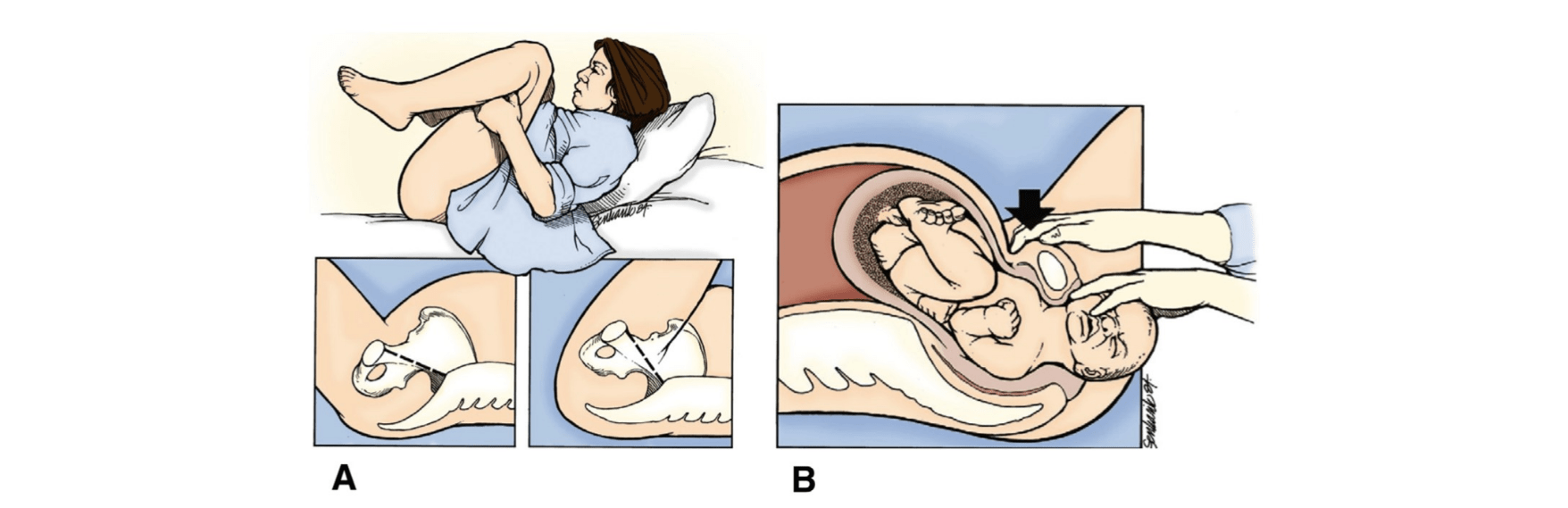
This is the appropriate positioning of the patient when an umbilical cord presents prior to fetal delivery.
What is trendelenburg or knee-to-chest?
Correct first-line drug and dosing for a patient who presents with seizure
What is 6 g magnesium IV bolus?
Maneuver necessary when encountering this obstetric emergency:

What is elevating the presenting fetal part off of the cord?
