This insulin is used for IV infusion only.
What is Regular insulin?
Clear in appearance. Used in insulin infusion as a bolus, drip, subQ, and in combination with an intermediate acting insulin for better insulin control.
This lab level is typically low if the patient is anemic.
What is a CBC (Complete Blood Count)?
Which levels in the CBC are you mostly concerned about related to anemia?
This type of service provides patient's with relief of symptoms related to terminal illness.
What is hospice care?
Complication of a long bone fracture when the patient presents with respiratory complications.
What is a fat embolism?
Fat globules released in the bloodstream because of trauma, like a bone fracture. Lungs are affected first, drop in oxygen. May need mechanical ventilation.
Increased amount of glucose puts the diabetic patient at risk for this
What is a UTI?
The body needs this to aid in wound healing.
What are protein, fluid, vitamin A, vitamin C, and zinc?
Used as a rescue inhaler in conditions like asthma.
What is Albuterol?
Short acting beta2 agonist that relieves acute asthma attacks. It dilates the airways, decreases wheezing, and improves oxygenation.
A condition caused by an insufficient production of cortisol causing a darkening of the skin.
What is Addison's disease?
The darkening of the skin is known as a hyperpigmentation. Other characteristics are muscle weakness, fatigue, low BP, and weight loss.
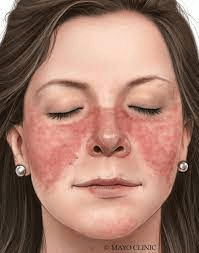
A cutaneous manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
What is a butterfly rash on the face?
Myelosuppression after receiving chemotherapy.
What is bleeding from the gums?
Due to inhibited bone marrow production of blood cells and platelets.
Other than pharmacologic agents, what reduces pain post knee arthroscopy.
What is apply ice.
Use immediately post op the first 24 hours.
Patient's with renal calculi are recommended to consume this amount of fluids per day.
What is 3L or 3000 ml per day?
A commonly used loop diuretic.
What is Furosemide?
Causes potassium loss. Add potassium rich foods such as nuts, dried fruits, bananas, citrus fruits.
Decreased oxygenation of the RBCs and cyanosis due to poor oxygen exchange.
What is hypoxemia?
A severe form of hypothyroidism
What is myxedema?

These are given to restore blood volume and replace hematocrit and hemoglobin levels.
What are RBCs?
How pain management should be handled in end of life care
What is administer medication to minimize breakthrough pain?
Test in which the patient holds his wrist in flexion for 60 seconds. If it produces tingling and numbness over the median nerve, palmar surface of the thumb, index, middle, and ring finger.
What is a positive Phalen's test?
Positive with carpal tunnel syndrome.
Ischemia around a newly created colostomy would show this color
What is purplish colored stoma?
Decreased platelet count putting the patient at risk for bleeding.
What is thrombocytopenia?
Priority assessment in anaphylaxis from a bee sting
What is auscultate for wheezing?
Bronchoconstriction or closure of the upper airway may occur.
Levothyroxine overdose
What is hyperthyroidism (clinical manifestations include insomnia, tachycardia, and hyperthermia)?
A condition characterized by an abnormal coagulation of fibrinogen.
What is disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)?
Recommendations to increase calorie and protein intake during chemotherapy.
What are dipping meats in eggs and bread crumbs before cooking to increase calories, use milk instead of water in recipes, add cream to soups, and top fruits with yogurt?
Normal findings in a postop patient in skeletal traction.
What are slight edema around pin site and slight pain; serous drainage early postop?
Hypercalcemia due to calcium supplements can cause this problem.
What are renal stones or calculi?
Encourage patient to increase water intake while taking calcium supplements.
Education for patient for safe administration of Warfarin.
What are take medication the same time each day, check INR level, eat a good source of vitamin K and maintain a consistent intake, and avoid herbals such as ginger root as it interferes with clotting.
Therapeutic INR: 2-3
A life-threatening condition in which air enters the pleural space that does not escape on expiration and increases the intrapleural pressure.
What is a tension pneumothorax?
This is a medical emergency. The pressure collapses the injured lung and shifts the mediastinal contents.
Hyposecretion of the pituitary hormone causing problems with vasopressin.
What is Diabetes Insipidus?
Increased intracranial pressure
What is headache, disorientaiton, pupillary changes, and slurred speech.
Denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance
What are Elizabeth Kubler Ross' stages of grief?
Increased pressure within the fascia that leads to reduced circulation to the affected area.
What is compartment syndrome?
Patient seeking a kidney transplant would be disqualified with this problem
What is alcohol use disorder?
A patient on digoxin complains of anorexia, vomiting, confusion, headache, and vision changes.
What is digoxin toxicity?
Antidote for digoxin toxicity is Digoxin immune Fab (Digifab, Digibind).
Excessive and continuous bubbling in the water-seal chamber.
What is an air leak in the drainage system?
The air leak usual occurs between the drain and the patient.