This structure allows blood to flow directly from the right atrium to the left atrium in the fetal heart.
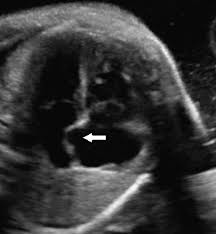
What is the foramen ovale?
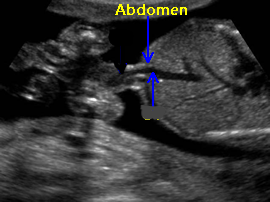
This fluid-filled structure in the left upper quadrant of the fetal abdomen appears anechoic on ultrasound.
What is the stomach?
This vessel carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetal liver.
What is the umbilical vein?
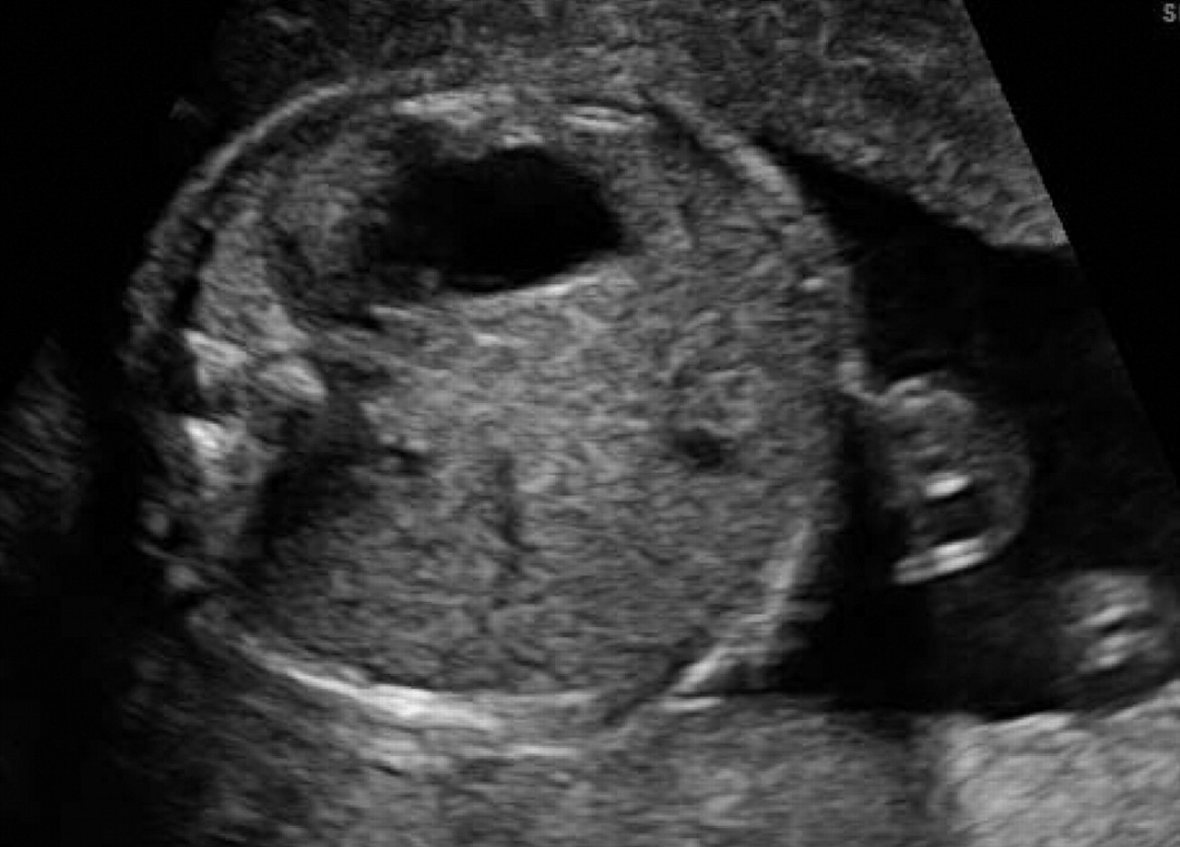
This midline structure separates the cerebral hemispheres and is visible as a bright echogenic line.