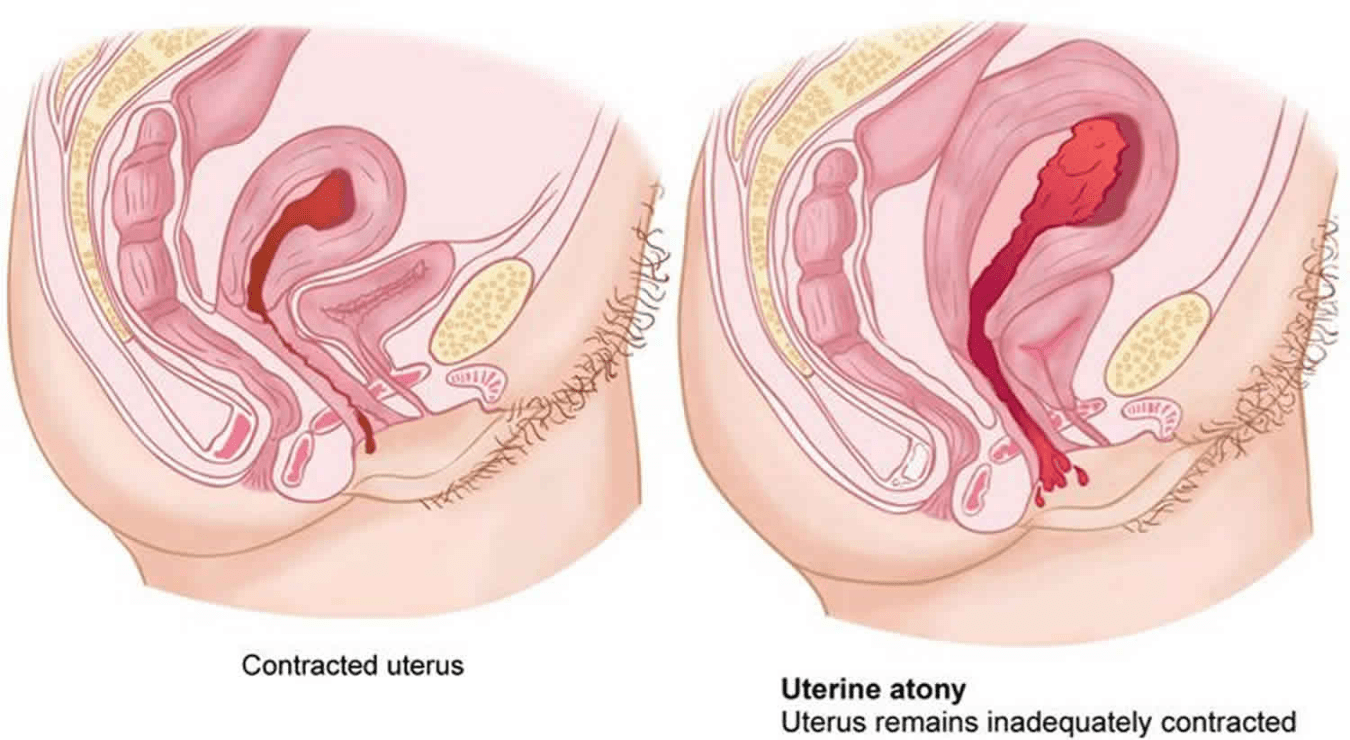
The most common cause of primary postpartum hemorrhage.
What is uterine atony?
Instead of the classic presentation, appendicitis in the gravid female can commonly present with pain in this abdominal quadrant.
What is RUQ?
This medication is given in all deliveries at SJH after delivery to prevent postpartum hemorrhage.
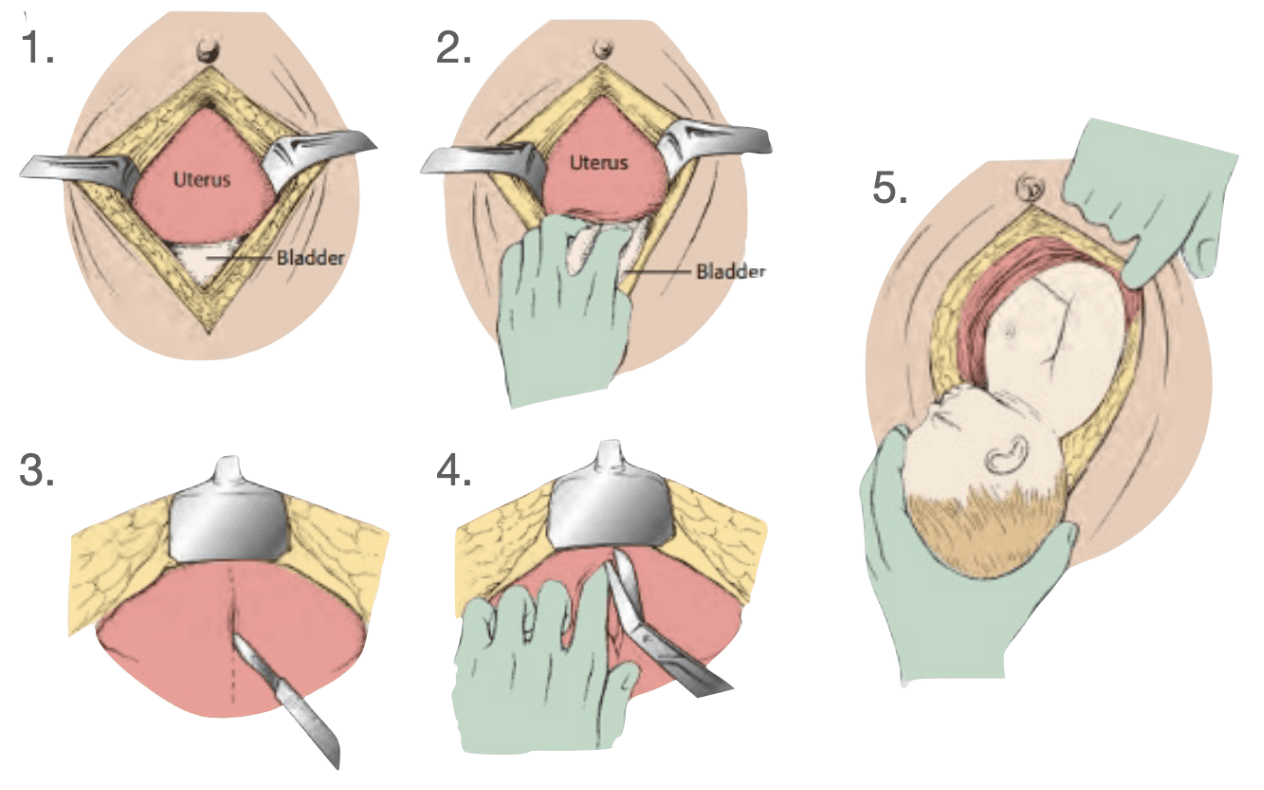
Orientation of the incisions for both the abdominal wall incision and uterine incision in a perimortem c-section.
