True or False: Both plants and animals absorb and release CO2.
False. Plants absorb and release, but animals only release CO2.
Give 1 example of a decomposer.
Worms, mushrooms, bacteria, insects, fungi
What percentage of energy is transferred through the food chain?
10%
Name 3 of the 5 levels of organization.
Organism
Population
Community
Ecosystem
Biome
What is the term for something non-living?
Abiotic
What is the transfer of Nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere called?
The Nitrogen Cycle
What is the term for a primary consumer?
Herbivore
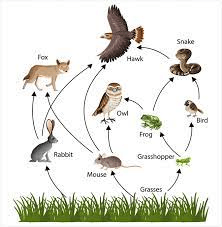
If the grass in the food web above contains 4000 kCal of energy, how many kCal would the owl get from eating the mouse?
40 kCal
(grass=4000 - mouse=400 - owl=40)
What is an omnivore?
An organism that eats both plants and animals (ex. humans)
What is a biological process involved in the hydrologic cycle?
Transpiration

Using the diagram, what would we consider the frog to be?
Secondary Consumer
What is the main difference between a community and an ecosystem?
A community is only living organisms, while an ecosystem is all living and non-living things.
What is an area that stores a lot of carbon, such as a forest, known as?
Carbon Sink
Where is ground water stored?
Aquifers
What provides energy for all other organisms?
Plants use carbon dioxide in photosynthesis to make what 2 things?
Sugar and oxygen
Explain the difference between a food chain and a food web.
Chain: single line of who eats whom
Web: all organisms that eat other organisms and are eaten by other organisms
How do humans impact the carbon cycle?
Through the combustion of fossil fuels adding carbon into the atmosphere.
What organism can convert nitrogen into a form that can be used by the rest of the ecosystem?
Bacteria
Name 3 abiotic things.
Climate, rocks, water, soil, etc.