There are 2 special areas of the heart that control rhythm (or the pulse) of the heart. Name both special sets of cells
1. SA node
2. AV node
A patient lying in bed for an extended amount of time would be at risk for? (select 2)
cor pulmonale
pneumonia
pneumothorax
pulmonary embolism
pneumonia
pulmonary embolism
What is this?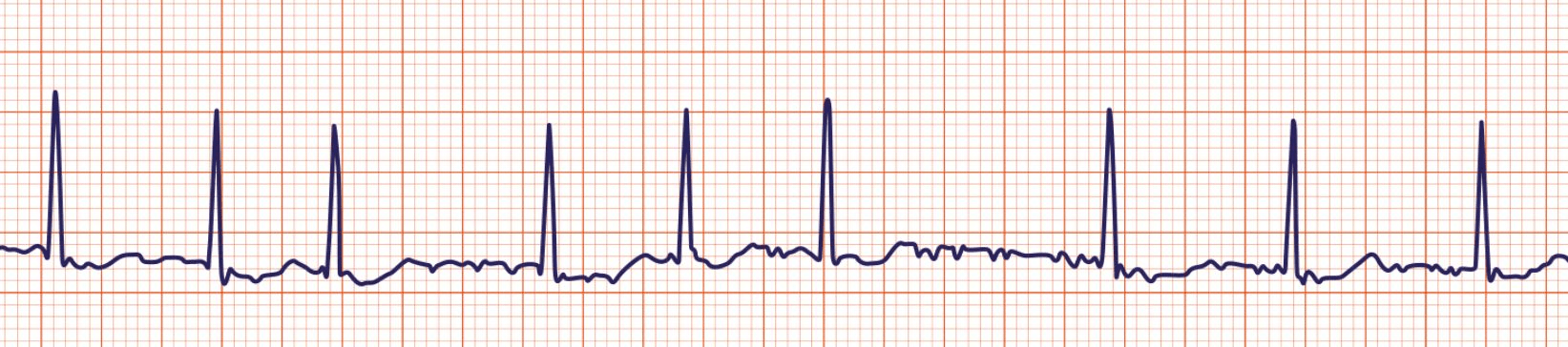
Atrial fibrillation
What is your first action (see option below)
cardioversion
defibrillation
pacemaker
mechanical ventilation
defibrillation
You notice fluctuations of fluid in the water seal chamber of a chest tube, what should you do?
empty the drainage
continue to monitor
encourage the pt. to take a deep breath
encourage the pt. to hold his/her breath
continue to monitor
What is this dysrhythmia?
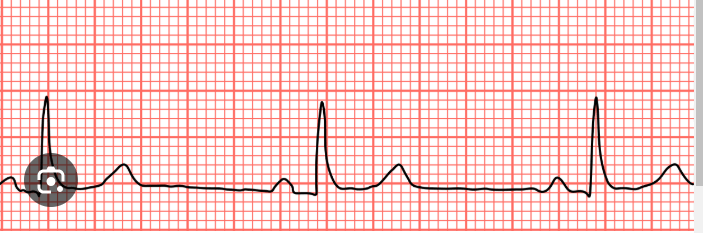
Bradycardia or sinus brady
Which type of tracheostomy tube will allow a patient to speak? (select two answers)
single cannula
double lumen
fenestrated tube
one way valve box
any cuffed tracheostomy
fenestrated tube & one way valve box
A pt is going to have a thoracotomy, following the surgery you would expect?
Pt. will remain in prone position
Checking for the return of gag reflex
Monitoring a chest tube
Assessing Babinski reflex
Monitoring a chest tube
A patient is returning post cardiac cath. Which action requires immediate intervention?
head of bed at 30 - 45 degrees
UAP is assessing pedal pulse
patient is drinking fluids
a head of bed at 30 - 45 degrees
A myocardial infarct can frequently cause this type of shock
hypovolemic
cardiogenic
obstructive
distributive
cardiogenic
You are caring for a pt. diagnosed w/ COPD. What acid/base imbalance would you suspect?
metabolic acidosis
metabolic alkalosis
respiratory acidosis
respiratory alkalosis
respiratory acidosis
Which disease/disorder may lead to possible respiratory acidosis?