What is vertically?
After delivering the head of the baby, the physician must check for this finding.
What is a nuchal cord? (Image from Peesay, M. Maternal Health, Neonatology, and Perinatology. 2017.)

Cause of sudden cardiopulmonary arrest and disseminated intravascular coagulation during or just after labor.
What is amniotic fluid embolism?
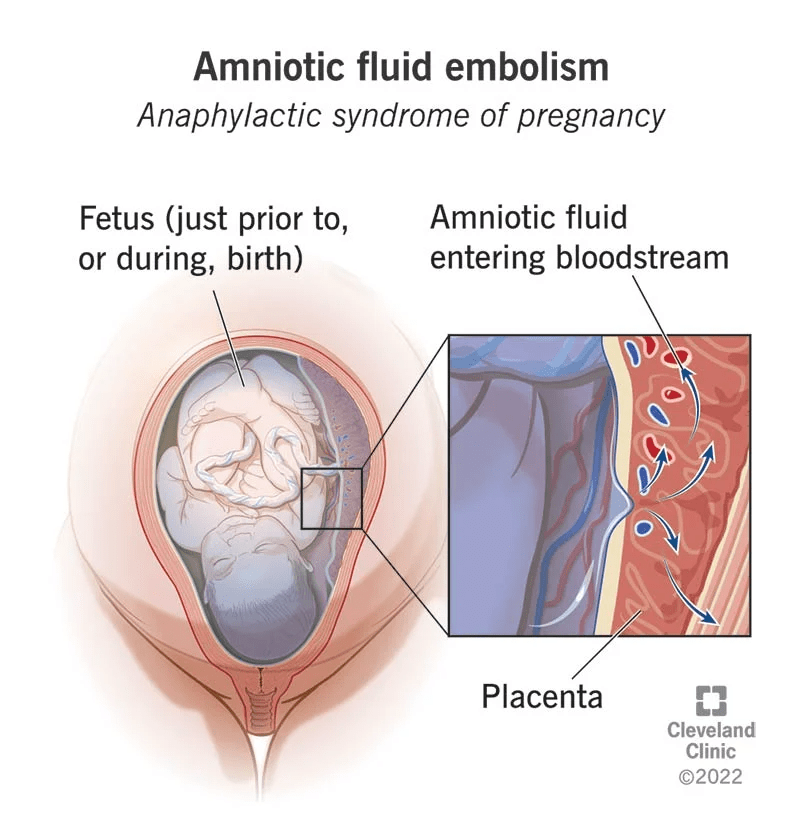
What must be remembered if performing a code blue on a pregnant patient.
