The 6 steps of the scientific method in order
What are 1. Observe 2. Question 3. Hypothesis 4. Experiment 5. Analyze 6. Conclude?
This is the monomer of Carbohydrates
What are monosaccharides?
Adenosine Triphosphate, a nucleotide, has this many phosphates
What is 3?
The meanings of the roots mono-, poly-, and macro-
What are "one", "many", and "big"?
This is the monomer of Lipids
What are fatty acids?
The kind of data that does NOT contain numbers
What is qualitative data?
This is where the simple sugar Galactose is found
What is milk?
These are the elements used in proteins
What are C, H, O, and N?
These are specialized parts of a cell (the cell's "organs")
What are Organelles?
Olive oil contains this kind of fatty acid
What are Unsaturated fatty acids?
In an experiment, this is the variable that YOU change
What is the Independent Variable?
This is the disaccharide that is a glucose plus a fructose
What is Sucrose?
There are this many amino acids that humans utilize
What is 20?
This is the inverse reaction of Dehydration Synthesis
What is Hydrolysis (adding water)?
This is what a unsaturated fatty acid has that a saturated fatty acid does not
What is a double bond?
This is a reason a hypothesis cannot be proven true
What is alternate hypothesis / science is always changing?
What is Cellulose?
The correct spelling AND pronunciation of the full name of DNA
What is Deoxyribonucleic Acid?
All of the populations in and interact in an area
What is a Community?
The name of this molecule
What is a triglyceride?
This is the type of reasoning that takes GENERAL knowledge to make a SPECIFIC conclusion
What is Deductive Reasoning?
This is the term for compounds that have the same formula, but different structures (Ex. Fructose and Glucose having C6H12O6)
What are Isomers?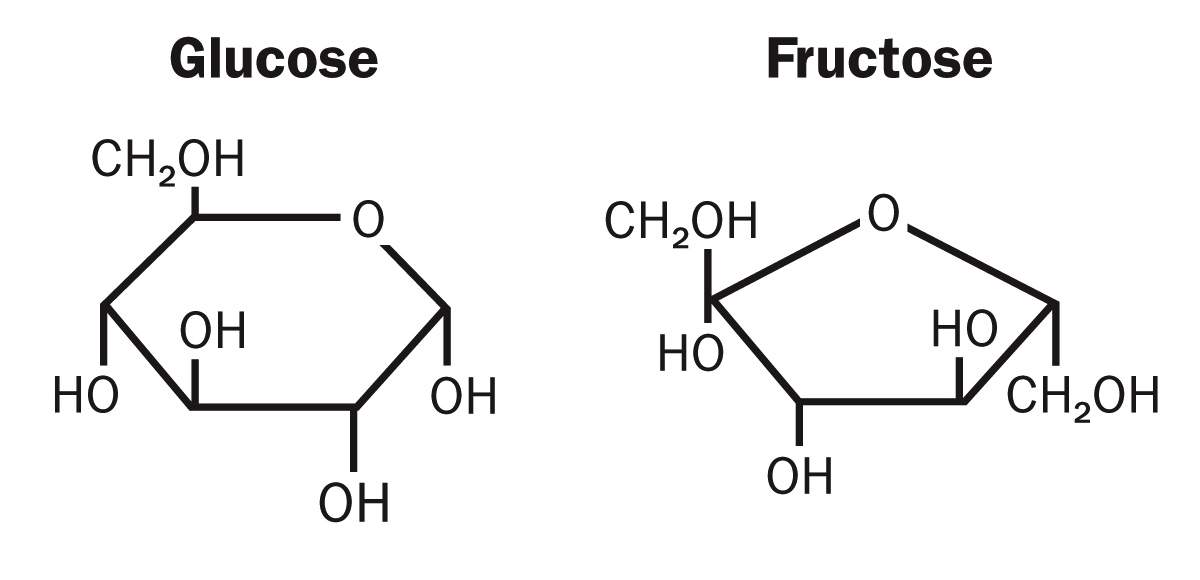
This is the group of proteins that act as catalysis in reactions within the body
What are enzymes?
This is the difference between organic and inorganic compounds
What is organic compounds can have C and H together, while inorganic can have the separately only?
The head of a phospholipid is hydro______
What is -philic? (hydrophilic - water loving)