (55 - 120)
eGFR 63 mL/min/1.73 m²
Which one of the following options describes the correct stage of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in this patient?
1
2
3a
3b
No CKD
E. No CKD
Although this patient's eGFR is reduced, her eGFR is above 60 and hence there needs to be evidence of kidney damage present for a diagnosis of CKD stage 2 to be made in this patient.
A 35-year-old man presents with recurrent syncope, particularly during exertion. His ECG shows ST elevation and negative T waves in leads V1-V3.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT)
B. Brugada syndrome
C. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
D. Long QT syndrome
E. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
B. Brugada syndrome
Brugada syndrome is defined by ST elevation and negative T waves in leads V1-V3 and is linked to mutations in the SCN5A gene, which encod es the myocardial sodium ion channel. It commonly presents with syncope or sudden cardiac death, especially during rest or exertion. Treatment typically involves an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) to prevent fatal arrhythmias.
Which country does this flag belong to?
Yemen
A 63-year-old woman presents to A&E with acute dyspnoea. On examination, her JVP is raised and fine crackles can be heard at the bases of both lungs. What does the CXR show?
A 24-year-old woman attends her GP practice at 12 week’s gestation for a routine antenatal appointment. Urinalysis shows no blood, protein or nitrites. Urine culture shows scanty growth of E. coli. She has no symptoms. What is the most appropriate treatment?
A. Nitrofurantoin MR 100mg OD PO for 7 days
B. Co-amoxiclav 625mg TDS PO for 5 days
C. Trimethoprim 200mg BD PO for 3 days
D. Advise the woman to attend if she becomes symptomatic
A. Nitrofurantoin MR 100mg OD PO for 7 days
Second line agents (NICE guidelines):
1. Cefalexin 500mg BD PO for 7 days
2. Amoxicillin 500mg TDS PO for 7 days
What are these cells called?
50 bonus points: Which disease are these cells present in?
Smudge cells in CLL
A 25-year-old woman presented to A&E with fluctuating consciousness and complaints of abdominal pain whilst intoxicated a few hours prior. ABG results:
pH 7.18 (7.35-7.45)
pCO2 4.3 kPa (4.7-6.0)
Bicarb 14 mmol/L (22-26)
Glucose 22.2 mmol/L
Ketones 4.5 mmol/L
Given the ABG results, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
(metabolic acidosis with partial respiratory compensation)
A 45-year-old woman presents with fatigue, gum bleeding, and petechiae. Bloods show:
Hb 82 g/L
WCC 2.1 × 10⁹/L
Pl 8 × 10⁹/L
The blood film is shown below. Blood tests show elevated LDH, and undetectable haptoglobin.
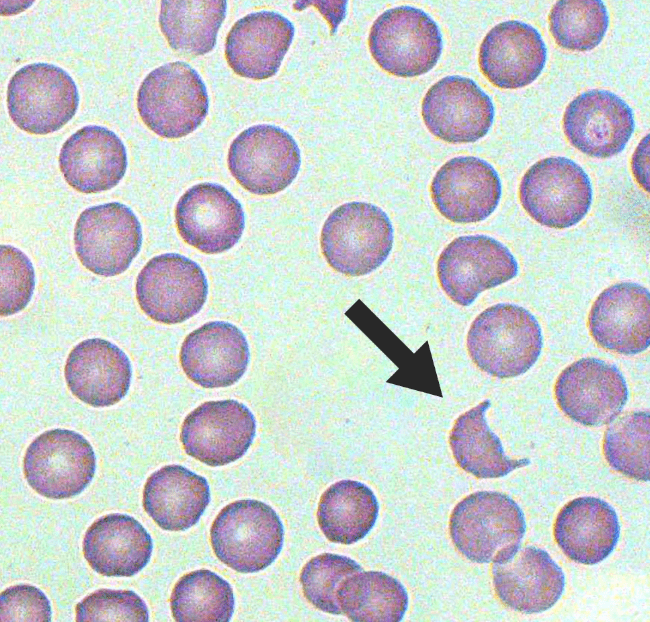 .
.
1. What is the most likely diagnosis?
2. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
A) IV methylprednisolone
B) Plasma exchange
C) IVIG
D) Transfuse platelets
E) Bone marrow aspiration
Answers:
1. The diagnosis is TTP (thrombocytopenia + haemolytic anaemia + schistocytes).
B) Plasma exchange is urgently required.
Incorrect answers:
A. While steroids can be used in some cases they are not the main treatment
C. IVIg is a treatment for many disorders and used in ITP when it is refractory to steroids. Not used in TTP
D. Platelet transfusion is contraindicated in TTP
E. Not a treatment option, not valuable as in TTP ADAMTS is being attacked by the immune system.
In which country do people eat 12 grapes for good luck in the New Year?
Spain
A 65-year-old woman has a 5-month history of dizziness. It is triggered when she rolls over in bed, and each episode is 30 seconds. Her symptoms are occasionally associated with nausea and vomiting, and her husband reports that he has noticed her eyes moving in "a funny way".