What is the falx cerebri or interhemispheric fissure (IHF)?
This protective sac, filled with fulid, cushions the fetus and allows for free movement.
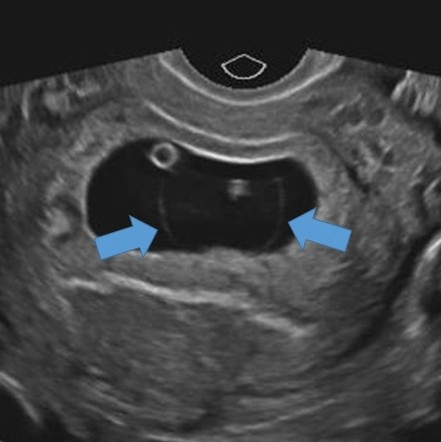
What is the amniotic sac?
The sonographic view used to evaluate all of the fetal heart ventricles and atria.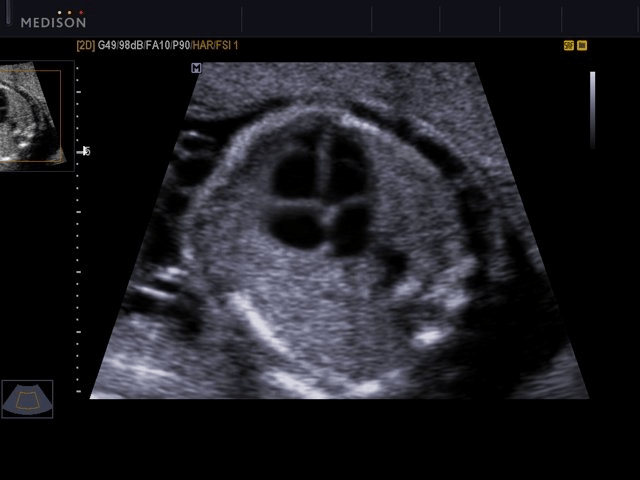
What is the four-chamber view?
This organ, seen as a homogeneous structure in the right upper quadrant, is the site of fetal red blood cell production.
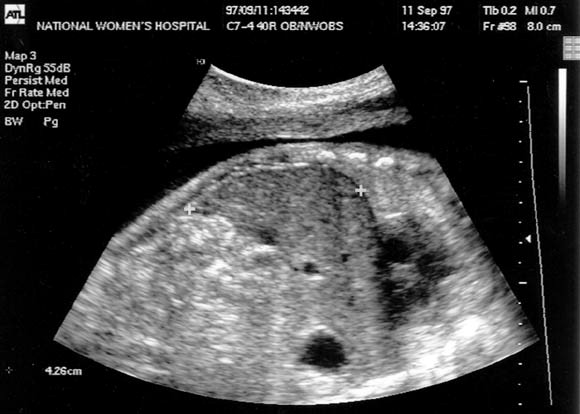
What is the liver?
The ductus venosus bypasses the fetal liver, allowing blood to flow directly into this vessel.
