Overarching goals of Healthy People 2030.
What is to improve the health and wellness of everyone in the United States.
The 5 general objectives include
1. Attain healthy lives free of preventable disease, disability & injury.
2. Eliminate health disparities.
3. Create social, physical, and economic environments that promote health and well beings.
4. Promote healthy development and behaviors across all life stages.
5. Engage leadership to take action and designs policies that improve health for all.
This Model of Health is explained as the individual's perception of susceptibility to an illness determines health and wellness actions.
What is the Health Belief Model
Vaccinations are an example of this level of prevention.
What is primary level of prevention.
Selyes General Adaptation Theory stages
What are
1. Alarm stage: body releases hormones that prepare it to either defend itself (fight) or run away (flight). |
2. Resistance stage:coping skills and defense mechanisms are used to stabilize the body
3. Exhaustion stage: body becomes overwhelmed and resources are depleted. Thinking becomes illogical and distorted.
Nurses overall goal in health promotion.
What is to educate and help patients live their at their best level of health and well being.
Health promotion in communities.
What is educating on healthy lifestyle choices and creating environments that support wellness.
This model of health describes how health is related to the relationship between body, mind, and spirit.
What is the Holistic Health Model.
Examples of secondary prevention.
What are screening for diseases such as
colonoscopy, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, mammography, BPH.
Interventions to prevent compassion fatigue
What are practicing self care practices.
Interventions to promote sleep.
Avoid smoking, alcohol, caffeine, and heavy meals close to bedtime. Avoid strenuous exercise before bedtime. Drink milk at bedtime, which contains L-tryptophan that promotes sleep. Use relaxation techniques to prepare for sleep, such as a warm bath, reading, and calming music. Take melatonin, a helpful supplement to regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Drink tea containing valerian root and chamomile, which helps with general relaxation and causes drowsiness. Alter the sleeping environment so that it is cool, dark, and quiet.
Social determinants of health
What are non-medical factors that influence health outcomes.
Prioritizing a patient's physiological problems before psychosocial problems is an example of this Model of Health
What is Mazlows Hierarchy of Needs Model.
Nurses would prioritize basic needs such as airway, breathing, circulation, sleep, safety (housing), food. security.

Examples of tertiary prevention.
What are diabetic foot care and eye exams, Alcoholics anonymous for recovering alcoholics, cardiace rehab for patient after heart attack,
Complimentary interventions to address stress and pain.
What are relaxation therapies suchs as deep breathing and progressive relaxation, healthy diet, healthy sleep, positive affirmations, music therapy, Rieki, guided imagery, social support, exercise, and spiritual practice.
Interventions to address food insecurity
SNAP benefits eligibilty is based on 130% of federal poverty guidelines which are approximately $1580/month for 1 person or about 3200/month for a family of four.
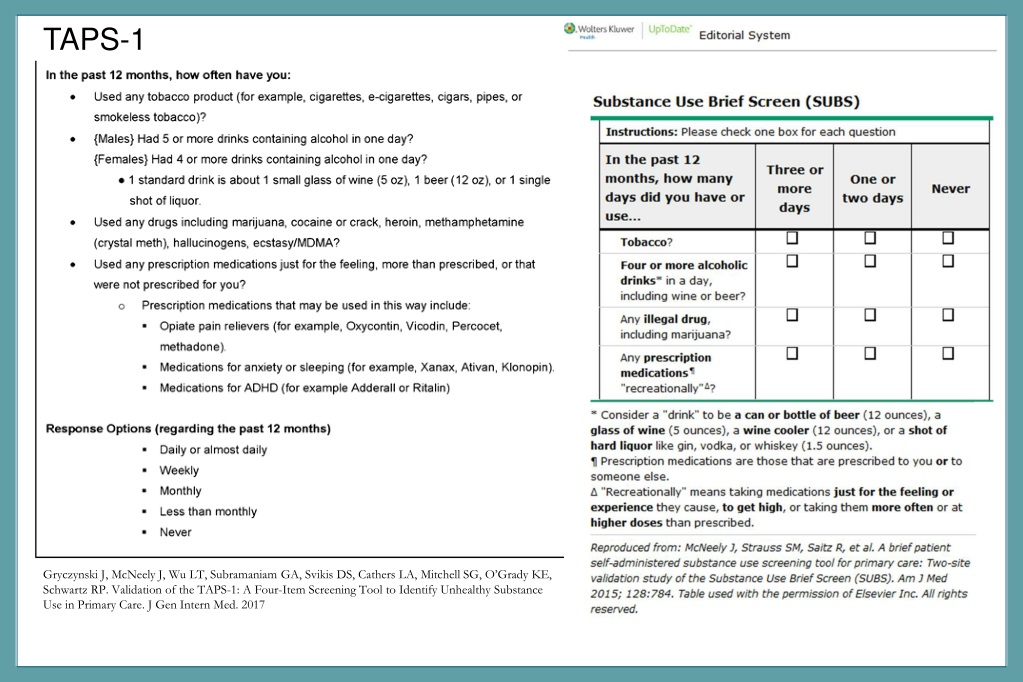
Students at risk of for drug substance abuse.
Who are students who may exhibit nuusual or inconsistent behaviors, agitation problems thinking clearly, remembering, or paying attention poor coordination seizures or respiratory depression self inflicted trauma and suicidal ideation (thinking about or planning suicide)
Tool to assess alcohol, tobacco, and substance use is the TAPs tool.
Penders Health Promotion Model.
What is addressing perceptions of health by focusing on individual experiences, behavior-specific knowledge, and behavioral outcomes to increase level of well being
Educating high school students about the risks associated with smoking is important for this level of prevention.
What is primary prevention because it reduces risk of smoking as an adult. Smoking increases the risk for high blood pressure, cancer, stroke, heart disease, tuberculosis, certain eye diseases, diabetes mellitus type 2, and autoimmune dysfunction.
Educating students to prevent them from using tobacco occurs before students start smoking. Easy access to tobacco products and vaping products increases risk for smoking.
Secondary Prevention would be assessing using the TAPS tool

Strategies to prevent burnout.
What are practicing self care; ensuring balanced work-life balance, build connections and support with colleague.
Explain Reiki, Progressive relaxation, Guided imagary, cognitive restructuring, and Biofeedback.
What is
1. Reiki:
2. Progressive relaxation:
3. Guided imagery: technique to visualize peaceful settings to promote mental well being
4. Cognitive restructing: Cognitive restructuring will help with identifying faulty and destructive thought patterns that are contributing to problems and reshaping those thoughts into accurate, helpful thinking.
5. "Biofeedback": holistic technique that uses devices to teach self-regulation and voluntary self-control over specific physiologic responses - Biofeedback.
Nonmodifiable risk factors for disease
What are age, race, gender. (non-modifiable)
Modifiable risk factors include health choices such as smoking, diet, and exercise,
Transtheoretical Model of Change Theory
What is a model for understanidng a person's readiness to change and recognizing where a patient is in the process.

Health promotion interventions to address hunger.
What are address unemployment, use nutritional assistance programs, contribute to food banks and encourage eating fresh fruits and vegetables
Primordial level of prevention.
What is the level of prevention that addresses underlying social, economic, and environmental risk factors to prevent the emergence of risk factors.
Examples include urban planning and improving sanitation and environmental hazards.
Leading health indicators for Healthy People 2030
A subset of 23 high priority health public health issues including reducing drug overdose deaths, reducing rates of homicides, reduce household food insecurity, increase flu vaccination rates, reduce rate of suicides, encourage healthier diets and reduce calories from added sugars, increase propotion of individuals with health insurance.