Name a body system in organisms.
(Plants or Animal is OK)
Digestive system, cardiovascular system, nervous system, roots system (plants), other answers are also acceptable.
In a molecule, where is energy stored?
In the bonds between the atoms.
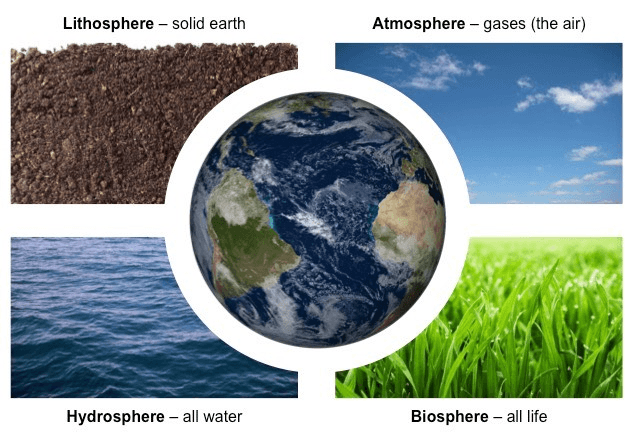
Define 'biosphere', 'atmosphere', 'hydrosphere', and 'geosphere'.
(Complex definition[s] not needed)
Bio- = life
Atmo- = air
Hydro- = water
Geo- = Earth
Give an example of a limiting factor.
Sample Answers: Food, water, shelter, predation, disease, natural disasters, other answers also possible.
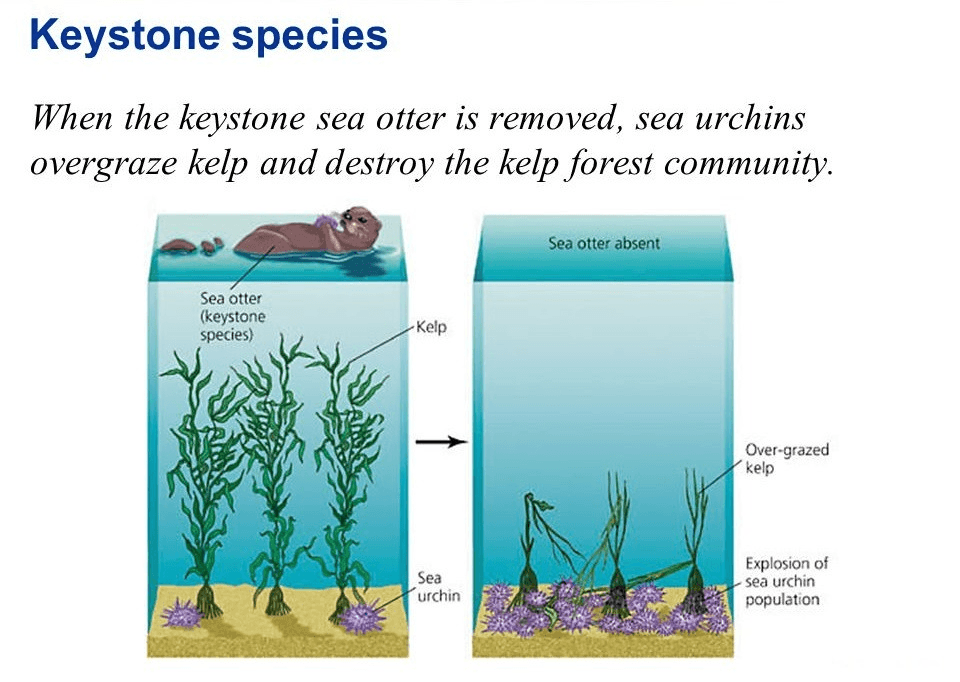
What is a keystone species?
A keystone species is an organism that, if removed from an ecosystem, will cause that ecosystem to collapse (this could mean that the populations settle at new, but vastly different, carrying capacities).
Give an example of a conductive material.
Any metal is conductive, like copper, silver, gold, and aluminum.
What is another name for thermal energy?
Heat

Is energy released when bonds between atoms are formed or broken?
Energy is released when bonds are broken, and energy is absorbed when bonds are formed.
Remember that in a chemical reaction, we consider the net energy, since bonds are being broken and formed at the same time.
