What is the primary pacemaker?
SA Node
EKG shows a p wave before every QRS, a T wave after the QRS, a narrow QRS, and a rate of 75 bpm
Normal sinus rhythm
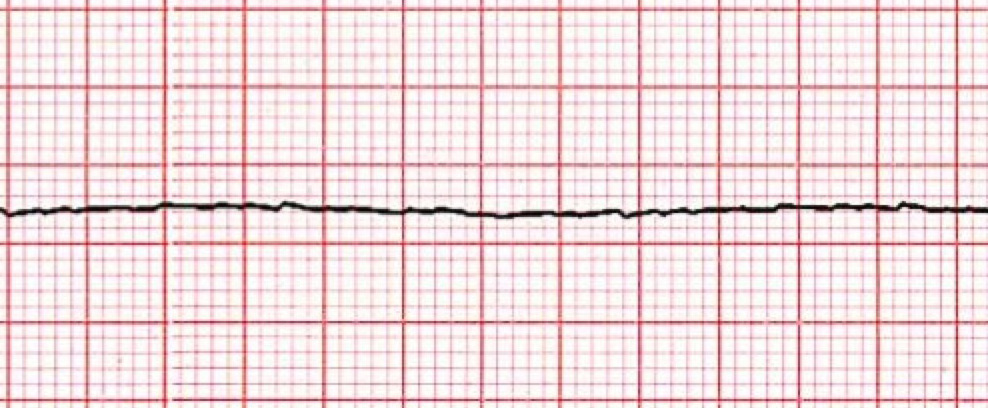
Asystole
What is treatment for asytole?
What is the primary treatment for heart blocks?
Pacemaker insertion
Where does the brown tele lead go?
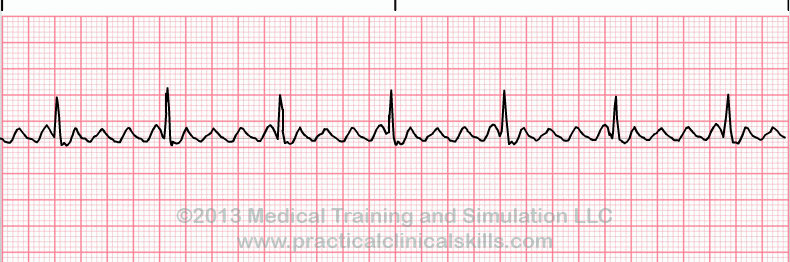
Bradycardia
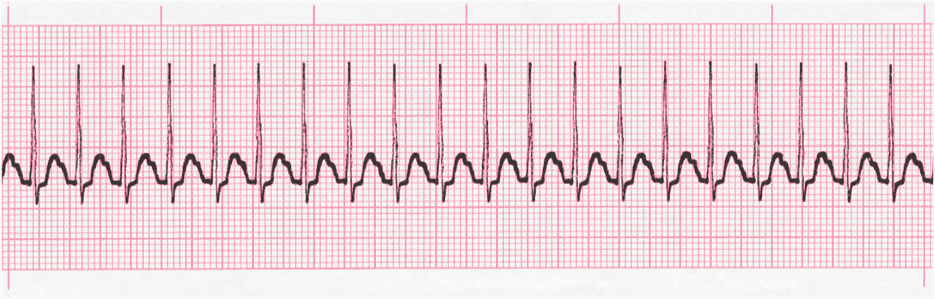
Atrial flutter
What is the treatment for stable A-fib (asymptomatic)?
Give a beta blocker, blood thinner, or amiodarone, or Cardizem.
What is the treatment for torsade's de pointes?
IV magnesium
Your patient's EKG at the nurse's station shows v-fib. What should you do FIRST?
Run to room. Check for pulse. Check leads. If no pulse, begin CPR and call code
SVT (supraventricular tachycardia)

Ventricular fib
What is the treatment for V-Fib?
BEGIN CPR & Defibrillation (shock). Follow ACLS protocol (epinephrine & amiodarone)
What is this called?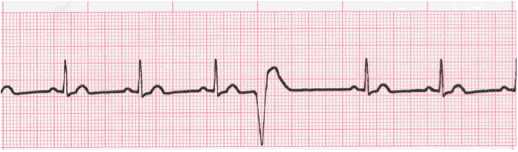
PVC (premature ventricular contraction)
What is the name of the back up pacemaker?
