A child with type 1 diabetes is receiving 15 units of regular insulin and 20 units of NPH insulin at 7:00 AM each day. Which time would the nurse anticipate a hypoglycemic reaction from the NPH insulin to occur?
1-With in 30 min
2. in the afternoon
3. in the evening
4. no need to worry about this.
2-in the afternoon
NPH insulin is an intermediate-acting insulin that peaks approximately 6 to 8 hours after administration. It was administered at 7:00 AM, so between 1:00 PM and 3:00 PM is when the nurse would anticipate that a hypoglycemic reaction would occur.
Noon is when a reaction from a short-acting (regular) insulin is expected. Short-acting insulin peaks 2 to 4 hours after administration. given at 0700- onset is 30min but check sugar in 2 hours for peak
Within 30 minutes of administration is when a reaction from a rapid-acting insulin (aspart / lispro) is expected. Rapid-acting insulin peaks 30 to 3 hours after administration. given at 0700- onset is 15 min but check sugar @ 800-930am
During the evening or nighttime is when a reaction from a long-acting (detemir) insulin is expected. Long-acting insulin has a small peak 10 to 16 hours after administration.
Which clinical manifestation would the nurse expect to find upon assessment of a client with Cushing syndrome? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
1- truncal obesity
2-osteoporosis
3- hypoglycemia
4- hyperglycemia
5- hypokalemia
1,2,4,5
Truncal obesity is caused by the overproduction of adrenal cortisol hormone associated with Cushing syndrome. and increase BS
osteo- disrupts bone metabolism, leading to increased bone breakdown (resorption) and decreased bone formation
hypokalemia-increase sodium reabsorption (hypernatremia) and, crucially, potassium excretion by the kidneys,
tx of cushings will result in improvement of BS and electrolytes. check BS / lytes. TMS / EKG monitoring
Which clinical manifestation exhibited by a client taking levothyroxine for hypothyroidism for 3 months would cause a nurse to suspect that a decrease in dosage is needed? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
1- Tremors
2- hypotension, bradycardia
3-heat intolerance
4-weight gain
1, 3
Excessive levothyroxine produces adaptations similar to hyperthyroidism, including tremors, heat intolerance, tachycardia, hypertension, and insomnia.
anticipate eleved t3/t4 and decrease TSH. decrease levothyroxine. propanolol for cardiac symptoms, and PTU worse case situations
take in am, avoid switching brands, continue with pregnancy and check levels.
The nurse is planning care for a client with diabetes insipidus (DI). Which intervention made by the nurse requires correction?
1-Assessing sodium levels
2-Measuring urine output
3-Restricting fluids at night
4-changing positions slowly
3
A client with DI is at risk for severe fluid volume deficit due to increased urination. Therefore the nurse would never restrict fluids for longer than 4 hours, because it can lead to severe dehydration.
maintain fall risk due to hypotension assoc with dehydration.
The nurse would assess sodium levels, measure urine output, and have the client change positions slowly. monitor for seizure precautions.
treatment would decrease thirst, improvement in low urine osm and specific gravity, and high serum osm
Which clinical finding is the priority requiring collaboration with the primary health care provider when a nurse reviews the medical record of an older adult client admitted with chronic kidney disease?

1-NA
2-K
3-CR
4-BP
K
The client has an increased potassium level outside the expected range for an adult, placing the client at risk for a cardiac dysrhythmia; the higher priority is treatment for the increased potassium, because elevated levels can be lethal.
place the client on Telemetry to monitor for dysrhythmia
The serum sodium of 135 mEq/L (135 mmol/L) is expected because of the electrolyte imbalance caused by the presence of chronic kidney failure. A creatinine clearance of 20 mL/min (0.33 mL/s) is low (normal range 95 mL/min in young women; 120 mL/min in young men); however, the client has chronic renal disease and this value reflects the disease process. The priority is the high potassium level. Clients with chronic kidney disease usually have hypertension, and notification is unnecessary.
Which clinical indicator would the nurse expect when assessing a client with Meniere disease? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
1-Nausea
2-Dizziness / vertigo
3-tinnitus
4-Decreased pulse rate
5-Increased temperature
1,2,3
Nausea along with diaphoresis is related to vertigo, which is associated with this disorder.
the sensation of spinning (vertigo) and dizziness occurs with inflammation of the inner ear along with ear fullness, tinnitus.
Jerky lateral eye movement (nystagmus), particularly toward the involved ear, occurs with Meniere disease.
The heart rate does not decrease with this disorder. Body temperature is not influenced by this disorder.