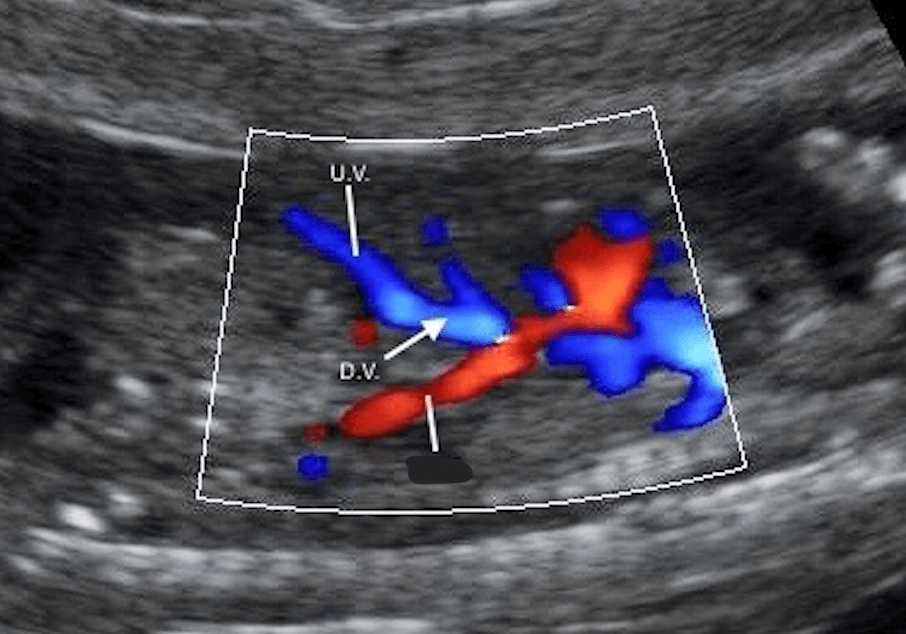
What is the inferior vena cava?
This fluid-filled space at the back of the fetal brain is a normal finding in the first trimester.
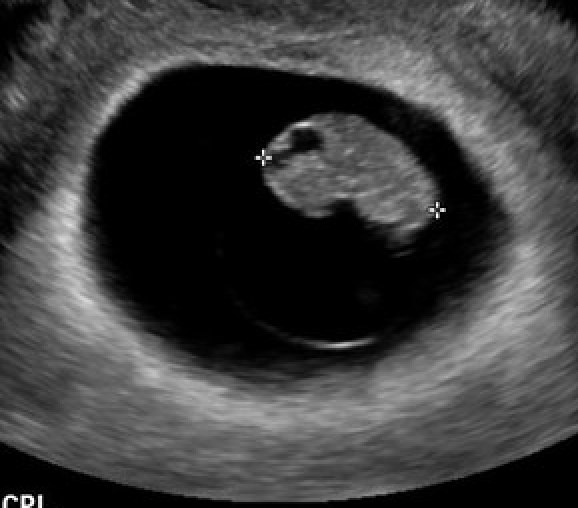
What is the rhombencephalon?
This fluid, produced by the fetal kidneys after 16 weeks, plays a key role in lung development.
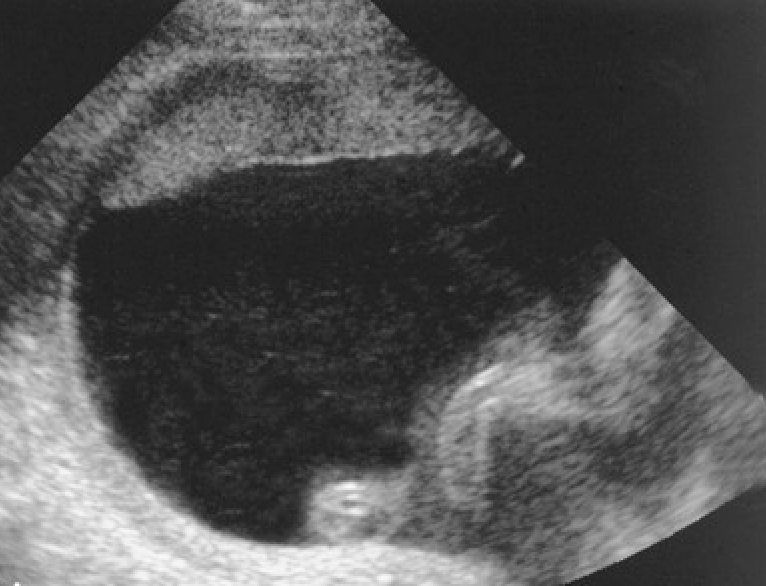
What is amniotic fluid?
This vessel connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta, bypassing the fetal lungs.