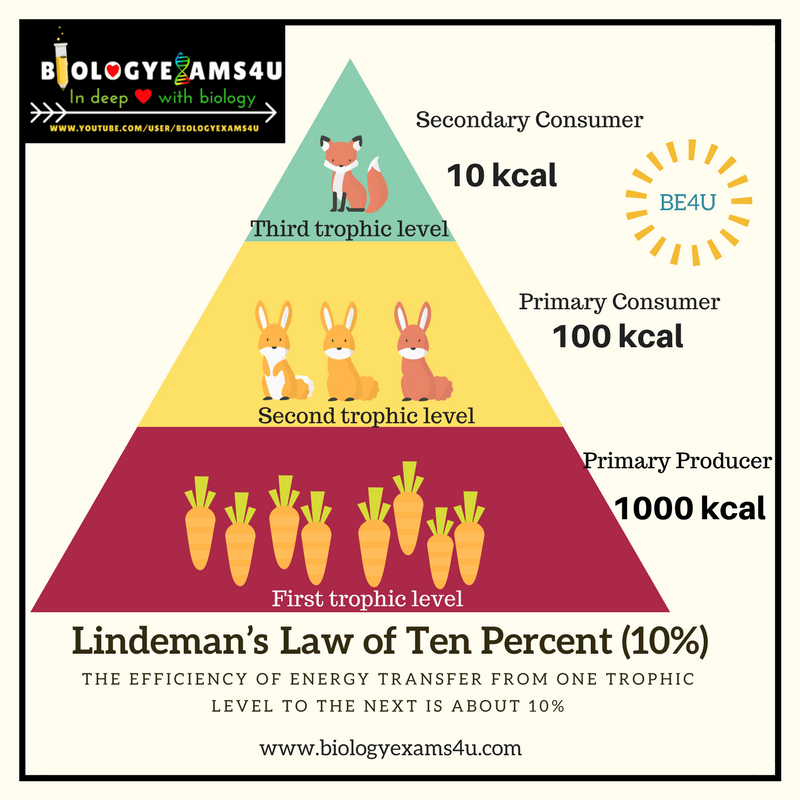
Up to what percentage of energy is able to move up a food chain when an organism is consumed?
10%
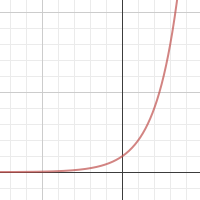
What does an exponential graph look like? Draw it to show your understanding.
Exponential growth occurs when the rate of increase INCREASES as time goes on.
What is a climax community?
In scientific ecology, climax community is a term for a community of plants, animals, and fungi which, through the process of ecological succession in the development of vegetation in an area over time, have reached a steady state.
What is the difference between a material that is hydrophobic and one that is hydrophilic?
Hydrophobic materials repel water, while hydrophilic materials "like", or absorb water.
Give an example of one level of organization higher than "organism" in the hierarchical structure.
Acceptable Answers: Population, community, ecosystem, biosphere
What is the difference between aerobic conditions and anaerobic conditions?
Aerobic respiration occurs when there is oxygen available in the environment.
Anaerobic respiration occurs when there is not enough oxygen available in the environment, so cells switch over to this type of respiration in order to still make some energy.
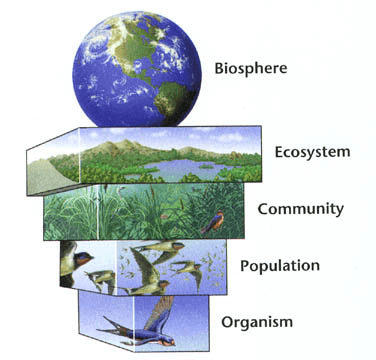
Organism on which trophic level have the most energy?
Producers/autotrophs, since the bottom of the energy pyramid contains the most biomass.
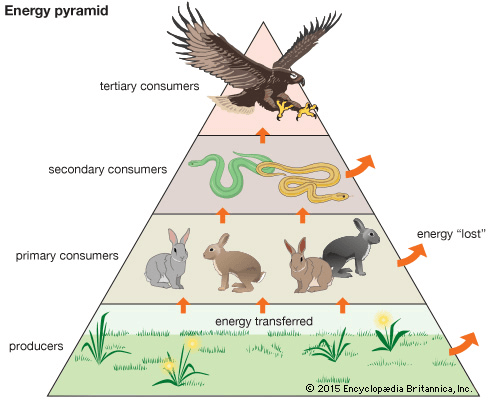
Draw a graph that shows logistical growth. Identify the carrying capacity on the graph.
