A nurse is assisting in performing an assessment on a client who suspects that she is pregnant and is checking the client for probable signs of pregnancy.
Positive pregnancy test, ballottment, Braxton-Hicks, Goodell Sign, Chadwick sign, Enlarging uterus
What are the 5 items that are part of a biophysical profile?
Amniotic fluid level
Fetal Tone
Fetal Heartrate
Fetal Breathing
Fetal movement
A nurse is caring for a client in labor. The nurse determines that the client is beginning in the second stage of labor. What signs may the nurse notes?
Fully dilated Cervix, bulging of the perineum
Ends after the birth of the baby
A nurse is monitoring a pregnant client with pregnancy induced hypertension who is at risk for preeclampsia. The nurse checks the client for which specific signs of preeclampsia?
HA, vision changes, epigastric pain, elevated BP, Edema
What
What type to decelerations are pictured here? What are your interventions?
Variables.
LOBO
What are some of the manifestations of an infant with cytomegalovirus?
Short term vs long term
Short term:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes)
- Microcephaly (small head)
- Low birth weight
- Hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen)
- Seizures
Long term:
- Hearing loss
- Developmental and motor delay
- Vision loss
- Microcephaly (small head)
- Seizures
Why are newborns at risk of hyperbilirubinemia?
Higher concentration of RBCs
Impaired ability for the liver to conjugate bilirubin
Gestations age
poor feeding
infection
ABO-incompatibilities
RH incompatibility
How can a nurse illicit the Babinski reflex in a newborn?
Stroking the lateral aspect of the sole of the foot in an upward motion and across the ball of the foot
What injection is given to newborns to protect them from bleeding after delivery?
Vitamin K
What are the assessments that a nurse should complete in the postpartum period?
Uterus, Bladder, Bowel, Lochia, Episiotomy, Emotions, Breats, Vitals
The chief function of progesterone is the:
Prepares the uterine lining, relaxes smooth muscle, and maintains the pregnancy
A client is given an NST. The client is asking about how the results are determined. How should the nurse respond?
Reactive: 2 accelerations that are 15x15 in a 20-minute period.
Nonreactive: no acceleration or 1 acceleration in a 40-minute time period
A nurse in the labor room is caring for a client in the active phases of labor. The nurse is assessing the fetal patterns and notes a late deceleration on the monitor strip. The most appropriate nursing actions for the nurse to do?
Turn to a left lateral position
Administer O2
Bolus IV Fluids
D/C oxytocin
Administer tocolytic
Rho (D) immune globulin (RhoGAM) is prescribed for a woman following delivery of a newborn infant and the nurse provides information to the woman about the purpose of the medication. What would the nurse tell the patient?
Administration of Rho(D) immune globulin prevents the woman from developing antibodies against Rh-positive blood by providing passive antibody protection against the Rh antigen.
What do you see?
Baseline FHR: 130-140
Moderate variability
Early Decels
An HIV-positive mother is preparing to give birth. WHat are some nursing interventions that should be included when planning the care of the newborn?
No breastfeeding
Administer antivirals after delivery
Use universal precautions
Do thorough cord care
The infant should receive all vaccines
What is the treatment for hyperbilirubinemia?
Phototherapy
Frequent and early feedings
Exchange transfusion (rare)
What is a collection of blood between the skull bone and the periosteum?
Cephalhematoma
What are some assessment findings that indicate necrotizing enterocholitis?
Bloated, swollen abdomen, Bloody stools, diarrhea, decreased activity, poor feedings, and preterm infants are at risk
A client is at risk of hemorrhage after delivery, What factors put her at risk?
What are the signs/symptoms?
Prolonged/precipitous labor, Adv maternal age, multifetal pregnancy, infection, preeclampsia, clotting disorders.
Massage the fundus, oxytocin, cytotec, methergine, hemabate, bolus fluids, O2
What are the chief functions of the placenta?
Oxygen and nutrient exchange, removal of metabolic waste
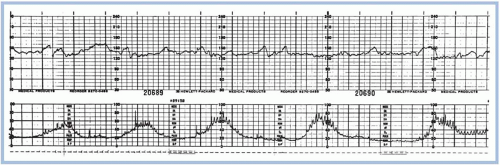
How would you interpret this NST?