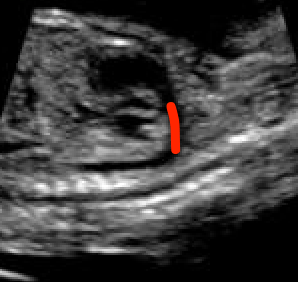
What is the ductus arteriosus?
The temporary herniation of this structure into the umbilical cord is a normal finding up to 12 weeks.
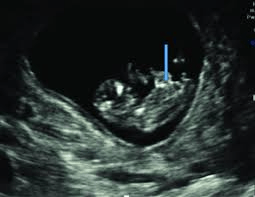
What is the midgut?
These vessels is responsible for returning deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta.
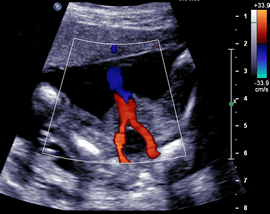
What are the umbilical arteries?
This structure, appearing as a bright, reflective line on ultrasound, connects the two hemispheres of the cerebellum.
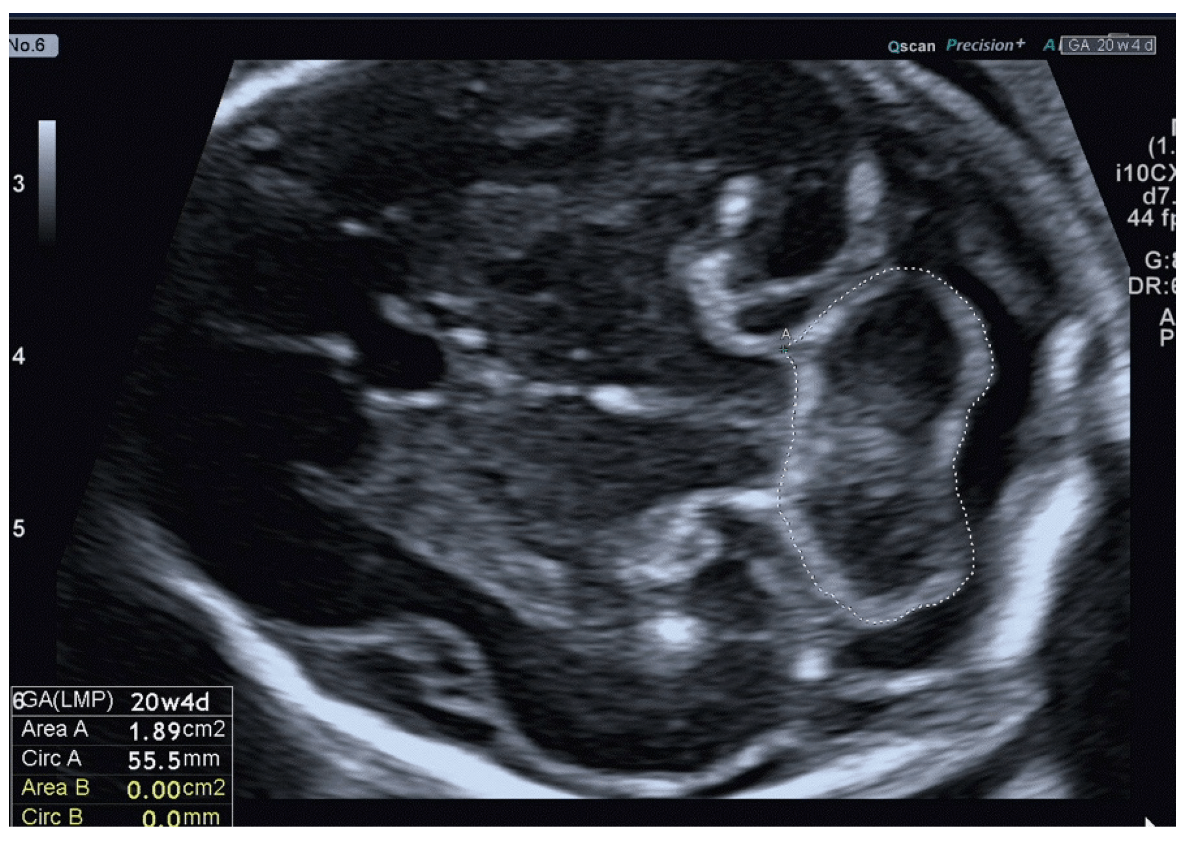
What is the cerebellar vermis?