What is a pioneer species? Give an example.
Pioneer species are hardy species which are the first to colonize barren environments or previously biodiverse steady-state ecosystems that have been disrupted, such as by fire. Some lichens grow on rocks without soil, so may be among the first of life forms, and break down the rocks into soil for plants.

What makes a material flexible on an atomic level?
Materials are flexible when the atoms are able to slide past each other, allowing a material to bend and stretch without breaking.
What is the difference between endoderms and ectoderms? Give an example if it's easier.
Endotherms are "warm-blooded", which means that their bodies regulate their internal body temperature, regardless of external conditions, like in mammals (including us humans!)
Ectotherms are "cold-blooded", which means that the environment regulates their body temperature, like in reptiles.
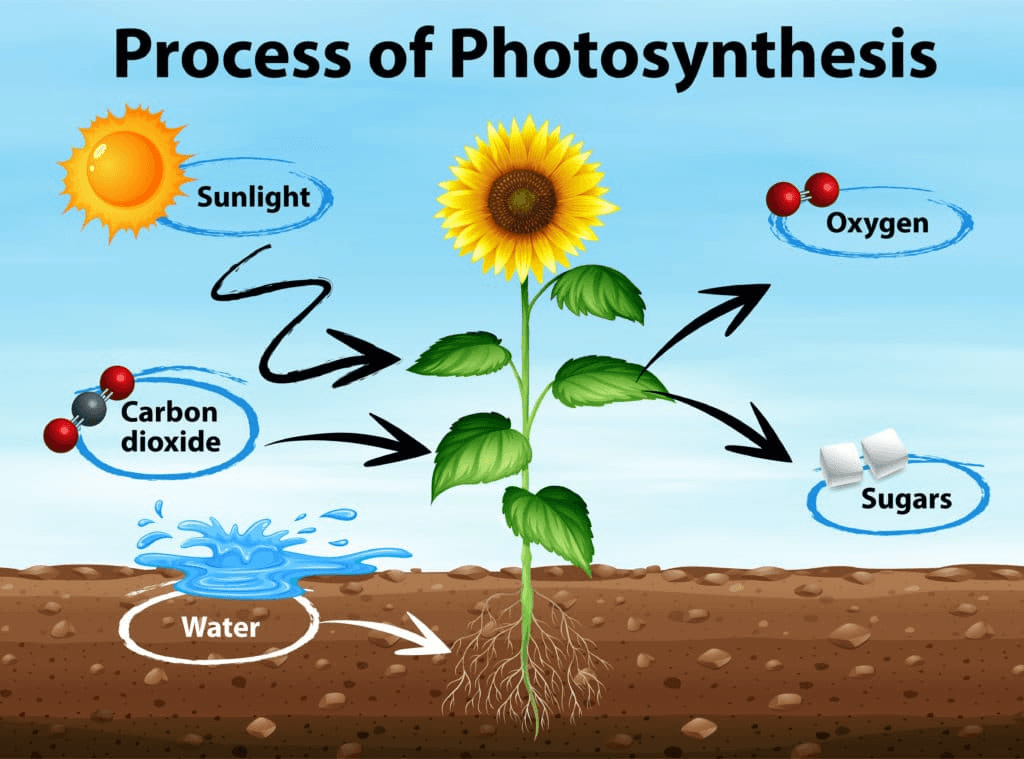
In photosynthesis, where does energy come from, and where is it mostly stored?
In photosynthesis, energy comes from the sun (or light) and is stored in the bonds of glucose (C6H12O6).
Where does the lost energy go when we move up a food chain or pyramid?