Reactive
What characteristics of contractions would the nurse expect to find in a client experiencing true labor?
More frequent, stronger, closer intervals.
More intense when walking or doing activity,
Persist in spite of resting and drinking water
A pregnant client is receiving magnesium sulfate for the management of preeclampsia. A nurse determines the client is experiencing toxicity from the medication if she notes what assessments?
Signs of toxicity relate to the central nervous system depressant effects of the medication and include respiratory depression, loss of deep tendon reflexes, and a sudden drop in the fetal heart rate and maternal heart rate and blood pressure.
What do you see?
Late decels
What are the complications to a fetus if the mother is exposed to rubella during pregnancy?
anemia, jaundice, microcephaly, deafness, fetal death
What are the types of hyperbilirubinemia? When do they start?
Physiologic: After 24 hrs of life
Pathologic: Before 24 hrs
What are the normal vital signs for a newborn?
Temp: 97.7-98.6
Resp rate: 30-60 breaths per minute
Pulse: 120-160 bpm
What are the complications and nursing interventions associated with a myelomeningocele?
Cover the lesion with a moist, sterile dressing, side-lying or prone positioning, and assessments of bradycardia, hypotension, apnea, and lower extremity movement/strength. keep the area clean and occlusive.
How often do we check the vital signs of a post partum mom during her recovery
Q15 mins for the 1st hour
Q30 mins for the second hour
Q4 hrs for 24 hrs
Q8 after that
A pregnant client is making her first antepartum visit. She has a 2-year-old son born at 40 weeks, a 5-year-old daughter born at 38 weeks, and 7-year-old twin daughters born at 35 weeks. She had a spontaneous abortion 3 years ago at 10 weeks. What is the client's GTPAL?
G5 T2 P1 A1 L4
A patient has undergone an amniocentesis for evaluation of fetal well-being. Which intervention would be included in the nurse’s plan of care after the procedure? Select all that apply.
- A. Perform ultrasound to determine fetal positioning.
- B. Observe the patient for possible uterine contractions.
- C. Administer RhoGAM to the patient if she is Rh-negative.
- D. Perform a mini catheterization to obtain a urine specimen to assess for bleeding.
B & C
How would you tell if the woman with PROM had an infection?
Maternal fever, fetal tachycardia, foul smelling vaginal discharge
A nurse is caring for a pregnant client with severe preeclampsia who is receiving IV magnesium sulfate. What nursing interventions are appropriate for the nurse to complete for this client?
- Cardiac and renal function are monitored closely. Eclampsia-associated renal abnormalities can include decreases in glomerular filtration rate, renal plasma flow, and uric acid clearance as well as proteinuria. Eclampsia is associated with cardiovascular derangements such as generalized vasospasm, increased peripheral vascular resistance, and increased left ventricular stroke work index. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) may vary from low to elevated. Importantly, central venous pressure (CVP) may not correlate with PCWP in patients with severe preeclampsia or eclampsia.
- Calcium gluconate is kept on hand in case of magnesium sulfate overdose because calcium gluconate is the antidote for magnesium sulfate toxicity.
- Deep tendon reflexes are assessed hourly. Ankle clonus indicated hyperreflexia and may precede the onset of eclampsia. Although brisk or hyperactive reflexes are common during pregnancy, clonus is a sign of neuromuscular irritability that usually reflects severe preeclampsia.
- Monitor fluid intake and urine output, maternal respiratory rate, and oxygenation, as indicated, and continuously monitor fetal status. Pulmonary arterial pressure monitoring is rarely indicated but may be helpful in patients who have evidence of pulmonary edema or oliguria/anuria.
- Check the urine output should be maintained at 30 ml per hour because the medication is eliminated through the kidneys.
What 
What is the frequency and duration of the contraction?
1.5-3 mins apart
50-80 secs
A baby who is born 12 hours ago has a yellow tint to the eyes and skin. What test is completed to test for jaundice of a newborn?
Direct Coombs
How do we assess for jaundice in newborns?
Determine the ABO and RH of the mother prior to delivery (Indirect coombs)
Direct coombs
Transcutaneous bili test
Serum bili (13-15mg/dL is high)
Dark urine
How do we assess for respiratory issues in newborns?