Which condition would the nurse identify as the likely cause of profound weakness and nervousness in a client that became confused shortly after self-administering the morning dose of 10 units of regular insulin and 25 units of NPH insulin after a light breakfast with no additional intake in the 3 hours since that time?
1-hyperglycemia
2-hypoglycemia
3- DKA
4-HHNS
2-hypoglycemia
Severe hypoglycemia is a finding in diabetic clients who take insulin and miss a meal. Signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia are nervousness, weakness, confusion, and disorientation. Hyperglycemia is rare in clients who are on insulin therapy and decrease their intake. Hyperinsulinemia is a condition where an excess of insulin is produced by the pancreas in response to conditions such as insulin resistance or insulinomas. Hypoinsulinemia refers to abnormally low levels of insulin in the blood.
Which outcome would be expected after a client received treatment for Cushing disease? SATA
1- increased cortisol level
2-decrease BS
3-increase Potassium
4-increase NA levels
2,3
treatment will decrease cortisol levels which will then cause decrease in BS and increase in potassium.
cushings syndrome will have increase NA so once treated you should see a decrease in levels.
The nurse is educating a client with hypothyroidism about the use of levothyroxine. Which information would the nurse provide? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
1.take dose same time each day.
2. Refrain from switching brands.
3. Have regular bloodwork drawn.
4.Hold medication for pulse >60 beats per minute.
5. Report weight loss more than 3 pounds.
1,2,3
Clients taking levothyroxine should take the same dose the same time each day and should not switch medication brands. The client should have regular thyroid levels drawn to ensure accurate dosage.
The medication should be held if the client is experiencing tachycardia, or a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute.
The client with hypothyroidism will begin to lose weight with medication as thyroid levels stabilize.
Which sign would the nurse expect to observe in a client with small cell carcinoma of the lung who develops syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
1.Oliguria
2-Seizures
3-Vomiting
4-Polydipsia
5-Polyphagia
1.2.3
causes fluid retention, resulting in increased blood volume and decreased urine volume. Fluid retention associated with SIADH can cause cerebral edema, resulting in confusion and seizures.
Fluid retention resulting in hyponatremia causes nausea and vomiting. The client will have nausea and vomiting, resulting in a decreased oral fluid and food intake.
Which sign is an associated complication of chronic kidney disease for a client undergoing peritoneal dialysis?
1. Petechiae
2. Abdominal bruit
3. Cloudy return dialysate
4. Increased blood glucose level
3
The returned dialysate should be clear; cloudy return dialysate solution is indicative of infection.
Petechiae do not occur during dialysis treatments. There is no danger of developing an abdominal bruit during dialysis. Dialysis does not affect the blood glucose level.
A nurse is caring for a patient experiencing an acute attack of Meniere's disease. The patient reports severe vertigo. Which medication should the nurse anticipate administering to help alleviate the patient's symptoms?
A) Meclizine
B) Prochlorperazine
C) Furosemide
D) Ondansetron
MECLIZINE
- Meclizine is effective for managing vertigo, which is a primary symptom during acute attacks of Meniere's disease.
- Prochlorperazine and ondansetron can help with nausea but do not specifically target vertigo.
- Furosemide is more of a long-term management option rather than for acute symptom relief.
Before having surgery, a client with type 1 diabetes insulin requirements are elevated but well controlled. Which insulin requirements would the nurse anticipate for this client postoperatively?
1- decrease
2-increase
3- stay the same
Emotional and physical stress may cause insulin requirements to remain elevated in the postoperative period. Insulin requirements will remain elevated rather than decrease.
-anticipate IV insulin to be used
- increase risk for infection
The nurse is caring for a client with Addison disease. Which dietary instruction would the nurse provide?
1-high potassium foods
2- high na foods
3- restrict fluids
4-low protein
encourage NA foods
Because of diminished mineralocorticoid secretion, clients with Addison disease are prone to developing hyponatremia. The addition of salt to the diet is advised. Clients with Addison disease are prone to hyperkalemia. High-potassium foods can be restricted. Protein is not omitted from the diet, they experience weight los; ingestion of essential amino acids is necessary for optimum metabolism and healing. Fluids are not restricted for clients with Addison disease, especially since they can experience hypotension.
Which instruction would the nurse teach a client with the diagnosis of Graves’ disease regarding propylthiouracil (PTU)?
1. "Increase sources of calcium."
2. "Observe for signs of infection."
3. "Take the medication through a straw."
4. "Wear sunglasses when exposed to sunlight."
2-monitor for bone marrow suppression
PTU may lower the white blood cell count, making the client prone to infection.
PTU does not cause hypocalcemia. Taking the medication through a straw is necessary with iodine preparations to prevent staining of the teeth; however, PTU does not contain iodine. PTU does not cause photophobia.