This condition occurs when the placenta covers the internal cervical os, potentially obstructing delivery.
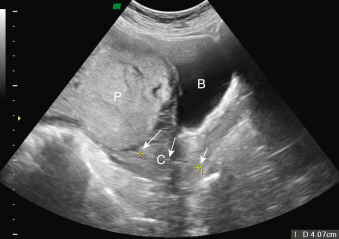
What is placenta previa?
This valve separates the right atrium from the ventricle and ensures one-way blood flow.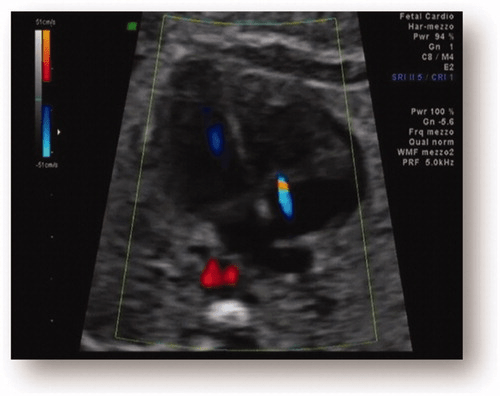
What is the tricuspid valve?
This small, anechoic, echogenic-lined structure in the fetal abdomen becomes difficult to visualize after 32 weeks due to contraction and bile release.
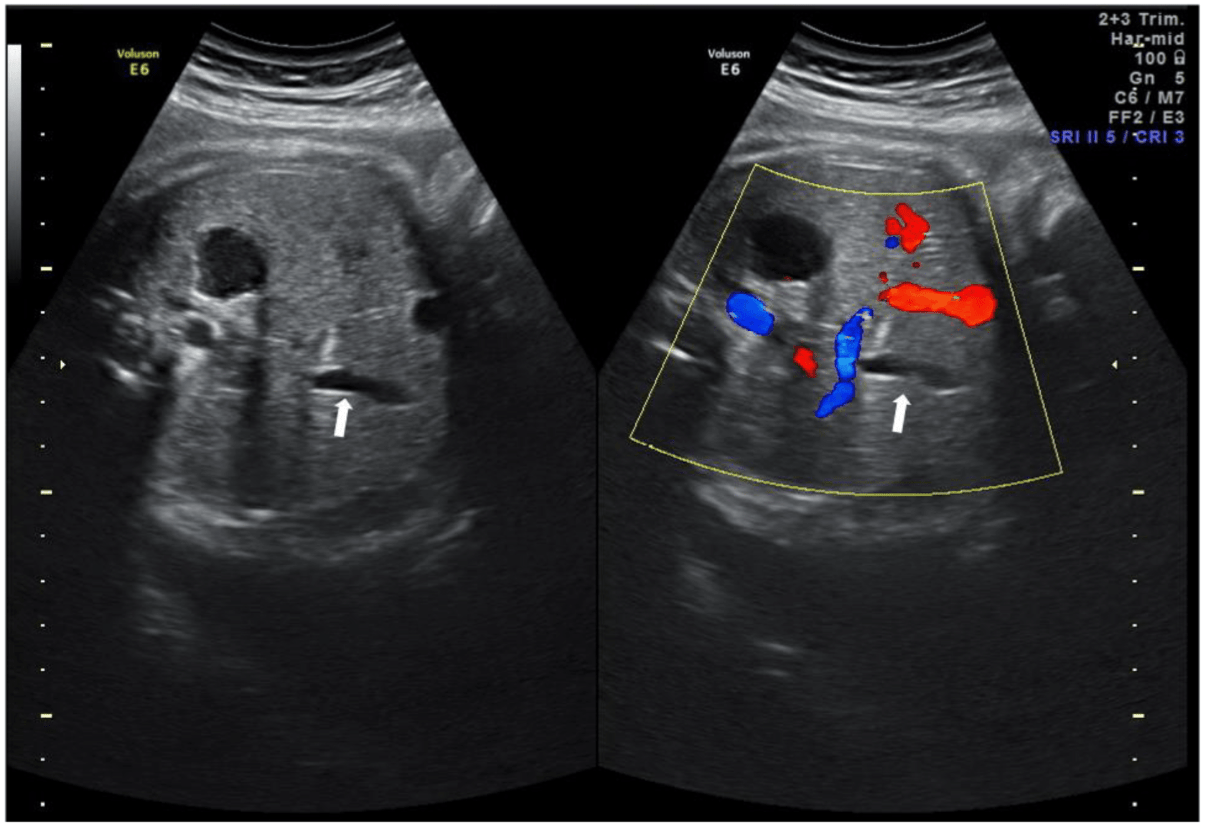
What is the gallbladder?
