The most common type of breast mass in adolescent girls and young women. On exam, it feels firm, well, circumscribed, and mobile.
What is a fibroadenoma?
Important information to obtain if the patient has had breast implants. (think of 4 questions)
What are year surgery performed, type of implant, saline, silicone, any tenderness or pain, and history of trauma to the breasts?
Lymph Node Assessment Label the Lymph Nodes (Scroll down)
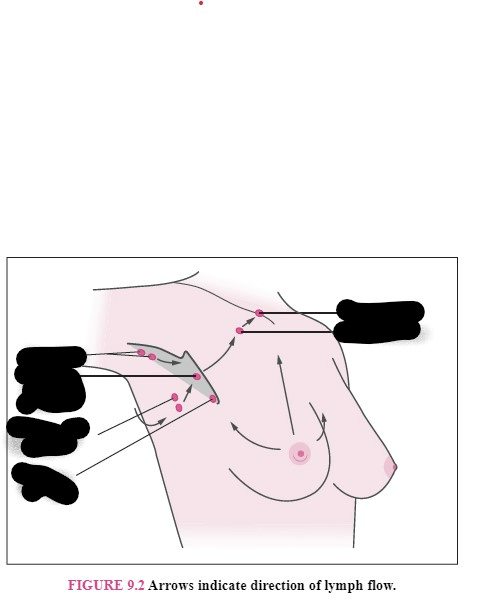
What is (scroll down)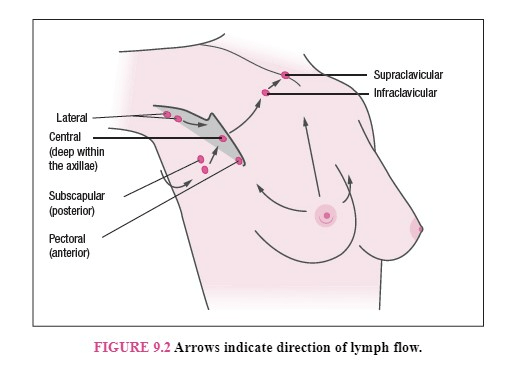
In females this cancer is associated with more deaths, and this cancer is the most common.
What is lung cancer (more deaths), and breast cancer (most common)?
The Gail Model.
What is the national cancer institute breast cancer RISK assessment tool. It estimates the risk of developing breast cancer over the next 5 years and in their lifetime. Women at increased risk are referred for possible prophylactic therapy.
Copy and paste the below to see the Gail model
https://bcrisktool.cancer.gov/calculator.html
The diagnostic test ordered in a young women with a breast mass that is younger than 40 years of age?
What is a breast ultrasound, not a MMG?
The type of MMG that is best ordered for patients with dense breast tissue.
What is the 3D breast picture - the Digital Breast Tomosynthesis MMG (DBT Digital Breast Tomosynthesis).
An important area to assess, where the most ducts are present in the breast.
What is the Tail of Spence?
The risk factors for breast cancer (Think of 6)
What are advancing age, family history, estrogen exposure, hormonal treatments, obesity, alcohol consumption?
Adjuvant (systemic) therapy used in the treatment of all stages of breast cancer.
What is chemotherapy and hormonal therapies
The type of breast cancer that occurs in both breasts?
What is lobular breast cancer?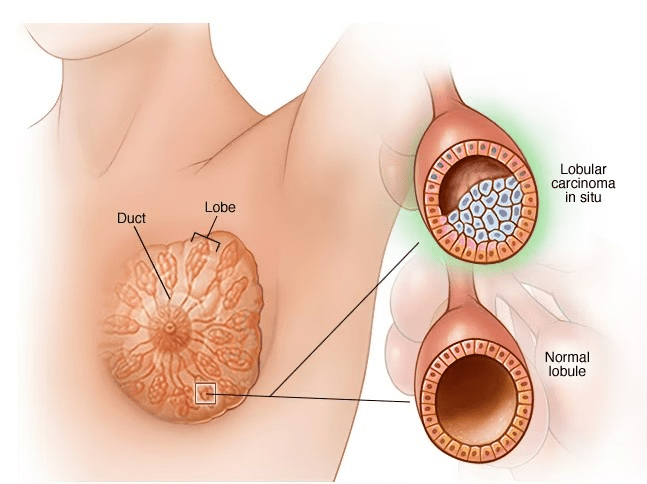
Patient is not breastfeeding and no postpartum. She is a 27 year old with bilateral breast discharge. The breast discharge is milky in color and is bilateral. The test that should be ordered and the possible diagnosis you are ordering the test for is this condition.