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
A 64-year-old woman presents to the Emergency Department with a cough, fever, diarrhoea and myalgia. The cough is non-productive and has been getting gradually worse since she returned from holiday in Spain one week ago.
Her husband is concerned because over the past 24 hours she has become more drowsy and febrile. He initially thought she had the flu, but her symptoms have got progressively worse. She is normally fit and well but drinks around 20 units of alcohol per week.
On examination pulse is 76/min, blood pressure 104/62 mmHg, oxygen saturations are 94% on room air and temperature is 38.4ºC. Bilateral coarse crackles are heard in the chest.
Initial blood tests show the following:
Hb 13.6 g/dl
Platelets 311 * 109/l
WBC 14.2 * 109/l
Na+ 131 mmol/l
K+ 4.3 mmol/l
Urea 9.2 mmol/l
Creatinine 91 µmol/l
Bilirubin 12 µmol/l
ALP 31 u/l
ALT 64 u/l
A chest x-ray shows patchy consolidation in the left lower zone with an associated pleural effusion.
What is the most likely causative organism?
A. Strep. Pneumoniae
B. Mycoplasma Pneumoniae
C. Staph. Aureus
D. Legionella Pneumophila
E. Klebsiella Pneumoniae
D. Legionella Pneumophilia
Clinical features of Legionnaire's Disease:
- incubation period 2-10 days
- fever, chills, headache
- relative bradycardia
- atypical pneumonia: non-productive cough, bilateral crackles, SOB
- diarrhoea
- neurological features
Ethiopia
Match the following types of neonatal soft tissue with the correct description.
1. Cephalohematoma
2. Caput succedaneum
3. Head molding
4. Subgaleal hemorrhage
A. Benign oedema of the scalp tissue that extends across the cranial suture lines
B. Subperiosteal hematoma that is limited to cranial suture lines.
C. Rupture of the emissary veins and bleeding between the periosteum of the skull and the aponeurosis that may extend across the suture lines
D. Transient deformation of the head into an elongated shape due to external compression of the fetal head as it passes through the birth canal during labor
1B
2A
3D
4C
Who was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, and in what field?
Marie Curie, Physics (1903)
A 50-year-old woman presents to her general practitioner with a 2-day history of right eye pain. She also complains of sensitivity to bright light. There is no history of trauma and she does not regularly wear contact lenses. Her past medical history includes Crohn's disease for which she takes methotrexate.
On examination, her observations are within normal limits. Her right eye is erythematous and watering. On fluorescein staining, a dendritic ulcer is seen.
1. What is the most likely diagnosis?
2. What is the recommended treatment for this patient?
A. Artificial tears
B. Topical aciclovir
C. Oral flucloxacillin
D. Topical chloramphenicol
1. Herpes simplex keratitis
This patient has herpes simplex keratitis given the history of eye pain, watering, and photophobia in combination with a characteristic dendritic ulcer seen on examination. Herpes simplex keratitis is more common in those who are immunosuppressed, such as this patient.
2B. Topical
A 31-year-old woman who gave birth two weeks ago presents for review with her husband. He is worried by her mood as she now seems depressed and is interacting poorly with the baby. He describes her mood three days ago being much different, when she was talking in a rapid and incoherent fashion about the future. The mother denies any hallucinations but states that her child has been brought into a 'very bad world'.
1. What is the most appropriate management?
A. Start fluoxetine
B. Start lithium
C. Arrange urgent admission
D. Provide reassurance and a visit from a health visitor.
2. Name two risk factors for the most likely diagnosis.
1. C Urgent admission - the mother may be suffering from puerperal psychosis and needs urgent admission to allow psychiatric evaluation.
2.
- Family history
- Previous episodes
- Mental health conditions
- Sleep deprivation
- Hormonal changes
- Physical stress
- Traumatic birth or pregnancy
- Substance use disorder
- Stillbirth
- Other medical conditions
A 56-year-old woman presents to the GP because she has been experiencing some visual changes. The doctor performs a fundoscopy and finds the following appearance:
The only previous fundoscopy was three years ago and was normal.
1. What additional feature would you likely find on examination?
A. Butterfly malar rash
B. New heart murmur
C. Irregularly irregular pulse
D. Hyperglycaemia
E. Hypertension
2. Name two features of the suspected disease visible in the fundoscopy.
E. Hypertension
The fundoscopy shows hypertensive retinopathy (stage 4):
Cotton-wool spots (widespread white-ish areas resulting from ischaemia)
Retinal haemorrhages (red blotches around the centre of the image)
A 'macular star' composed of intraretinal lipid exudates (the radial, sunburst pattern of white streaks around the macular)
The optic nerve head is swollen, which is the feature that separates grade 3 and grade 4 hypertensive retinopathy
A 35-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with sudden abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. She has a past medical history of complicated pelvic inflammatory disease resulting in scarring of the right fallopian tube. Her last period was 6 weeks ago.
