What is the study of drugs?
Pharmacology
What is the Nursing Process?
ADPIE
True or False. We need to inform the doctor about ALL medications the patient is taking, including Over-The-Counter ones. EVERYTHING.
True
What class of drugs does furosemide fall under?
Calcium Sparing Diuretics
True or False. Glipizide will increase insulin secretion and you have to take it before meals.
True
Which insulin should you draw up first, Regular or NPH?
Regular
Single Order (Once)
STAT Order (NOW)
Routine Order (Every)
Standing Order (Protocol)
PRN Order (As Needed)
What is the generic name?
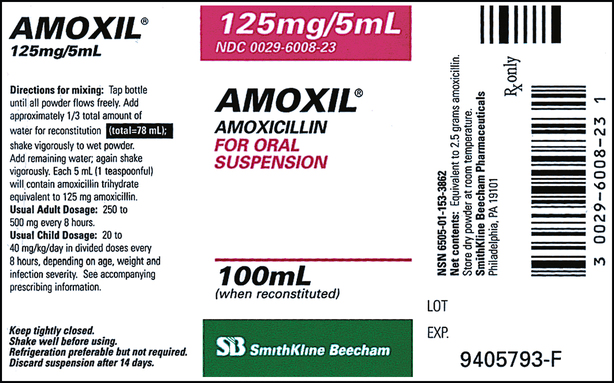
Amoxicillin
True or False. Herbal Supplements and OTC medications are always safe to take with other medications.
False
Which electrolyte is spared with spironolactone administration?
Potassium
Significant vital sign in patients who are dehydrated by taking too much diuretics.
Tachycardia
How often do you need to check your A1C Level?
3 months
How long can you store opened insulin on room temperature and in the refrigerator?
28 Days Room Temperature
3 months Refrigerator
What is a drug called when it could potentially hurt the fetus?
Teratogen
What kind of data involves vital signs, lab tests, and observations made by the nurse?
Objective
False
The best indicator of fluid status.
Daily Weights
Give 3 foods that you should avoid when taking spironolactone.
Avocado
Banana
Cantaloupe
Dried Fruits
Juicy Fruits
Mrs. Dash
White Beans
Glucagon
Why do you need to rotate insulin injection sites?
Prevent lipodystrophy
Difference between Primary Effect and Secondary Effect?
Primary (Intended Therapeutic Effect)
Secondary (Side Effect)
Define Visual, Kinesthetic, and Auditory Learning.
Visual (Seeing)
Auditory (Hearing)
Kinesthetic (Doing)
Type of drug effect wherein drugs pile up in the body faster than it can eliminate, which causes toxicity.
Cumulative Effect
What part of the kidneys do thiazide diuretics affect?
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Which diuretic should you avoid when your patient is taking ACE Inhibitors?
The best lab test for Diabetes, and what are the ranges?
Hemoglobin A1C
<5.7 = Normal
5.7-6.4 = Prediabetes
>6.5 = Diabetes
Which insulin can you give IV and which Insulin should be used in pumps?
Regular (IV)
Rapid (Pumps)
Branch of Pharmacology that deals with how the body is affected by the drug.
Pharmacodynamics
Define Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor Domain.
Cognitive = Intellect
Affective = Emotions
Psychomotor = Skills
Synergistic Reaction
What is the normal potassium level?
3.5-5 mEq/L
Why do you need to hold Metformin 48 hours before contrast procedure?
Prevent Lactic Acidosis
Can you recall BATTLE?
BAT = Increases Insulin
TLE = Decreases Insulin
Enumerate the processes in Pharmacokinetics, and what body part is most likely involved.
Absorption (GI)
Distribution (Tissues)
Metabolism (Liver)
Excretion (Kidneys)
What gauge needle for subcutaneous injections and how much?
G 23-25, 0.5-1mL
Type of drug effect that is peculiar and often unexpected.
Idiosyncratic Reaction
How much weight gain is bad on patients with diuretics?
Gain of >2 pounds in 1 day
Gain of >5 pounds in 1 week
Ototoxicity
In DKA, what kind of breathing is expected?
Kussmaul's Respirations, Has a Fruity odor breath
Give the Onset, Peak, and Duration for all 4 insulins.
Lispro – 5-10 min, 0.5hr-1.5 hr, 3-5hr
Regular – (short) 30-60 min, 2-4 hr, 5-8 hr
NPH – (intermediate) 1.5 hr, 4-10 hr, 14 hr
Glargine – (long) 1 hr, no peak, 24 hr