What is the term for when the baby’s head is engaged in the mother’s pelvic inlet?
Engagement
What is the nurse's priority duty when a patient has eclampsia?
stay w/ the patient, call for help, onset of seizure, lateral position, seizure pads
Why do we assess for hypotension after epidural?
loss of vascular tone/constriction=vasodilation= hypotension= decreased blood flow and 02 to fetus
What is the priority nursing intervention with a patient experiencing BRB vaginal bleeding with hemodynamic instability?
IV access (large bore, anticipating fluid and blood products)
what is the purpose/indication of prepidil (prostaglandin gel)?
cervical ripening for labor induction
What is the name of what can be seen under the microscope when amniotic fluid is observed?
ferning
Which of the following are in order for the cardinal movements?
A.Engagement, descent, flexion, internal rotation, restitution and external rotation, extension, expulsion
B.Engagement, internal rotation, extension, flexion, restitution and external rotation, descent, expulsion
C.Engagement, descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, restitution and external rotation, expulsion
D.Engagement, internal rotation, extension, flexion, restitution and external rotation, expulsion, descent
C
What are the abnormal lab values in HELLP?
hemolysis (low hemoglobin)
elevated liver enzymes
low platelets
What does V indicate in the acronym "VEAL CHOP"?
v= variable decelerations. This can indicate umbillical cord compression (and vessel compression in cord)
Why is magnesium infusion for pre-eclampsia a risk factor for PPH?
muscle relaxation= uterine relaxation
Fetal ______ is a baseline of more than 160 beats/min for a duration of 10 minutes or longer.
Tachycardia
What are nursing priority interventions for nonreassuring FHR tracings?
stop pitocin (oxytocin)
IV fluids
notify provider STAT
02
tocolytic-prn
side lying= knee to chest
Dilation is measured in ________ and effacement is measured in _______
centimeters and %
What type of deceleration is this?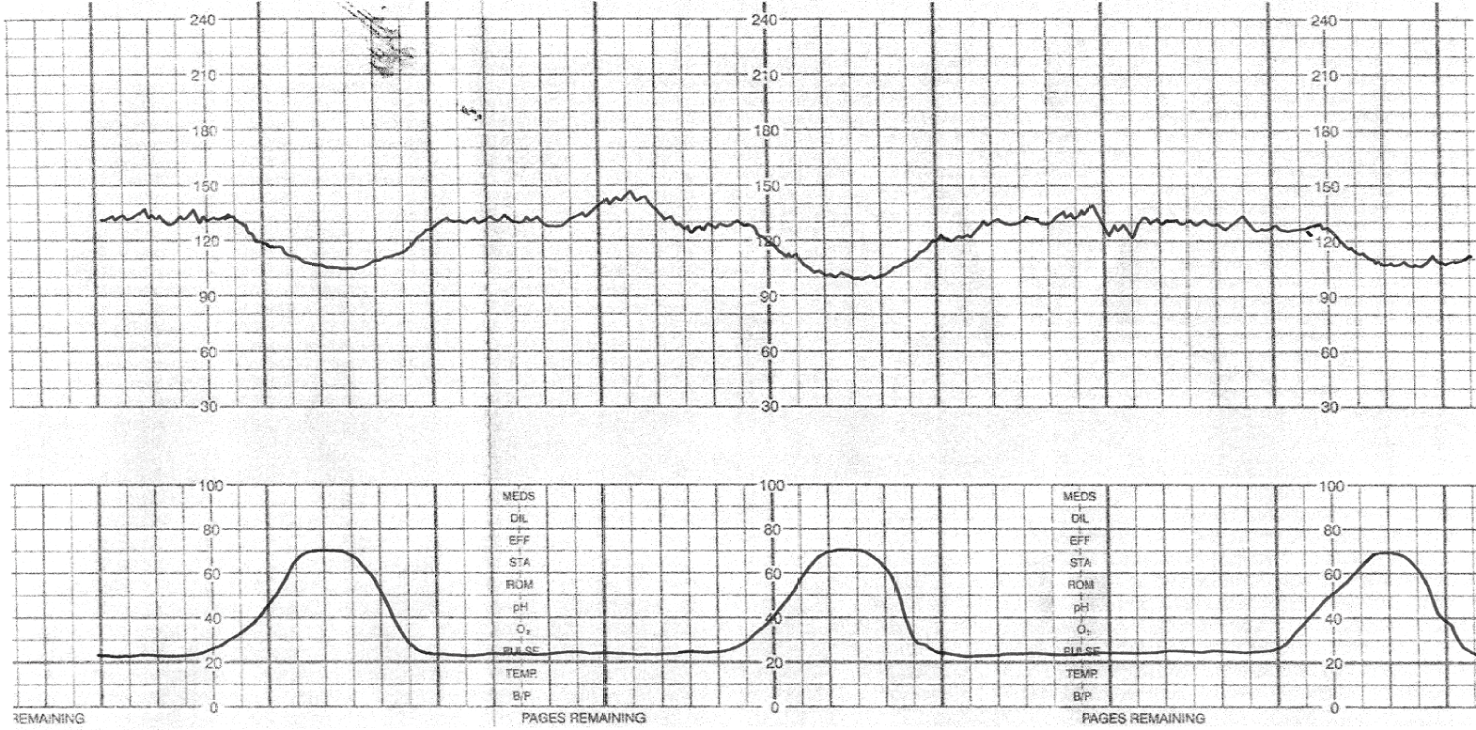
early decelerations
Magnesium sulfate is administered for pre-eclampsia. What are s/s of magnesium toxicity?
absent DTRs (patellar and brachial most common)
lethary
muscle weakness
bradypnea
<30ml/hr urine output
What procedure is done when an amniohook is used (artificial rupture of membrane)? What is nursing assessment priority after this procedure?
amniotomy; assess FHR (tracings that indicate cord compression)
Which of the following information on a laboring patient would be concerning to the nurse?
1.Duration of contractions over 90 seconds
2.Frequency of contractions every 5 minutes
3.Fetal heart rate 120 bpm
4.Fetal heart rate with moderate variability
1
2nd stage of labor has started when cervical dilation is __ cm and __ % effacement
10 and 100%
What is this a picture of? What are priority nursing interventions?
prolapsed umbillical cord; sterile glove to hold presenting part off umbillical cord
What is the procedure that can manually turn the baby from breech to cephalic? What if the mom is Rh-?
external cephalic version (ECV). Rh- mom needs Rh immune globulin prior to version.
What is the name of the medication given in preterm labor to promote lung maturity?
betamethasone
A patient has 550 ml of QBL 2 hours after a vaginal delivery, what is the nurse most concerned for and what are the associated interventions?
PPH; pitocin(oxytocin), assess for uterine atony (fundal massage!), foley catheter, IV fluids
A patient has a hemoglobin A1C >8.5%. What instructions should the nurse provide the patient to reduce blood glucose?
meet with diabetes educator
monitor blood glucose closely
take medications as directed
The most lower part of the fetus is the level of the ischial spine. What station is this.
0
The nurse assesses incomplete uterine relaxation between hypertonic contractions. The nurse is concerned by this contraction pattern due to reduction in fetal:
oxygen supply