Her heart rate is 93 bpm, and her blood pressure is 136/76 mmHg. Palpation of the left iliac fossa elicits pain. A urinary pregnancy test is positive and further investigations are performed:
Serum b-hCG 5200 IU/L
Ultrasound45 mm left adnexal mass present, no heartbeat seen
1. According to NICE guidelines, what is the first line treatment for suspected gonococcal infection in PID?
A. ceftriaxone 1 g as a single intramuscular (IM) dose, followed by oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily plus oral metronidazole 400 mg twice daily for 14 days
B. Oral ofloxacin 400 mg twice daily plus oral metronidazole 400 mg twice daily for 14 days
C. Oral levofloxacin 500 mg once daily plus oral metronidazole 400 mg twice daily for 14 days
D. Oral moxifloxacin 400mg once daily for 14 days.
2. What is the most appropriate management?
A. Expectant management and observation
B. Laparoscopic salpingectomy and monitoring
C. Laparoscopic salpingotomy and monitoring
D. Methotrexate and monitoring
E. Vaginal misoprostol and monitoring
1. ceftriaxone 1 g as a single intramuscular (IM) dose, followed by oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily plus oral metronidazole 400 mg twice daily for 14 days
2. Ectopic pregnancy requiring surgical management: Salpingotomy (rather than salpingectomy) should be considered for women with risk factors for infertility such as contralateral tube damage.
Given that the size of the ectopic pregnancy is greater than 35 mm, and the beta-hCG levels are higher than 5000 IU/L, the most appropriate step in this patient's management is surgical.
Methotraxate: no significant pain, the size of the ectopic pregnancy <35 mm, beta-hCG less than 1500 IU/L, and no foetal heartbeat present.
Vaginal misoprostol is used for medical management of miscarriage
A 25-year-old woman with type 1 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency department with blurry vision in her right eye. She describes her vision in that eye as 'foggy and washed out'. This began several hours ago and there is associated pain worse on eye movement. The external appearance of her eyes looks normal with no signs of trauma or infection. Her most recent HbA1c and capillary blood glucose are within normal limits.
1. What is the most likely diagnosis?
2. What examination finding is associated with the suspected condition?
A. Absent corneal reflex
B. Holmes-Adie pupil
C. Inferolateral deviation of the affected eye
D. Peripheral visual field loss
E. Relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD)
1. Optic neuritis (visual impairment, pain on eye movement, typically monocular)
E. Relative afferent pupillary defect; an early sign of MS, can be associated with DM.
A: not assiociated with optic neuritis
B: benign condition most associated with women; dilated pupil reacts (constricts) to accomodation but reacts slowly to light
C: oculomotor nerve palsy
D: central visual field loss is more likely in optic neuritis
A 35-year-old man with schizophrenia has been on clozapine for five years and has been well controlled and stable for that time. However, at his most recent check-up, the clozapine levels were found to be above the recommended range and his dose is therefore reduced.
1. Clozapine is an example of a second generation anti-psychotic (SGA) which may cause hyperoprolactinaemia. Which ONE SGA does not cause this?
2. Which of the following is most likely to cause a rise in clozapine blood levels?
A. Alcohol abstinence
B. Omitting doses
C. Smoking cessation
D. Weight loss
E. Stress
1. Aripiprazole (it acts as a partial agonist at D2 receptors
2C Smoking cessation
Match the following cytotoxic agents with the correct side effects.
A. Doxorubicin
B. Cisplatin
C. Azathioprine
D. Dactinomycin
E. Vincristine
F. Methotrexate
G. Bleomycin
H. Cyclophosphamide
I. Paclitaxel
J.Pentostatin
1. Lung fibrosis
2. Haemorrhagic cystitis
3. Peripheral neuropathy in a patient being treated for lymphoma
4. Cardiomyopathy
5. Myelosuppression
1G Bleomycin
2H Cyclophosphamide
3E Vincristine
4A Doxorubicin
5F Methotrexate
A 78-year-old gentleman was seen in your GP clinic during your FY2 rotation in General Practice. He complained of blurring of vision in the right eye for the past 4 months but finally decided to come to see you because he felt his vision is now very distorted. On dilated fundoscopy, the left eye is normal. In the right eye, you can see drusen at the macula. You suspected age-related macular degeneration.
1. State one of the differences between DRY and WET ARMD?
2. Which ONE of the following is your next step in management?
A. Administer anti-VEGF injections
B. Refer to ophthalmology urgently within 1 week
C. Refer to ophthalmology within 1 month
D. Prescribe multi-vitamin
E. Prescribe atorvastatin 40mg
1.
- dry macular degeneration
- 90% of cases
- also known as atrophic
- characterised by drusen - yellow round spots in Bruch's membrane
- wet macular degeneration
- 10% of cases
- also known as exudative or neovascular macular degeneration
- characterised by choroidal neovascularisation
- leakage of serous fluid and blood can subsequently result in a rapid loss of vision
- carries the worst prognosis
2B. Refer to ophthalmology urgently within 1 week