Assessment of this fluid imbalance include low BP, weak thready pulse, and poor skin turgor.
What is hypovolemia, or FVD?
A patient with this ABG imbalance may present with confusion, history of opioid overdose, and an RR of 12.
What are S/S of respiratory acidosis?
A "trigger" is often the cause of this respiratory exacerbation.
What is asthma?
Administration of this generic drug should provide relief of dyspnea/SOB in a patient with left sided HF.
What is administration of furosemide?
Therapeutic level of this drug is an INR between 2 and 3.
What is warfarin?
Patient education for this disease include avoid smoking, control BP, reduce cholesterol, and take prescribed peripheral vasodilators.
What is peripheral arterial disease (PAD)?
Nursing considerations for this drug include monitoring for hypotension and refractive tachycardia.
What is nitroglycerin?
This is the most common cause of hypokalemia.
What is diuretic use?
This ABG imbalance may be caused by vomiting and/or NGT suctioning.
What is metabolic alkalosis?
A respiratory infection is frequently the cause of this exacerbation.
What is COPD exacerbation?
A low-sodium diet and avoidance of canned foods are two teaching points for this disease state.
What is patient education for patients with hypertension (or heart failure)?
Stroke prevention and rate control are two nursing goals for a patient with this dysrhythmia.
What are priority nursing goals for a paitient with atrial fibrillation?
Nursing interventions for this disease include elevate extremities to reduce edema, apply compression stockings, and educate patient on smoking cessation.
What is venous insufficiency?
This class of IVF is indicated for fluid resuscitation (dehydration, hypovolemia, etc.).
What are isotonic IVF?
This is an expected electrolyte imbalance resulting from metabolic acidosis.
What is hyperkalemia?
Applying a nonrebreather mask without O2 is a possible intervention for this ABG imbalance.
What are interventions for respiratory alkalosis?
Thinned secretions is the expected outcome when administering this drug class.
What is an expectorant?
The patient with this disease complains of chest pain with exertion.
What is stable angina?
This dysrhythmia looks like this on an ECG:
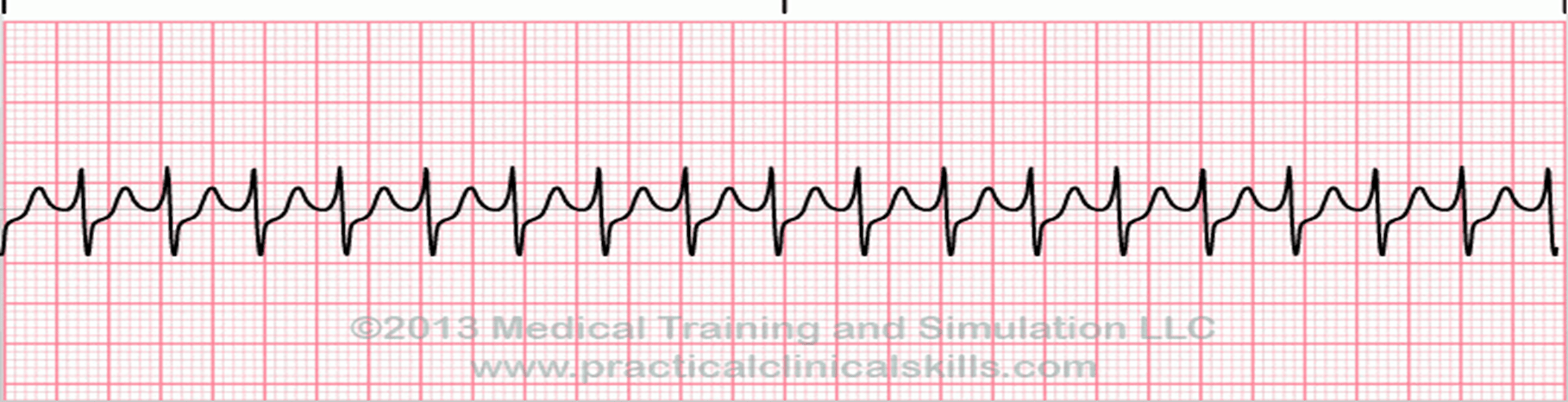
What is Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)?
A classic presentation of this disease state is pain in both legs with physical activity that is relieved by rest.
What is peripheral arterial disease/intermittent claudication?
This generic drug inhibits an enzyme in the liver that results in decreased cholesterol production.
What is simvastatin, atorvastatin?
This is an ECG finding associated with hyperkalemia.
What is a peaked T wave?
This ABG imbalance may be caused by a patient with DM Type I who does not take prescribed insulin.
What is metabolic acidosis?
Assessment of this disease state include dyspnea on exertion, an increased A-P diameter, and no smoking history.
What is emphysema?
Long-term complications of this disease include kidney failure, hemorrhagic stroke, and blindness.
What is hypertension?
Interventions for this dysrhythmia include chest compressions and preparation for immediate defibrillation.
What is ventricular fibrillation?
The pathophysiology of this disease is peripheral arterial spasm triggered by cold temperatures.
What is Raynaud's Phenomenon?
Protamine sulfate is the antidote for this drug.
What is heparin?
This generic drug can cause hyperkalemia and hyponatremia.
What is spirinolactone?
This is the interpretation for the following ABG:
pH: 7.36
paCO2: 48 mm Hg
HCO3: 28 mEq/L
paO2: 78 mm Hg
What is fully compensated respiratory acidosis?
Administration of this relax's smooth muscles in the airways and improve the ventilation of the lungs
What are bronchodilators?
A classic presentation of this disease includes chest pain 10/10 with radiation, shortness of breath, and diaphoresis.
What is myocardial infarction (MI), or heart attack?
Interventions for this dysrhythmia include IV atropine and cardiac pacing.
What is symptomatic bradycardia?
A systemic disorder that involves the narrowing of peripheral blood vessels (vessels situated away from the heart or the brain). This happens as a result of arteriosclerosis, or a buildup of plaque, and can happen with veins or arteries.
What is Peripheral vascular disease, or PVD
Adenosine is first line drug for this disease state.
What is SVT?