This fetal heart chamber receives blood directly from the ductus venosus via the largest vein in the abdomen.
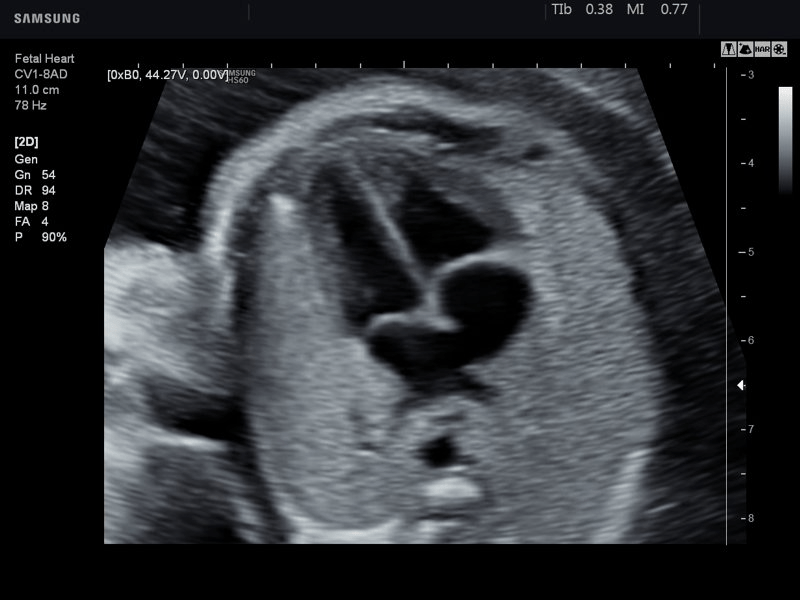
What is the right atrium?
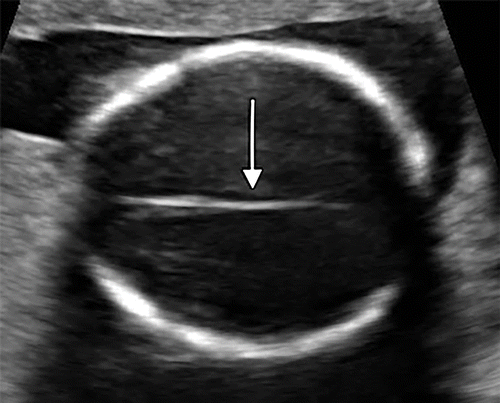
This ventricle, located between the thalami, is visible in the correct plane for biparietal diameter measurement.
