Which of the following are the ROMs associated with the shoulder joint? Select all that apply.
A.) External rotation
B.) Inversion
C.) Circumduction
D.) Extension
E.) Abduction
A.) External rotation
C.) Circumduction
D.) Extension
E.) Abduction
You have a patient that might have a urinary tract infection (UTI). Which statement by the patient suggests that a UTI is likely?
A.) 'I pee a lot'.
B.) 'It burns when I pee.'
C.) 'My pee smells sweet'.
D.) 'I go hours without the urge to pee'.
B.) 'It burns when I pee'.
A common symptom of a UTI is dysuria. A patient with a UTI often reports frequent voiding of small amounts and the urgency to void. Symptoms of uncomplicated UTI are pain on urination (dysuria), frequent urination (frequency), inability to start the urine stream (hesitation), sudden onset of the need to urinate (urgency), and blood in the urine (hematuria). Usually, patients with uncomplicated UTI do not have fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, or back pain, which are signs of kidney involvement or upper tract disease/pyelonephritis.
The wife of a 65-year-old man tells the nurse that she is concerned because she has noticed a change in her husband’s personality and ability to understand. He also cries very easily and becomes angry. What part of the cerebral lobe is responsible for these behaviors?
A.) Frontal lobe
B.) Parietal lobe
C.) Occipital lobe
D.) Temporal lobe
A.) Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe has areas responsible for personality, behavior, emotions, and intellectual function. The parietal lobe has areas responsible for sensation; the occipital lobe is responsible for visual reception; and the temporal lobe is responsible for hearing, taste, and smell.
Which of the following organs are located in the left lower quadrant?
A.) Appendix
B.) Pancreas
C.) Sigmoid Colon
D.) Gallbladder
C.) Sigmoid Colon
The nurse is reviewing an assessment of a patient’s peripheral pulses and notices that the documentation states that the radial pulses are “2+.” The nurse recognizes that this reading indicates what type of pulse?
A.) Weak
B.) Absent
C.) Normal
D.) Bounding
C.) Normal
When documenting the force, or amplitude, of pulses, 3+ indicates an increased, full, or bounding pulse, 2+ indicates a normal pulse, 1+ indicates a weak pulse, and 0 indicates an absent pulse.
A nurse observes that a client has complete range of motion against gravity with partial resistance. What grade of muscle strength should the nurse document?
A.) 1
B.) 3
C.) 4
D.) 2
E.) 5
C.) 4
Full ROM against gravity, some resistance is a muscle strength of a 4 according to the grade scale.
How would a nurse know that a client has impaired renal function during their 12-hour shift?
We would look at their urine output.
Normal urine output is >0.5 ml/kg/hour.
Roughly a client should produce 33.3-83.3 ml/hr. Therefore, if urine output is calculated to be less than 30 ml/hr, there is impaired renal function.
During an assessment of a 67-year-old male client with a traumatic brain injury, the nurse notices that the patient responds to pain by extending, adducting, and internally rotating his arms. His palms pronate, and his lower extremities extend with plantar flexion. Which statement concerning these findings is most accurate? What do these findings indicate?
A.) A lesion of the cerebral cortex
B.) A completely nonfunctional brainstem
C.) Normal findings that will resolve in 24 to 48 hours
D.) A very ominous sign and may indicate brainstem injury
D.) a very ominous sign and may indicate brainstem injury
These findings are all indicative of decerebrate rigidity, which is a very ominous condition and may indicate a brainstem injury
Think about what decorticate posturing is...
During an abdominal assessment, the nurse is unable to hear bowel sounds in a patient’s abdomen. How long should the nurse listen before reporting absent bowel sounds?
A.) 1 minute
B.) 5 minutes
C.) 2 minutes per each quadrant
D.) 10 minutes
B.) 5 minutes
Absent bowel sounds are rare. The nurse must listen for 5 minutes before deciding that bowel sounds are completely absent.
The nurse is performing an assessment on an adult. The adult’s vital signs are normal, and capillary refill time is 5 seconds. What should the nurse do next?
A.) Ask the patient about a history of frostbite.
B.) Suspect that the patient has venous insufficiency.
C.) Consider this a delayed capillary refill time, and investigate further.
D.) Consider this a normal capillary refill time that requires no further assessment.
C.) Consider this is a delayed capillary refill time, and investigate further
Normal capillary refill time is less than 1 to 2 seconds. A capillary refill time of 5 is a decrease in capillary refill which indicates vasoconstriction or decreased cardiac output. The nurse should investigate further. Decreased capillary refill is not a characteristic of previous frostbite or venous insufficiency and some conditions can skew the findings: a cool room, decreased body temperature, cigarette smoking, peripheral edema, and anemia.
Which of the following spinal deformities are associated with pregnant woman?