When assessing a client with diabetes insipidus, which sign would the nurse anticipate finding? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
1.Excessive thirst
2.dry mucous membranes
3.Increased blood pressure
4.Decreased serum osmolarity
5.Decreased urine specific gravity
1, 2, 5
As excessive fluid is lost through urination, dehydration triggers the thirst response.
As excessive fluid is lost through urination, dehydration occurs, resulting in dry mucous membranes and poor skin turgor.
Because water is not being reabsorbed, urine is dilute, resulting in a low specific gravity (less than 1.005). Diabetes insipidus is not a disorder of glucose metabolism;
Loss of fluid may decrease the blood pressure because fluid is lost from the intravascular compartment. As fluid is lost from the intravascular compartment, serum osmolarity increases, not decreases.
Which food would the nurse encourage the client requiring hemodialysis to include in his or her dietary intake?
1-Rice
2-Potatoes
3-canned salmon
4-Barbecued beef
1
Foods high or moderately high in carbohydrates and low in protein, sodium, and potassium are encouraged for clients on hemodialysis.
Potatoes are high in potassium, which is restricted.
Canned salmon is high in protein and sodium, which usually are restricted.
Barbecued beef is high in protein, sodium, and potassium, which usually are restricted.
Which medication is a beta-adrenergic blocker used to reduce intraocular pressure?
1. Timolol
2. Travoprost
3. Carbachol
4. Apraclonidine
TIMOLOL
Timolol is a beta-adrenergic blocker used in the treatment of glaucoma.
monitor for hypotension / bradycardia- move slowly
monitor for bronchospasm--avoid in asthma, copd, emphysema
Travoprost is a prostaglandin agonist, and apraclonidine is an adrenergic agonist used in the treatment of glaucoma.
Carbachol is a cholinergic agonist used to treat glaucoma.
Which unique response is associated with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) that is not exhibited with hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS)? SATA
1-kussmauls respirations
2. 7.36, 50, 27
3. 7.25, 35, 17
4-abd pain
1, 3, 4.
diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
Kussmauls resp -body attempts to correct a low pH caused by accumulation of ketones (ketoacidosis).
Which complication would the nurse expect if a client with Addison's disease receiving cortisone therapy abruptly stops the medication? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
1- hypotension
2- circulatory collapse
3-alkalosis
4-hypokalemia
1,2
An Addisonian (adrenal) crisis is triggered by an abrupt withdrawal from chronic corticosteroid therapy and can result in hypotension, shock and circulatory collapse. Inadequate circulating corticosteroids result in excessive renal excretion of sodium and water, leading to hyperkalemia, cellular dehydration, acidosis, hyponatremia,and reduction of extracellular fluid volume.
Which interventions would the nurse include in the plan of care during the first 4 hours after a thyroidectomy? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
1-Ensure that the client lies flat.
2-Monitor vital signs every hour.
3-Monitor for stridor or dyspnea.
4-Monitor for the signs and symptoms of tetany.
5-Assess the sides and back of the client's neck for evidence of bleeding.
3, 5
After a thyroidectomy, it is critical to monitor for stridor, dyspnea, or other symptoms of acute airway obstruction that may result postoperatively.
It is important to inspect the neck dressing and the sides of the neck and behind the neck for blood that may drain in that direction by gravity.
The client needs to be placed in a semi-Fowler position to decrease tension on the suture line.
Vital signs need to be monitored every 15 minutes until the client is stable, then every 30 minutes for 24 hours.
Although this may be a complication of this surgery, tetany will not occur during the first 4 hours after surgery.
The registered nurse (RN) delegates a task to the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP). Which client care task is able to be delegated to the UAP?
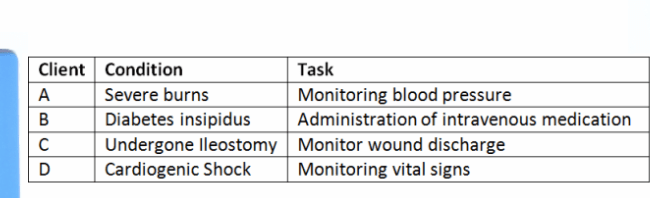
C
The task of delivering care to client C is delegated to the UAP because the UAP can monitor the wound discharge in clients who have undergone surgery.
Severe burns are an acute condition where the vitals are unstable. The UAP is not authorized to provide care to client A with severe burns.
The UAP’s scope of practice is limited for administration of intravenous fluids or medications, so the UAP is not authorized to provide care to client B, who has diabetes insipidus and requires intravenous administration of medications.