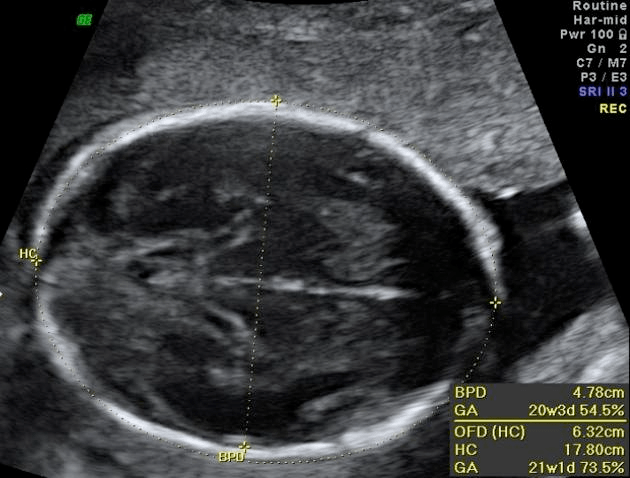
What is the third ventricle?
This structure, formed by the trophoblast during early pregnancy, anchors the placenta to the uterine wall.
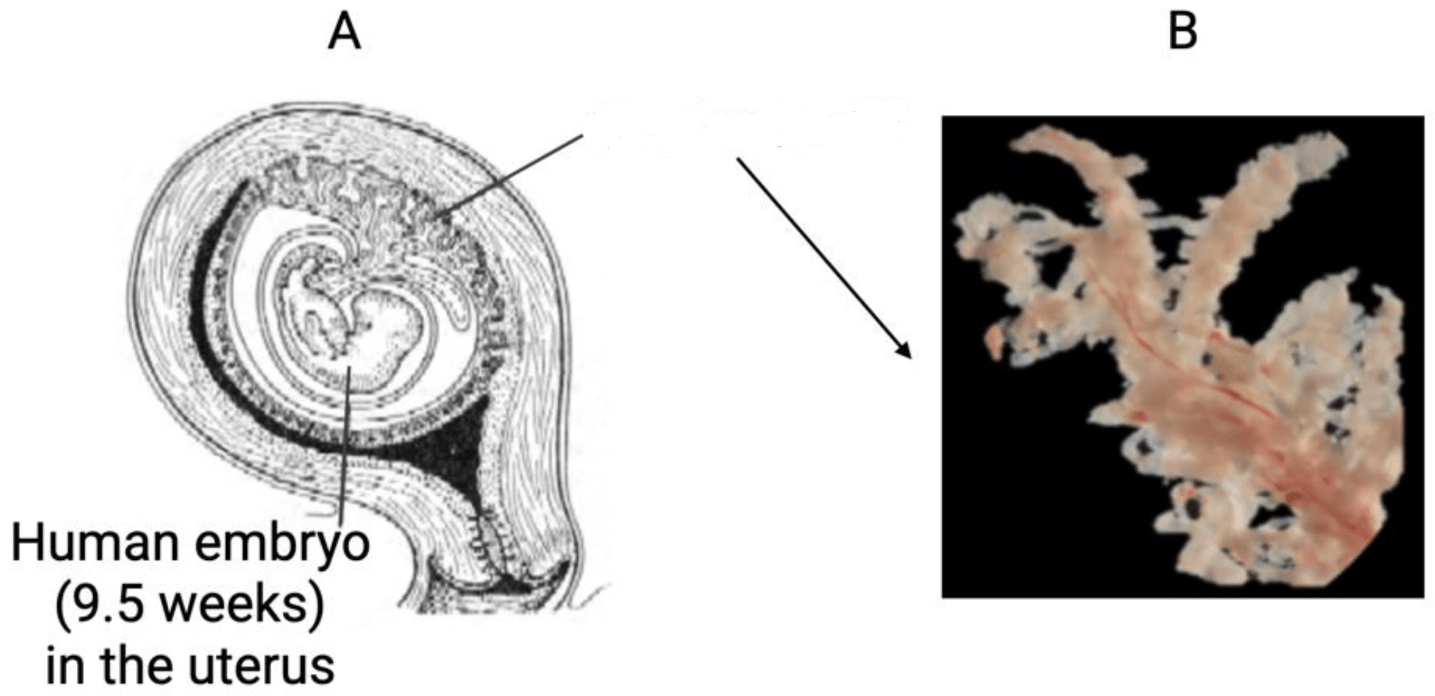
What is chorionic villi?