A.) Scoliosis
B.) Lordosis
C.) Kyphosis
D.) Ankylosis
B.) Lordosis
Pregnancy leads to increased inward curvature of the lumbar spine, also called lordosis. Kyphosis refers to increased forward curvature of the thoracic spine. Ankyloses are fused joints, which would not be typical for a pregnant client. Scoliosis is the lateral curvature of the spine and is not expected during pregnancy.
When performing a genital examination on a 25-year-old man, the nurse notices deeply pigmented, wrinkled scrotal skin with large sebaceous follicles. On the basis of this information, how should the nurse proceed?
A.) Squeeze the glans to check for the presence of discharge.
B.) Consider this finding as normal, and proceed with the examination.
C.) Assess the testicles for the presence of masses or painless lumps. Incorrect
D.) Obtain a more detailed history, focusing on any scrotal abnormalities the patient has noticed.
B.) Consider this finding as normal, and proceed with the examination.
After adolescence, the scrotal skin is deeply pigmented and has large sebaceous follicles and appears corrugated.
When assessing the neurologic system of a hospitalized patient during morning rounds, what should the nurse include during the assessment?
A.) Blood pressure
B.) Patient’s ability to communicate
C.) Patient’s personal hygiene level
D.) Patient’s rating of pain on a scale of 1 to 10
B.) Patient's ability to communicate
Assessment of a patient’s ability to communicate is part of the neurologic assessment. Blood pressure and pain rating are measurements, and personal hygiene is assessed under general appearance.
During an abdominal assessment, the nurse would consider which of these findings as normal?
A.) Presence of a bruit in the femoral area.
B.) Tympanic percussion note in the umbilical region.
C.) Dull percussion note in the left upper quadrant at the midclavicular line
D.) Palpable spleen between the ninth and eleventh ribs in the left midaxillary line.
B.) Tympanic percussion note in the umbilical region
Tympany should predominate in all four quadrants of the abdomen because air in the intestines rises to the surface when the person is supine. Vascular bruits are not usually present. Normally the spleen is not palpable. Dullness would not be found in the area of lung resonance (left upper quadrant at the midclavicular line).
Which of the following clinical manifestations are present in a post-operative client who underwent a right knee arthroscopy? Select all that apply.
A.) Bilateral swelling of the legs.
B.) Unilateral swelling of the leg.
C.) Redness and warmth of leg
D.) Severe pain
C.) Redness and warmth of leg
D.) Severe pain
A patient is being assessed for range-of-joint movement. The nurse asks him to move his arm in toward the center of his body. What is this movement called?
A.) Extension
B.) Flexion
C.) Abduction
D.) Adduction
D.) Adduction
Adduction is the movement of extremities towards the center or midline of the body
When performing a scrotal assessment, the nurse notices that the scrotal contents show a red glow with transillumination. How should the nurse proceed?
A.) Assess the patient for the presence of a hernia.
B.) Suspect the presence of serous fluid in the scrotum.
C.) Refer the patient for evaluation of a mass in the scrotum.
D.) Consider this finding normal and proceed with the examination.
B.) Suspect the presence of serous fluid in the scrotum.
Normal scrotal contents do not allow light to pass through the scrotum. However, serous fluid does transilluminate and shows as a red glow. Neither a mass nor a hernia would transilluminate.
During an assessment of the cranial nerves (CNs), the nurse finds the following: asymmetry when the patient smiles or frowns, uneven lifting of the eyebrows, sagging of the lower eyelids, and escape of air when the nurse presses against the right puffed cheek. These findings indicate dysfunction of which cranial nerve(s)?
A.) Motor component of CN IV
B.) Motor component of CN VII
C.) Motor and sensory components of CN XI
D.) Motor component of CN X and sensory component of CN VII
B.) Motor Component of CN VII
The nurse’s findings all reflect motor dysfunction, none are sensory. The specific cranial nerve affected is the facial nerve (CN VII). Cranial nerve IV, the trochlear nerve, innervates a muscle in the eye muscle and is responsible for eye movement, not the symptoms this patient is experiencing. The nurse’s findings all reflect motor dysfunction, none are sensory, therefore options c and d can be eliminated because they each contain a sensory component.
A patient is suspected of having inflammation of the gallbladder, or cholecystitis. The nurse should conduct which of these techniques to assess for this condition?
A.) Obturator test
B.) Test for Murphy sign
C.) Iliopsoas muscle test
D.) Assess for rebound tenderness
B.) Test for Murphy sign
Normally palpating the liver causes no pain. In a person with inflammation of the gallbladder, or cholecystitis, pain occurs as the descending liver pushes the inflamed gallbladder onto the examining hand during inspiration (Murphy test). The person feels sharp pain and abruptly stops midway during inspiration. The obturator and iliopsoas muscle tests assess for an inflamed appendix. Although a patient with cholecystitis may have rebound tenderness, the presence of rebound tenderness indicates peritoneal inflammation which could be caused by several things so it is not specific to cholecystitis.
