and Chromosomal
Metabolism
Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) is the most common underlying condition leading to a newborn being which gestation age:
Small for gestational age SGA
Maternal diabetes, genetic makeup, obesity, gender, multiparous are all contributing factors of:
LGA
What can happen after a gavage feeding
Gastric Residual
What gestation weeks is considered postterm and also the weight of the infant:
>42 weeks gestation
infant is postterm regardless of weight
How should we teach families to lay their infant down to sleep until at least 6 months:
Supine
Nurses assess what for a patient with Hydrocephalus:
Head Circumference DAILY
BP in upper extremities are higher than the lower extremities
Coarctation of the aorta (constriction or narrowing of aortic arch)
How do you feed an infant with an omphalocele
TPN
Diagnosis and Treatment for Congenital Hypothyroidism
Diagnosis:
T3 and T4 levels
Treatment:
Replacement of thyroid hormone (Levothyroxine); monitor levels
Therapy must be continued for life
What does SGA, AGA, LGA stand for:
Small for gestational age
Appropriate for gestational age
Large for gestational age
What is this called?
Lanugo
Name RDS treatments:
Surfactant replacement therapy, antenatal steroids, appropriate resuscitation techniques, immediate use of nasal continuous positive airway pressure, gentle ventilation procedures, supportive care
Define Polycythemia related to Postterm newborns
due to intrauterine hypoxia
Related to Fetal alcohol syndrome...When should a mom stop drinking?
3 months prior to pregnancy and throughout pregnancy
Failure of the posterior laminae of the vertebrae
Spina Bifida
Loud harsh murmur associated with systolic thrill
Ventricular septal defect
What needs to occur if an infant is born with a diaphragmatic hernia
surgery to repair
Gluteal fold higher on one side than the other
Dysplasia of the hip
3 measurements used to help determine gestational age after birth:
Weight
Length
Head Circumference
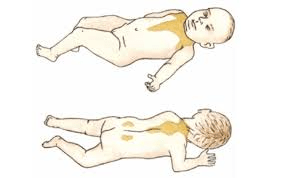
Brown Fat
*Remember premature infants do not have this
What complication might require laser surgery:
Retinopathy of prematurity
Which syndrome shows the following:
Amniotic fluid stained green/greenish black or seen on newborn
Difficulty initiating respirations after birth
low Apgar score
Tachypnea or apnea
Retractions
Grunting
Nasal Flaring
Cyanosis
Confirmed with CHEST x-ray
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Nursing care for Neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS):
Providing physical and emotional support
Meds to assist with withdrawal and prevent complications such as seizure
Holding and gently rocking infant, swaddling
Minimize stimulation in environment
Maintain airway and monitor respiratory status
Frequent feedings, I&O, supplemental fluids
Non-judgement toward mother and family
When is the last week of gestation will a doctor perform a intrauterine surgery to fix spina bifida:
26 weeks
When the ductus arteriosus remains open after birth, shunts blood from aorta to pulmonary artery
Corrected by medication and/or surgery
Patent Ductus arteriosus
Cleft lip and palate
Diagnosis:
Treatment (surgery)-what should you teach the caregiver
Diagnosis:
Physical appearance
Trouble feeding/sucking
Treatment teaching:
After feeding keep incision clear of crusting
Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (clubfoot)
Treatment
Nonsurgical and when is surgical done
Nonsurgical: use of plastic splint or cast; casts changed frequently until radiographic evidence of correction
Surgical: used if no response to nonsurgical treatment
What are the 2 major categories of maturity assessed and what is the system called:
Ballard Scoring System
Neuromuscular maturity
Physical maturity
Nursing care for a SGA newborn
Monitor respiratory status, maintain neutral thermal environment, monitor blood glucose levels, monitor other blood studies, observe feeding tolerance, monitor I&O and daily weights, observe for jaundice, encourage family caregivers to care for infant
Common Complications of a Preterm Newborn:
RDS, thermoregulation, maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance, has high caloric needs but inadequate digestive system, hyperbilirubinemia, infections, intraventricular hemorrhage, retinopathy of prematurity, NEC, jaundice, and infection
The 5 contributing factors related to Transient tachypnea of the newborn
Cesarean delivery
prematurity
SGA
Maternal Diabetes
Maternal Smoking
S/S for infant with a congenitally acquired infection
Cyanosis
Pallor
Thermal instability
Convulsions
Lethargy
Apnea
Jaundice
OR Just "not looking right"
Clinical manifestations with Hydrocephalus:
Rapid head growth with widening cranial sutures
Anterior fontanelle becomes tense and bulging
Skull enlarges in all diameters
Scalp becomes shiny and veins dilate
Eyes appear to be pushed downward slightly, sclera visible above iris
Neck muscles fail to develop sufficiently, newborn has difficulty raising or turning head
Increasingly helpless, increased intracranial pressure
Extra X chromosome present (characteristics not evident until puberty); most common in males
Klinefelter Syndrome
If an infant has a hypospadias or epispadias why does the pt have to wait for a circumcision
The foreskin is used in the repair
Early feeding difficulties with vomiting and diarrhea, producing dehydration, weight loss, jaundice
Galactosemia
What is this called?

Ballard Scoring System
Potential complications for a LGA birth:
Cesarean delivery, breech presentation and shoulder dystocia resulting in birth injuries and trauma: fractured skull or clavicles, cervical or brachial plexus injury or Erb palsy.
Subtle and nonspecific s/s; no ORAL feedings, NG suctioning, IV fluids, TPN, Antibiotics; possible bowel perforation
Issues with feeding, maintaining a stable temp, and vomiting bile
Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Treatments for TTN and what do we monitor for:
IV fluids
Gavage feedings
Supplemental oxygen
Care:
Supportive
Monitor VS and oxygen saturation levels
IV fluids
Supplemental oxygen
Assist family to understand
Education about situation
Clinical manifestations for FAS:
When withdrawing:
hyperactive
Irritable
Trouble Sleeping
Tremors or seizures
FAS s/s:
LBWA
Small height and head circumference
Short palpebral fissures
Reduced ocular growth
Flattened nasal bridge
Newborn prone to respiratory difficulties
Hypoglycemia
Hypocalcemia
Hyperbilirubinemia
Growth during infancy and childhood below average
Brain damage permanent resulting in intellectual disability
Treatment options for Hydrocephalus:
Surgical Intervention
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting
Clinical Manifestations:
Brachycephaly; short stature; upward and outward slanted eyes with epicanthic fold at inner angle; short, flattened bridge of nose; thick, fissured, protruding tongue; dry, cracked, fissured skin that may be mottled; small hands with short broad fingers and curved fifth finger; single deep crease on palm of hand; wide space between first and second toes; lax muscle tone; heart and eye anomalies; greater susceptibility to leukemia
Down Syndrome
Difficulty feeding, chocking, cyanotic and frothy sputum
Esophageal Atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Clinical Manifestations:
Frequent vomiting, aggressive and hyperactive traits, severe, progressive mental disability, convulsions, eczema, musty smell to urine