This tract is responsible for carrying blood from the left ventricle to the ascending aorta.
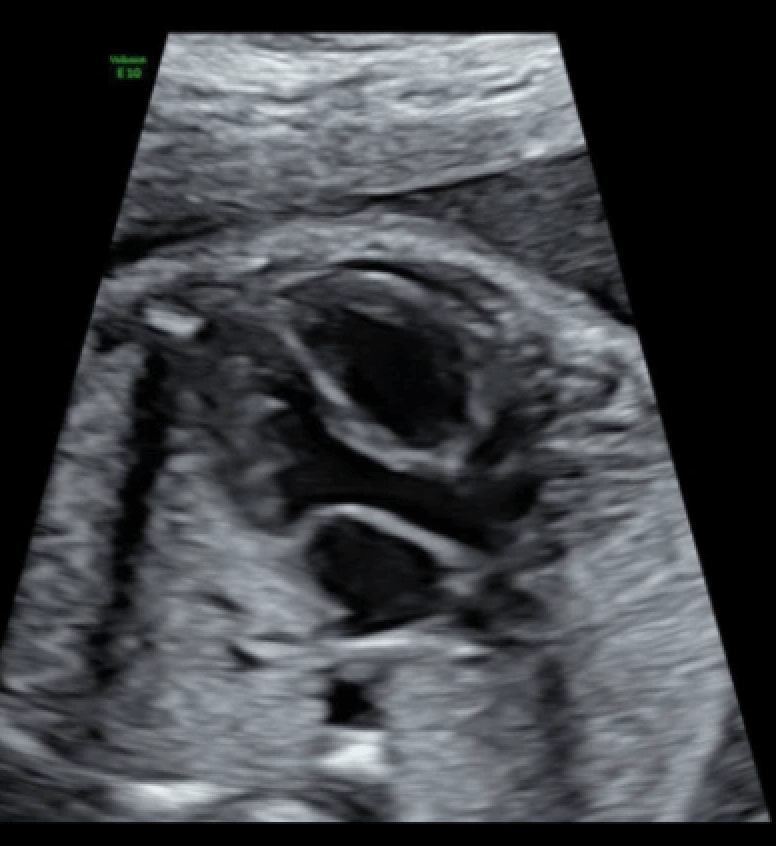
What is the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT)?
This tubular structure connects the fetal bladder to the umbilical cord and can sometimes be seen on sonography.
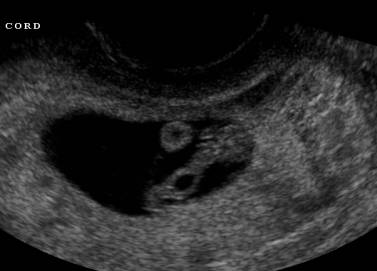
What is the allantois? (image shows an allantoic cyst)
This fetal circulation pattern ensures oxygen-rich blood is preferentially delivered to the brain and heart.

What is the "head-sparing" theory?
This crescent-shaped cavity within the fetal brain is bordered by the thalami and contains cerebrospinal fluid.
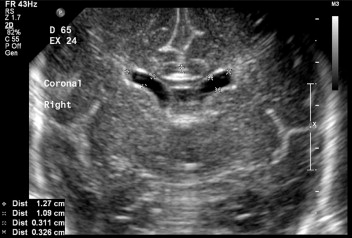
What are the lateral ventricles?
This decidualized layer of the endometrium forms the maternal side of the placenta.
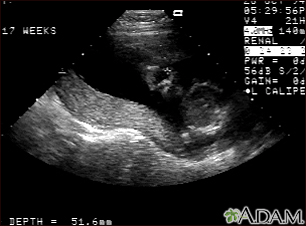
What is the decidua basalis?