Name three objective signs of pregnancy
Goodwells sign
Hegars sign
Braxton hicks contractions
Positive pregnancy test
Abdominal enlargement
Ballottement
This stage of labor is when the placenta is delivered
Third Stage
Main sign and symptom is painless vaginal bleeding
Placenta previa
What drug is given during an ectopic pregnancy as an IM injection?
methotrexate
(Stops cells from growing which ends the pregnancy, pregnancy is then absorbed by the body within 4-6 weeks)
These are also called practice contractions
Braxton Hicks
Patients date of last menses was 9/14/2021, what would be her due date?
June 21 2022
At this station the babies head is at the ischial spine
During cervical insufficiency, physicians may place this to prevent dilation
cervical cerclage
This medication is given during severe preeclampsia to prevent seizures
magnesium sulfate
How do we check for clonus?
By dorsiflexing the patients foot
At the umbilicus
If the patient has had a rupture of membranes we need to make sure to do what?
Monitor FHR for deaccelerations and take mom's temp every 2 hours
With this disorder, patients are told not to get pregnant for up to a year because their HCG levels will be high.
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
What does VEAL CHOP stand for?
V- Variable Decel C - Cord Compression
E- Early Decel H - Head Compression
A- Accelerations O - OK
L- Late Decels P- Poor placental perfusion
This is checked for twice during pregnancy and if positive is given penicillin before deliver
Group Step B
Signs and symptoms are hypotension and dizziness, what is the cause?
Vena Cava Syndrome
What maneuvers are used to fix shoulder dystocia?
suprapubic pressure & McRoberts maneuver (pulling knees back as far as possible while admin suprapubic pressure)
What occurs (term) in severe preeclampsisa?
HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets)
What are the 5 interventions during cord compression or poor placental perfusion?
Lie on left side
IVF
Oxygen
Notify provider
Stop pitocin
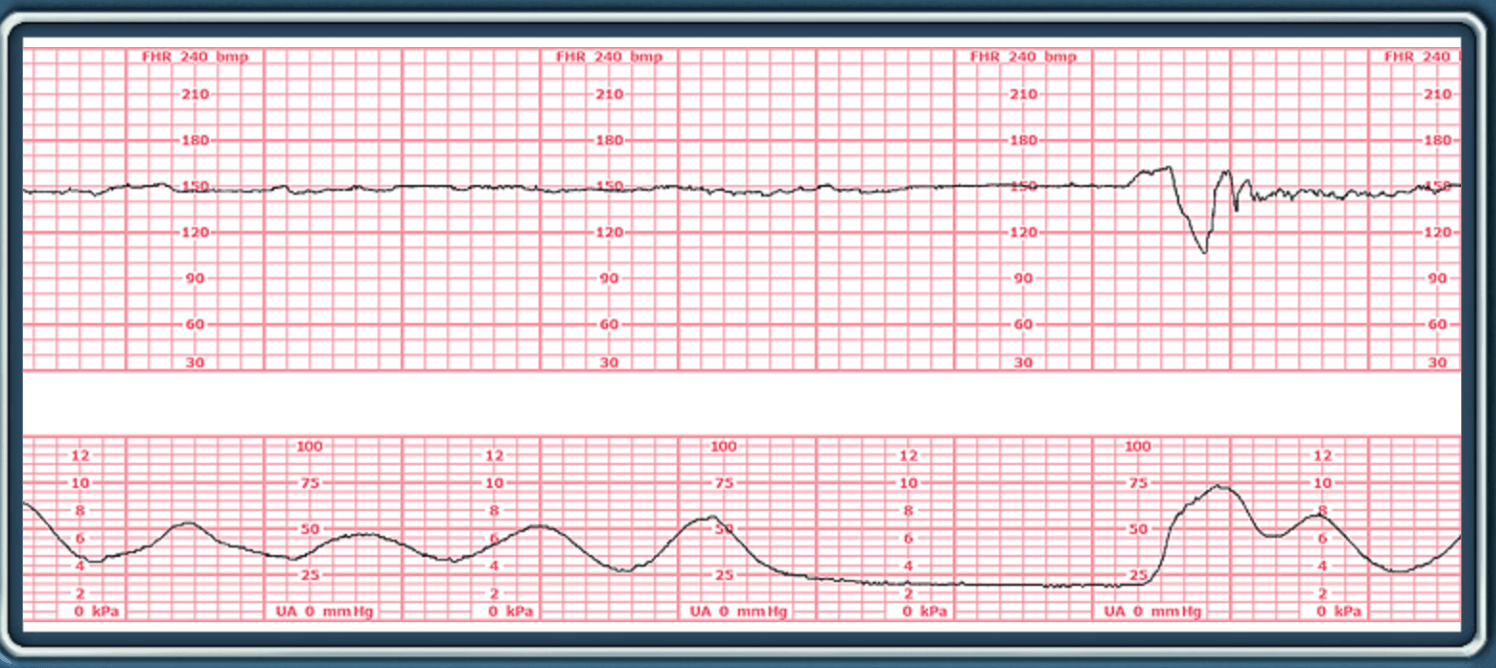
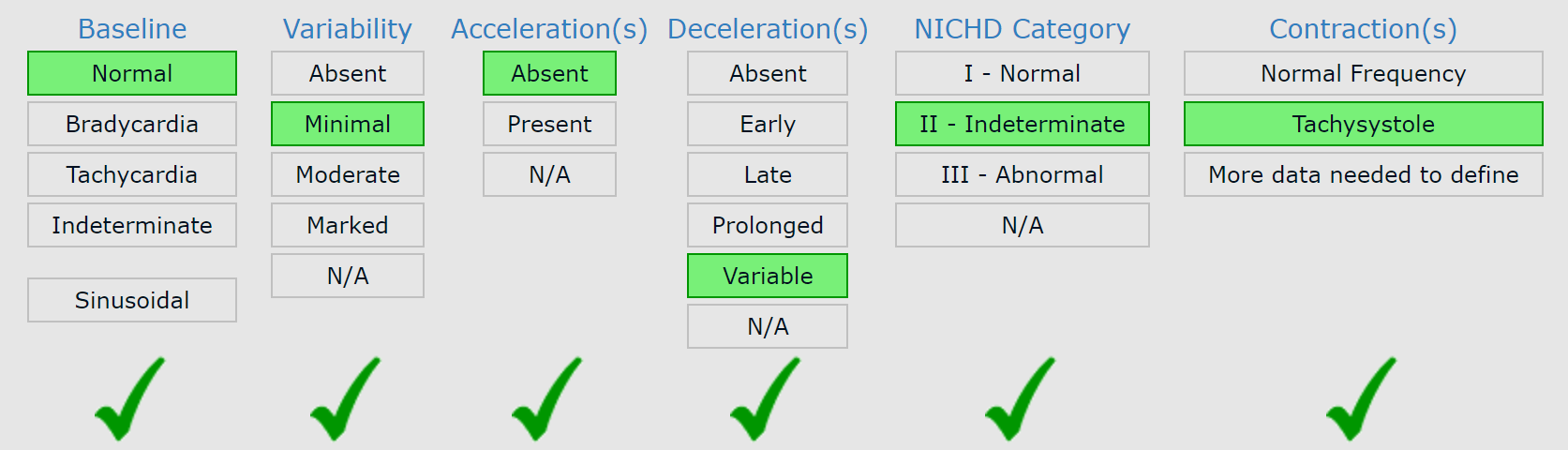