What is a prolactin level with a possible diagnosis of prolactinoma?
Where the tail of spence is located.
What is the upper outer quadrant of the breast?
The times when MRI is needed for breast assessment.
Ordered in those with increased risk of breast cancer (15%-20% greater lifetime risk than normal risk).
Important information to know about Tamoxifen.
What is Tamoxifen is a selective selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) medication used to treat breast cancer. Tamoxifen exhibits both estrogenic agonist and antagonist effects in different parts of the body. It selectively binds to estrogen receptors, producing both estrogenic and anti-estrogen effects; because it has two actions, it is patient-specific as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). In the breast tissue, it competes with estrogen for binding sites. In bone and uterus, it stimulates estrogen. It can cause endometrial proliferation, risk of uterine cancer with use. Important to monitor for vaginal bleeding. Patients will experience menopausal symptoms since it binds to some not all estrogen receptors.
The most common type of breast cancer?
What is invasive ductal carcinoma?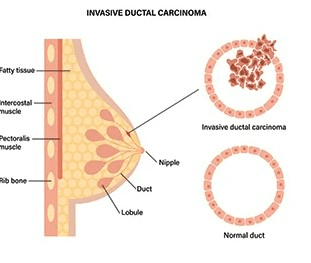
A patient presents with unilateral serous and bloody discharge from the nipple. These are the 2 differential diagnoses.
What is breast cancer or intraductal papilloma?
MMG Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System Called the BI-RADS System. is 1-6 scores. The scores that are suspicious on a MMG report.
What are BI=RADS 4, 5, 6?
This presents as an ulcerated, crusted, or scaling lesion
on the nipple that can extend to the areola. The nipple
can be retracted or hyperpigmented, and the patient may have pain, burning, or itching.
What is Paget disease?
The important to know about Aromatase Inhibitors
What is there are 3 ARs used to treat breast cancer, but the most commons is Anastrozole (Arimidex). Indicated for postmenopausal breast cancer patients ONLY. In postmenopausal women, the conversion of androgens to estrogens via this pathway in the adrenal glands, the skin, the muscle, and the adipose tissue, is the primary source of estrogen. Aromatase inhibitors block this pathway and consequently suppress estrogen levels in postmenopausal women. The breast cancer cells also demonstrate aromatase activity, a likely source of local estrogen for the tumor cells. The inhibition or inactivation of aromatase suppresses serum estrogen levels, which decrease estrogen-mediated cancer cell proliferation in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. The common side effects are ulcers and blisters are common skin manifestations and bone loss due to estrogen deficiency. The most common reason for discontinuing use is arthralgia syndrome - joint pain and swelling.
This is the recommendation for assessment of complex cysts beside ultrasound.
What is biopsy?
The way to distinguish between nipple discharge that is worrisome and more likely benign.
What is enign discharge is
more likely to be bilateral, only present when expressed, milky or green in color, and multiductal. Discharge that is unilateral, uniductal, and spontaneous indicates a higher risk of malignancy and requires more thorough evalua-
tion.
Ultrasound can help distinguish between fluid and solid mass, used to biopsies, assess axillary lymph nodes, help identify smaller lesions not seen on MMG.
Two possible diagnoses for patient that presents with a presentation where one breast is that warm, and erythematous?
What are mastitis or inflammatory breast cancer? It would not be engorgement because that occurs in both breast at the same time.
The breast cancer screening recommendations for BRCA carriers.
What are monthly self breast exams beginning at age 18-20 years, annual clinical breast exams from a provider (will not know to perform a breast exam if you do not ask about family history in well visit), screening MMGs beginning at age 25 or 5-10 years BEFORE the age of breast cancer diagnosis in the affected relative. MRI is recommended as a supplement for MMG which means, one year MMG and next year MRI.