VA Node
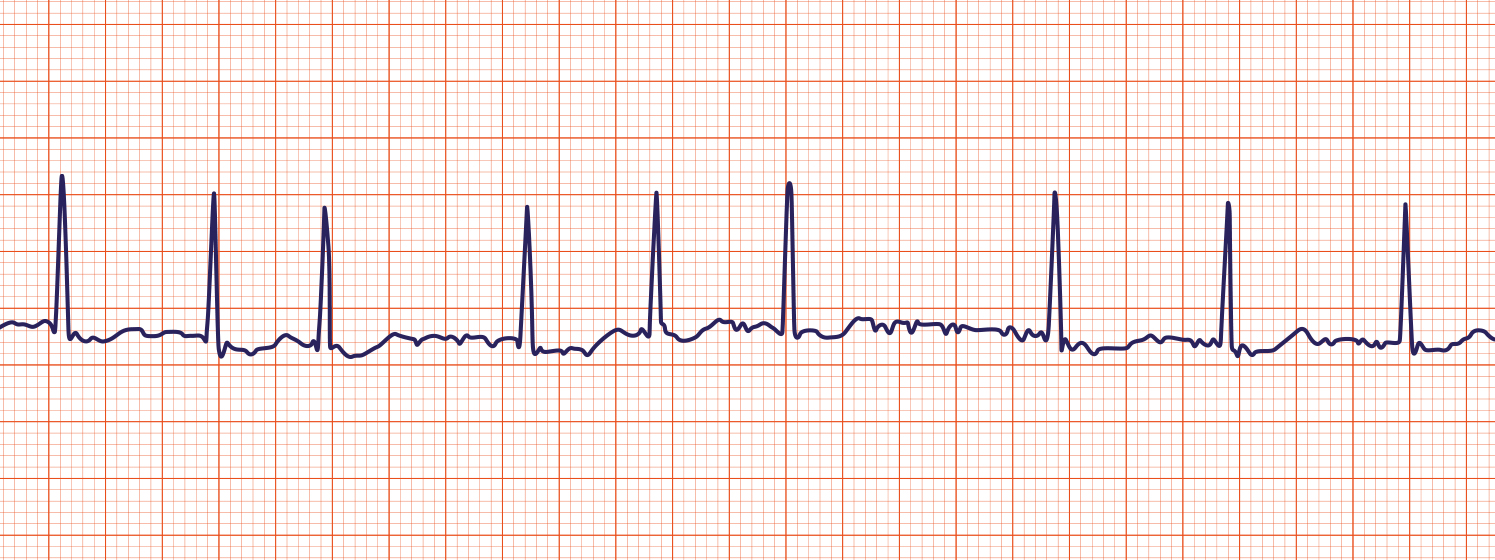
Atrial fib

Ventricular tachycardia
What is the medication treatment for SVT?
Adenosine IV injection.
PUSH FAST (6 TO 12 SECONDS) THROUGH IV IN THE AC. Dose is 6mg, then 12mg, & 12 mg again if unsuccessful.
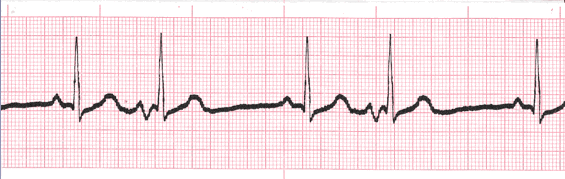
PAC (premature atrial contractions)
This may be seen with excessive moving or leads not placed correctly; the EKG waves may appear wavy, bumpy and tremulous.
Artifact
Torsade's de pointes
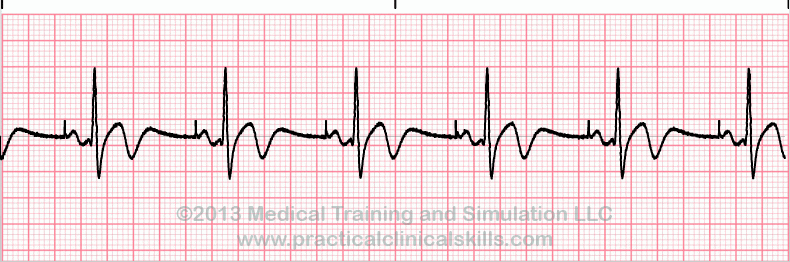
Atrial-paced rhythm
What is it called to send a synchronized shock on the R wave to covert the heart rhythm back into NSR?
Cardioversion
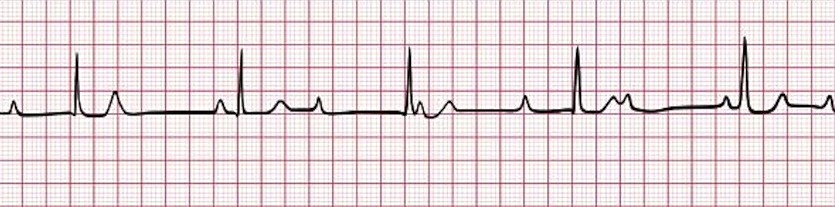
Third-degree heart block