Cardiogenic shock is an acute condition where the vitals are unstable, so the UAP is not qualified to provide care to client D with cardiogenic shock, an acute condition which may require continuous monitoring of vital signs.
A client who has renal failure asks the nurse why anemia keeps recurring. Which reason would the nurse explain to the client?
1-Increase in blood pressure
2-Decrease in erythropoietin
3-Increase in serum phosphate levels
erythropoietin,
produced by the kidneys, stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells. In renal failure, there is a deficiency of erythropoietin that often results in the client developing anemia.
tx: erythropoietin- should see increase in HCT/RBC. monitor for HTN since bp can increase
In renal failure, increased blood pressure is due to impairment of renal vasodilator factors and is not treated by administration of blood.
Phosphate is retained in the body during renal failure, causing binding of calcium leading to bone demineralization, not anemia. tx: Sevelamer carbonate (renvela)
Which eye problem is the leading cause of blindness in clients with diabetes?
1. Cataracts
2. Glaucoma
3.Retinopathy
4. Astigmatism
retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of blindness in diabetics.
Glaucoma and cataracts also are associated with diabetes, but retinopathy is the most common eye problem.
Astigmatism is not associated with diabetes.
A client is scheduled for a computed tomography (CT) of the brain with contrast. The nurse reviews the client’s medical record before the start of the procedure. The nurse would report which significant finding to the primary healthcare provider before the test is performed?
1-patient was not NPO
2. patient took their metformin in the morning .
3. patient did not receive their sedation medication
4. patient took their levothyroxine
2- metformin
A CT often requires a contrast agent to be administered. The contrast agent can cause temporary changes in kidney function. This change in kidney function can cause clients on metformin to have an increased risk of developing a serious side effect called lactic acidosis / ARF.
A client with Cushing syndrome asks why a low-sodium, high-potassium diet has been prescribed. Which response by the nurse is accurate?
1-"Excessive aldosterone and cortisone cause the retention of sodium and loss of potassium."
2-"An inadequate intake of potassium contributed to the disease."
3-"The client will gain excessive weight if sodium is limited."
1
Clients with Cushing syndrome or those receiving cortical hormones must limit their intake of sodium and increase their intake of potassium, because the kidneys are retaining sodium and excreting potassium. Limiting sodium will not cause weight gain. An excessive secretion of adrenocortical hormones in Cushing syndrome, not inadequate potassium intake, is the problem.
The nurse would monitor a client for which manifestation indicating a thyroid storm? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
1-Increased heart rate
2-Increased temperature
3-Decreased respirations
4-Decreased blood pressure
1,2
Thyroid storm is severe hyperthyroidism; excessive amounts of thyroxine increase the metabolic rate, thereby causing an increased heart rate (tachycardia). Because of the increased metabolic rate associated with thyroid storm, body temperature will increase.
Because of the increased metabolic rate associated with thyroid storm, the respiratory rate increases (tachypnea) to meet the body's oxygen needs.
The blood pressure will increase to meet the oxygen demand caused by the increased metabolic rate during thyroid storm.
The nurse is reviewing the electronic health record of a client admitted with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). Which medication order would the nurse question?
1. Furosemide (Lasix)
2. Tolvaptan (Aquaretic)
3. Intravenous (IV) 0.9% sodium chloride
4. Demeclocycline (Declomycin)
IV fluids
IV 0.9% sodium chloride should be administered cautiously in clients with SIADH, as it can further potentiate fluid volume overload.
Instead, a 3% sodium chloride is hypertonic and can be used to treat severe hyponatremia related to SIADH.
Diuretics such as furosemide (Lasix) can be used to treat heart failure if the sodium level is normal.
Tolvaptan (Aquaretic) and demeclocycline (Declomycin) are both medications used to treat SIADH.
Give examples of
1-pre-renal
2-intra-renal
3-post renal
Pre renal
1- hypotension, dehydration, sepsis, cardiogenic shock, acidosis
Intra-Renal
1- glomerulonephritis, NSAIDS, dye, pyelonephritis
Post Renal
1- Renal Calculi, BPH
Which information would the nurse include in postoperative teaching for a client who had cataract surgery? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct.
1. Do not blow your nose.
2. Remain flat for 3 hours.
3. eat a soft diet for 2 days.
4.Breathe and cough deeply.
5. wear Sunglasses
6. Avoid bending from the waist
1. 5, 6.
The client needs to avoid activities that cause a sudden rise in intraocular pressure, such as blowing the nose, bending from the waist, sneezing, and coughing.
wear sunglasses to protect eyes after surgery
It is not necessary to remain flat in bed for 3 hours after surgery and it will increase IOP, and the diet is not restricted.