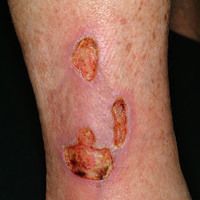
A 53-year-old female client arrives to the emergency department with the following problem. The nurse understands which other clinical manifestations will be present with this condition. Select all that apply.
A.) Heaviness in bilateral legs.
B.) Pain with activity that is relieved by rest.
C.) Pallor in lower extremities.
D.) Low hair distribution in legs.
E.) +2 normal pulses.
B.) Pain with activity that is relieved by rest.
C.) Pallor in lower extremities.
D.) Low hair distribution in legs.
All are consistent with arterial insufficiency findings as noted with the image.
Which of the following assessment findings are consistent with a 78-year-old female client with an osteoarthritis diagnosis? Select all that apply.
A.) Pain that worsens with movement
B.) Swan neck deformities
C.) Heberden and Bouchard nodes
D.) Symmetrical deformities in the joints
A.) Pain that worsens with movement
C.) Heberden and Bouchard nodes
Osteoarthritis is a noninflammatory, localized, progressive disorder involving deterioration of articular cartilages (cushion between the ends of bones) and subchondral bone remodeling, synovial inflammation, and formation of new bone (osteophytes) at joint surfaces. Assessment findings include Heberden and Bouchard nodes and pain worsening with movement. It is a 'wear and tear' disease progression. Rheumatoid arthritis assessment findings include swan neck deformities, pain that improves with movement and symmetrical deformities in the joints due to inflammation.
A 65-year-old woman is in the office for routine gynecologic care. She had a complete hysterectomy 3 months ago after cervical cancer was detected. Which statement does the nurse know to be true regarding this visit?
A.) Her cervical mucosa will be red and dry looking.
B.) She will not need to have a Pap smear performed.
C.) The nurse can expect to find that her uterus will be somewhat enlarged and her ovaries small and hard.
D.) The nurse should plan to lubricate the instruments and the examining hand adequately to avoid a painful examination.
D.) The nurse should plan to lubricate the instruments and the examining hand adequately to avoid a painful examination.
In the aging adult woman, natural lubrication is decreased; therefore, to avoid a painful examination, the nurse should take care to lubricate the instruments and the examining hand adequately. Menopause, with the resulting decrease in estrogen production, shows numerous physical changes. The cervix shrinks and looks pale and glistening. With the bimanual examination, the uterus feels smaller and firmer and the ovaries are not normally palpable. Women should continue cervical cancer screening up to age 65 years if they have an intact cervix and are in good health. Women who have had a total hysterectomy do not need cervical cancer screening if they have 3 consecutive negative Pap tests or 2 or more consecutive negative HIV and Pap tests within the last 10 years.
*Think about how there may cancerous lesions surrounding the cavity, despite the complete removal of uterus*
A 45-year-old female client comes in nuchal rigidity, vomiting, and fever. Which of these maneuvers would the nurse conduct to assess for meningitis? Select all that apply.
A.) Assess the client’s ability to raise the legs without pain.
B.) Assess the client for flexion of the hips and knees when flexing the neck.
C.) Assess the client for extension of the knees when extending the neck.
D.) Assess the client for external rotation of the hip.
A.) Assess the client's ability to raise the legs without pain
B.) Assess the client for flexion of the hips and knees when flexing the neck.
2 tests to screen for meningeal inflammation include Kernig’s sign (positive result would be pain when raising the leg straight) and Brudzinski’s sign (positive result would be flexion of the hips and knees when the head is flexed.
During an assessment, the nurse notices that a patient’s umbilicus is enlarged and everted. It is positioned midline with no change in skin color. The nurse recognizes that the patient may have which condition?
A.) Flatulence
B.) Abdominal tumor
C.) Intra-abdominal bleeding
D.) Umbilical hernia
D.) Umbilical Hernia
The umbilicus is normally midline and inverted with no signs of discoloration. With an umbilical hernia, the mass is enlarged and everted. The other responses are incorrect.
The nurse is reviewing the risk factors for venous disease. Which of these situations best describes a person at highest risk for the development of venous disease?
A.) Person who has been on bed rest for 4 days.
B.) Older adult taking anticoagulant medication.
C.) Woman in the second month of her first pregnancy.
D.) Person with a 30-year, 1 pack per day smoking habit.
A.) Person who has been on bed rest for 4 days.
Efficient venous return depends on contracting skeletal muscles, competent valves in the veins, and a patent lumen. Problems with any of these three elements lead to venous stasis. People who undergo prolonged standing, sitting, or bed rest are at risk for venous disease because they do not benefit from the milking action to the veins that walking accomplishes. Hypercoagulable (not anticoagulated) states and vein wall trauma also place the person at risk for venous disease. Obesity and multiple pregnancies are also risk factors. Smoking is a risk factor for arterial disease, not venous disease