What is the baseline (Normal, Brady, Tachy) What is the variability (Absent, Minimal, Moderate, Marked) Accelarations (Absent or Present) Decels (Absent, Early, Late, Prolonged, Variable), NICHD Category (I, II, III) Contractions (Normal, Tachy)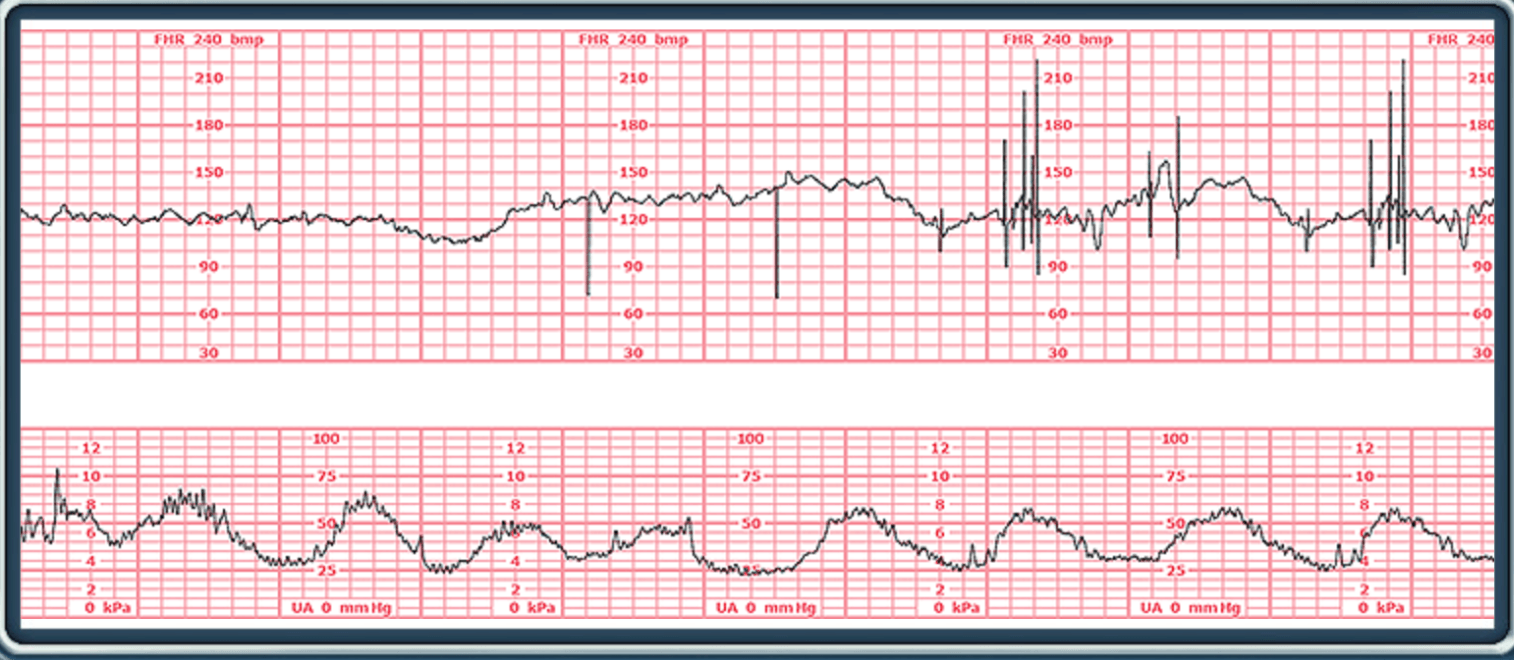
Patient comes in for her prenatal visit at 32 weeks. She has a 2 year old son that was born at 38 weeks and an 8 year old daughter who was born at 40 weeks. She had a miscarriage 6 years ago at 18 weeks. What is her GTPAL?
G: 4
T: 2
P: 0
A: 1
L: 2
What medications are used during a post-partum hemorrhage? (Name as many as you can)
Pitocin, methergine, cytotec (misoprostol), hemabate, tranexamicacid (TXA) (promotes clotting)
What are the immediate treatments for a patient who is eclamptic?
1. Clear the airway
2. Position her on the left side
3. Admin IV fluids
4. Give magnesium sulfate to prevent further seizures
What drugs will you give for hypertension?
Labetalol & Hydralazine
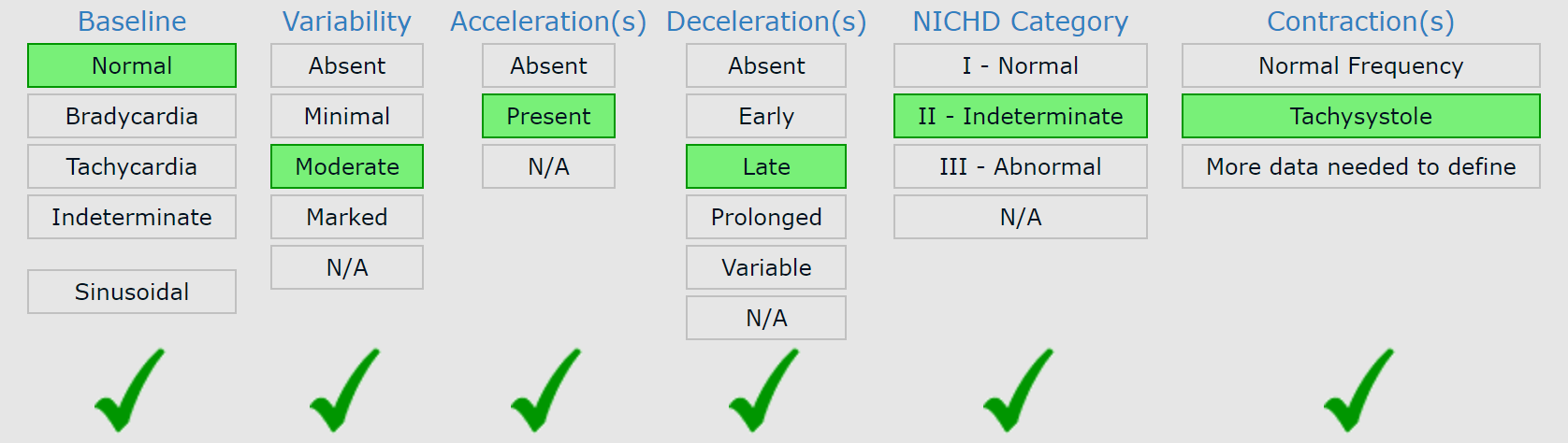
What is the baseline (Normal, Brady, Tachy) What is the variability (Absent, Minimal, Moderate, Marked) Accelarations (Absent or Present) Decels (Absent, Early, Late, Prolonged, Variable), NICHD Category (I, II, III) Contractions (Normal, Tachy)