What is Anatomy?
The study of the structure and shape of the
body and body parts & their relationships to one
another.
What is Audiology?
The science concerned with the sense of hearing
What are the 4 main vital signs?
Blood pressure, Temperature, Respiration and Pulse
Define Pharmacology
The study of drugs or chemicals and the effects they have
on living animals is called pharmacology.
Lying on the back with arms at sides.
Purposes: For physical examination, resting in bed, undergoing anesthesia. this position is called?
Supine
The human body exhibits 6 levels of structural complexity, what are they?
a person trained in the manipulation of the
vertebral column is called?
Chiropractor
73/55 mmHg is the Blood Pressure for what age?
Newborns
A chemical that interacts with proteins in the
body to affect a physiological function is called?
Describe the Trendelenburg Position.
Lying on back with arms at sides, bed positioned so foot is higher than the head.
Purposes: During some abdominal surgeries to shift abdominal contents upward
Waterproofs, cushions, protects deeper tissue
Excretes salts & urea; pain, pressure
Regulates body temp; synthesize vitamin D are the functions of which Human system?
Integumentary System
process of cutting across and
producing images of single
layers of tissue is called?
Tomography
°C=(F-32) x 5/9
What kind of drugs are also known as smart drugs or memory enhancers?
Nootrophic Drugs
Describe this position and the purpose: High Fowler’s
head of bed elevated 90 degrees
Purposes: To eat and drink without risk of choking. To assist patients who have difficulty breathing
farther from the origin of a body or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
This direction is called?
Distal
x – ray recording of the blood
vessels using radiopaque
contrast medium is called
Angiogram
Name some locations of the body a nurse can check for pulse.
Temporal artery Carotid artery
Brachial artery Radial artery
Femoral artery Popliteal artery
Posterior tibial Dorsalis Pedis artery
How many types of names a drug can have?
3 types
Client on knees with chest resting on bed. Arms above head or to the side; head turned to side. Thighs straight up and down; lower legs flat on bed. Client may become dizzy; do not leave alone. Name this position
Genupectoral AKA Knee-chest
cut made along the lengthwise or longitudinal plane of the body dividing it into left and right parts
what is this section called?
Sagittal
Subcutaneous is found where?
Beneath the skin
Convert 380 mg/dL to mmol/L
21.1
Dosage form is made to look exactly like a real drug but
do not contain an active ingredient (inactive), usually contains sugar
or starch used in research studies. what is this called?
Placebos
What is this position called?
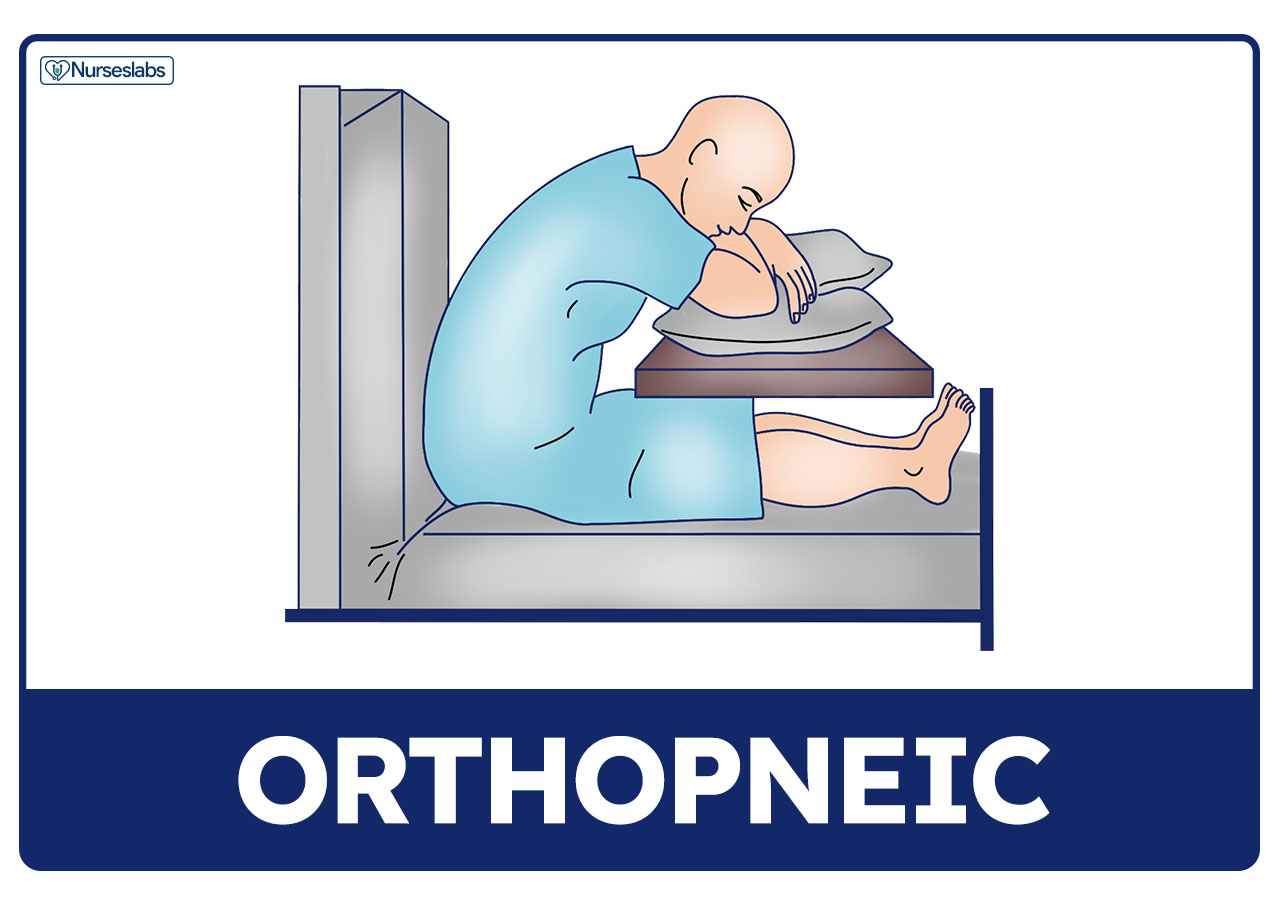
Orthopneic