What are our interventions?
cyanosis, retractions, nasal flaring, grunting
Suctioning (mouth before nose)
administer O2
Keep newborn warm
Sighs and symptoms of neonatal abstinence syndrome?
- Fussiness, irritability, and inconsolability
- Tremors and/or jitteriness
- Excessive crying or high-pitched crying
- Poor caloric intake and slow weight gain
- Altered breathing patterns
- Hyperactive reflexes
- Yawning, sneezing, and/or bothersome jerking movements
- Difficulty falling and staying asleep
- Sweating or clammy skin
What are the signs and symptoms of endometritis
pain in lower abd, fever, foul-smelling discharge, malaise
A pregnant woman’s last menstrual period began on April 8, 2020, and ended on April 13. Using Naegele’s rule her estimated date of birth would be:
January 15, 2021

How would you interpret this CST?
Negative
Which of the following factors involve risk for shoulder dystocia?
Macrosomic baby
Post-term pregnancy
Inadequate pelvis
Malpositioning
What would the nurse assess in a client experiencing abruptio placenta?
A client with abruptio placentae may exhibit concealed or dark red bleeding, possibly reporting sudden intense localized uterine pain. The uterus is typically firm to board-like, and the fetal presenting part may be engaged.
What are the criteria that must be met for an FSE and IUPC to be placed?
The amniotic fluid must be broken
The woman must be dilated
What are the interventions for newborns on phototherapy?
Cover the newborn's eyes and assess every 2 hours
Make sure that the newborn is undressed to the diaper
Turn Q2 hrs
Assess the stools of the newborn
Assess for dehydration
Assess temp Q2 hrs
Monitor bilirubin levels
What are the assessment findings for a newborn with hypoglycemia?
Lethargy, tremors, jitteriness, decr muscle tone
What are the 3 reflexes that need to be assessed with the mouth and neck?
Rooting: turns head side to side
Sucking: when object is placed in the mouth
Tonic neck: fencer position ( neck moves freely)
Nursing interventions for Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome?
- Monitoring infant vital signs
- Observing and recording behavioral changes
- Administering medication as prescribed
- Assessing nutrition and hydration needs
- Carrying out infant comfort care
- Providing emotional support and assistance to parents
- Recommending and/or referring to appropriate community services
What are nursing interventions to help with perineal pain in the postpartum period?
Medications, ice packs, analgesic spray, sitz baths, witch hazel, assess for hematoma
What are the shunts and what are their functions to fetal circulation?
Ductus venosus: takes blood from the umbilical vein to the vena cave bypassing the liver
Foreman Ovale: Takes blood from the right atrium to the left atrium and bypasses the lungs
Ductur Ateriosus: takes blood from the lungs and takes it to the aorta. Kept open by prostaglandins
What is an appropriate indicator for performing a contraction stress test?
Hypertension, diabetes, post-term pregnancy
The nurse would expect which maternal cardiovascular finding during labor?
Incr in maternal blood pressure
Drop in Maternal pulse
Why is GBS status so important to a mother and baby during labor?
How do we treat it?
- Early: Maternal colonization with GBS is most important risk factor. Onset from 0-6 days. Usually presents with pneumonia and sepsis. Much more common than late infection.
- Late: GBS can come from the mother or other sources. Onset after 7th day. Usually presents with meningitis (also deafness, death, and intellectual disabilities)
Antibiotics Q4 hours while in labor.

What do you see?
FHR: 150
Variability: Minimal
Accelerations
Late decels
Thermoregulation is very important in newborns. What are the nursing interventions to prevent hypothermia?
Maintain a thermoneutral environment
Reduce drafts around the baby
Dry the newborn right after delivery
Assess temp
Put a hat on them and wrap them in a blanket
Assess oxygenation and for hypoglycemia
What infants are at most risk of developing hypoglycemia?
LGA, babies of diabetic mothers, hyperbilirubinemia, RDS,
What does a normal abdominal assessment look like on a newborn?
soft, dome-shaped, round, moves with respirations, active bowel sounds
What are some ways that a parent can assist in helping siblings cope with the addition of a new sibling?
Start early talking about the new baby
Encourage and praise good behaviors
Make safety a priority
Teach soft touch/being gentle
Include the sibling in tasks involving the baby
Give alone time to the older sibling
What patient education can we offer for patients who have mastitis?