diabetes
anxiety
lung cancer
emphysema
Signs of possible throat cancer include all of the following except
hoarseness that lasts more than 3 weeks
sore throat that last more than 2 weeks
consistent pain around the ear when swallowing
dry persistent cough
excessive thick mucus
excessive thick mucus
You suspect a pt. is in respiratory failure because (select 3 answers)
PaO2 is lower than 60 mm Hg
PCO2 is greater than 50 mm Hg
cyanosis
cherry red mucous membrane
PaO2 is lower than 60 mm Hg
PCO2 is greater than 50 mm Hg
cyanosis
Instructions for a patient with a permanent pacemaker would include all of the following except?
lift the arm away from the body to prevent contractures
keep incision dry for at least 4 days
monitor pulse daily
lift the arm away from the body to prevent contractures
Pt. arrives in ED w/ severe GI bleeding & hypovolemic shock. What is the nursing priority?
insert a NG tube & attach to low wall suction
draw a blood sample for a type & crossmatch
measure the amount of emesis & check for blood
establish two large-bore peripheral IV sites
establish two large-bore peripheral IV sites
Care of a pt. w/ a chest tube would include all of the following? (multiple select)
pin the tubing to the bed linens
ensure all connections remain airtight
ensure all connections are taped & secured
monitor tubing for any kinks
empty the drainage from the chamber daily
all connections remain airtight
all connections are taped & secured
monitoring tubing for any kinks
Diabetic pts can have diabetic ketoacidosis, how would the body attempt to compensate for this?
excrete NaHCO3
increase respiratory rate
decrease respiratory rate
release more insulin
increase respiratory rate
Immediate postoperative care post a tracheostomy would include (select two)
a patent airway & observation for hemorrhage
absence of swelling or purulent discharge
assessing for abdominal distention
vocal communication
a patent airway & observation for hemorrhage
absence of swelling or purulent discharge
What is the imbalance? pH - 7.5, PCO2 - 32, HCO3 - 24
metabolic acidosis
metabolic alkalosis
respiratory acidosis
respiratory alkalosis
respiratory alkalosis
Examples of serous membranes (select one)
a. line the lungs
b. line the heart
c. line the abdominal cavity
d. all of the above
d. all of the above
pleural, pericardial and serous membranes
A 44 yr old pt has sudden, severe chest tightness unrelieved by rest & nitro and profuse sweating. What elevated lab would the LVN suspect if a MI?
serum troponin
blood urea nitrogen
myoglobin level
prothrombin time
serum troponin
You suspect a pt. is having SIRS when? (multiple select)
temp > 102.2 or < 96.8
HR > 90
PaCO2 < 32 mm Hg
WBC 10,000 cells/mm
temp
HR
PaCO2
Which pt is at greatest risk for developing a PE?
has a central line that was started 2 days ago
is 3 mos pregnant w/ her first child
has been immobile for 1 week & is mildly dehydrated
is ambulating 2 days after abdominal surgery
has been immobile for 1 week & is mildly dehydrated
What types of food would a patient avoid "if" they were on a low sodium diet? (must list 3 categories to get full points)
processed meats
canned foods
salty snacks
convenient/fast food
over the counter meds
Pt. arrives in the ED w/ severe chest pain, diminished breath sounds right side & tachypnea. You suspect?
pulmonary edema
pneumothorax
pulmonary hypertension
pneumothorax
You suspect your pt has right side heart failure based on which 2 findings?
a. crackles in the lungs
b. dependent edema
c. decreased urine output
b & c dependent edema & decreased urine output
A pt has suffered a spinal cord injury. The LVN suspects autonomic dysreflexia post neurogenic shock when the pt. displays
sudden tachycardia
pallor of the face and neck
severe throbbing headache
severe & sudden hypotension
severe throbbing headache
The HCP has ordered IV fluids, epinephrine & steroids
a. anaphylactic
b. neurogenic
c. septic
d. hemorrhagic
anaphylactic
You are monitoring a pt following a cardioversion. Which observation would be of highest priority?
blood pressure
status of airway
oxygen flow rate
level of consciousness
status of airway