In each trophic level, a significant amount of energy is dissipated as heat as organisms carry out cellular respiration and go about their daily lives.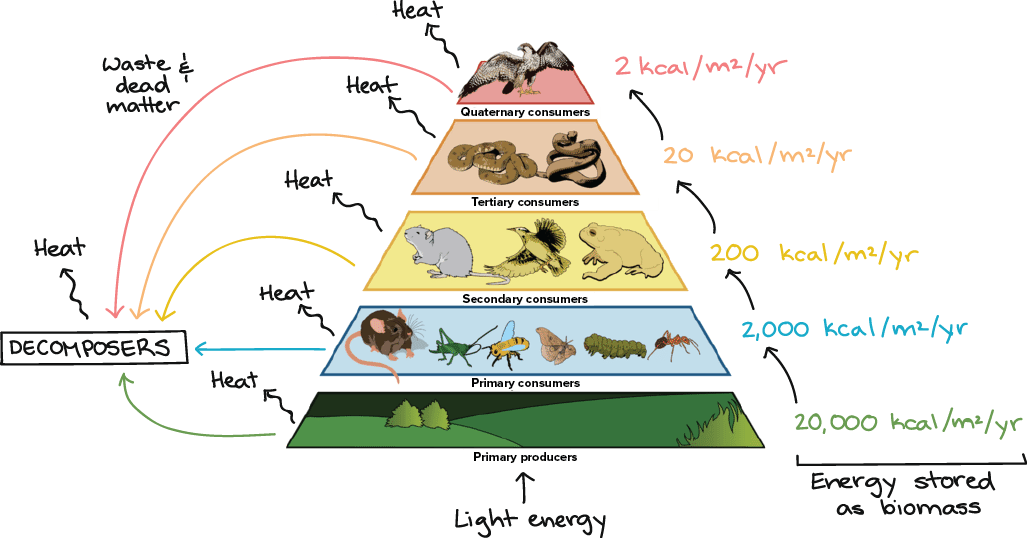
Explain what would happen if a population continues exponential growth, rather than reaching a carrying capacity? Give an example if it's easier.
When a group of organisms overpopulate, this causes the populations of the next lowest trophic level to drop, and then causes the overpopulated group of organisms to starve. In the worst case scenario, it can cause an ecosystem to collapse.
What is the main difference between primary and secondary ecological succession?
Primary succession happens when an ecological disturbance causes there to be no usable soil for vegetation or plants. This happens during volcanic eruptions, glacier movement, and landslides.
Secondary succession happens when an ecological disturbance only destroys the biomass in an area, but leaves usable soil behind. An example of such a disturbance is a wildfire.
What are microplastics, and why are they harmful?
Most plastics in the ocean break up into very small particles. These small plastic bits are called "microplastics." Other plastics are intentionally designed to be small. They're called microbeads and are used in many health and beauty products. They pass unchanged through waterways into the ocean. This is a problem because microplastics are building up in our bodies and we don't know the long-term effects of this.

Give an example of a positive feedback mechanism.
Positive feedback mechanisms increase something in response to a stimuli. For example, your body increases its heart rate and breathing rate during exercise in order to get enough oxygen to its cells.
Another example is blood sugar. When blood sugar gets too high, the body increases its production of insulin in response so that the body can absorb the sugar from the bloodstream.
In cellular respiration, where does the energy come from, and where does the energy go?
In cellular respiration, energy comes from breaking the bonds between the atoms in a sugar molecule (like C6H12O6, glucose), and the energy goes into a complex molecule nicknamed ATP (Adenosine Tri-Phosphate). ATP is used to do work in the organism's body.
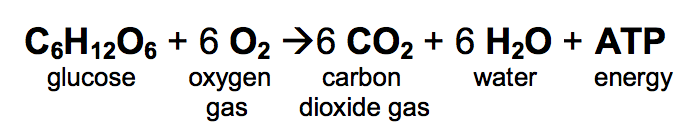
Why are there generally fewer organisms (apex predators) at the highest levels of a food web?
There are less apex predators than other consumers and producers because it requires a massive amount of biomass to support one top predator.
What does it mean when a population is resilient?
Resilience includes the resistance of populations to change after disturbance and their recovery from it.
Explain what would happen to the trophic levels below a keystone species if that species were removed from an ecosystem.
Bonus: Are all keystone species apex predators?
If a keystone species is removed, the trophic level directly below that species would increase in population, since there's no longer a major predator. The level BELOW that one would decrease in population (including autotrophs/plants) due to the increase in the level above it.
While many keystone species are apex predators, not all of them are. One example would be the wildebeest of the Serengeti.
Why is the process of making plastic harmful?