This is a rare complication of HELLP syndrome resulting in acute onset RUQ abdominal pain and hemodynamic instability.
What is hepatic rupture?
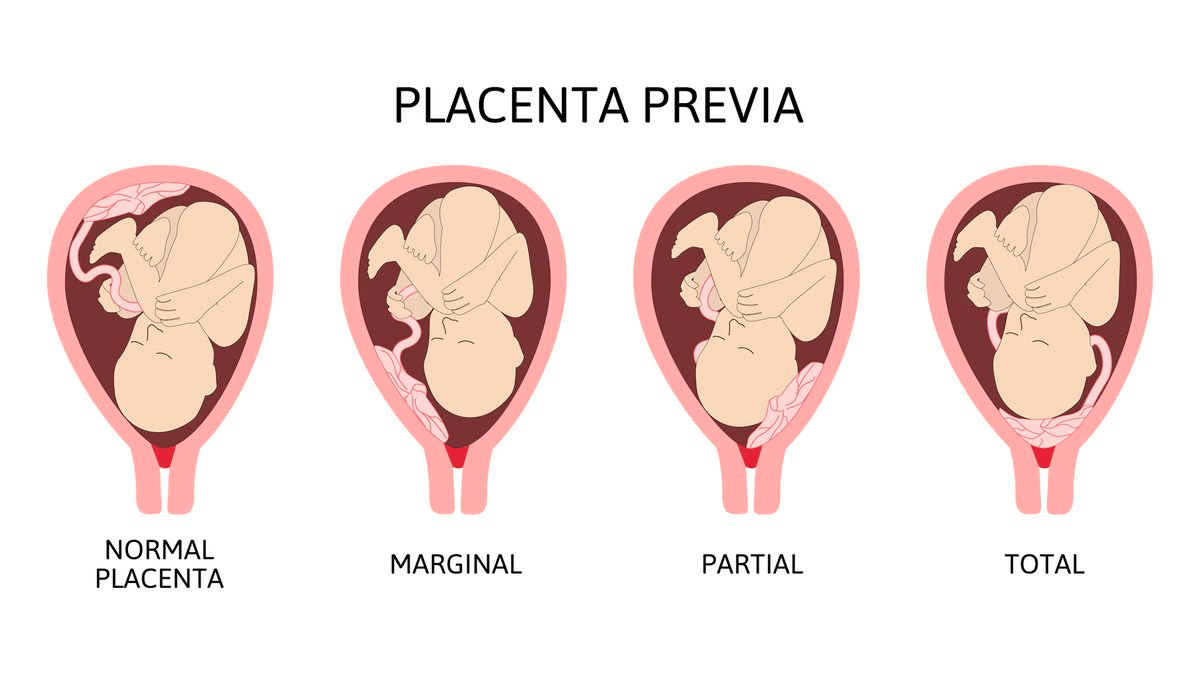
This part of the examination should not be performed in any second or third trimester with unknown prenatal history who presents with vaginal bleeding until an ultrasound is performed.
What is pelvic examination?
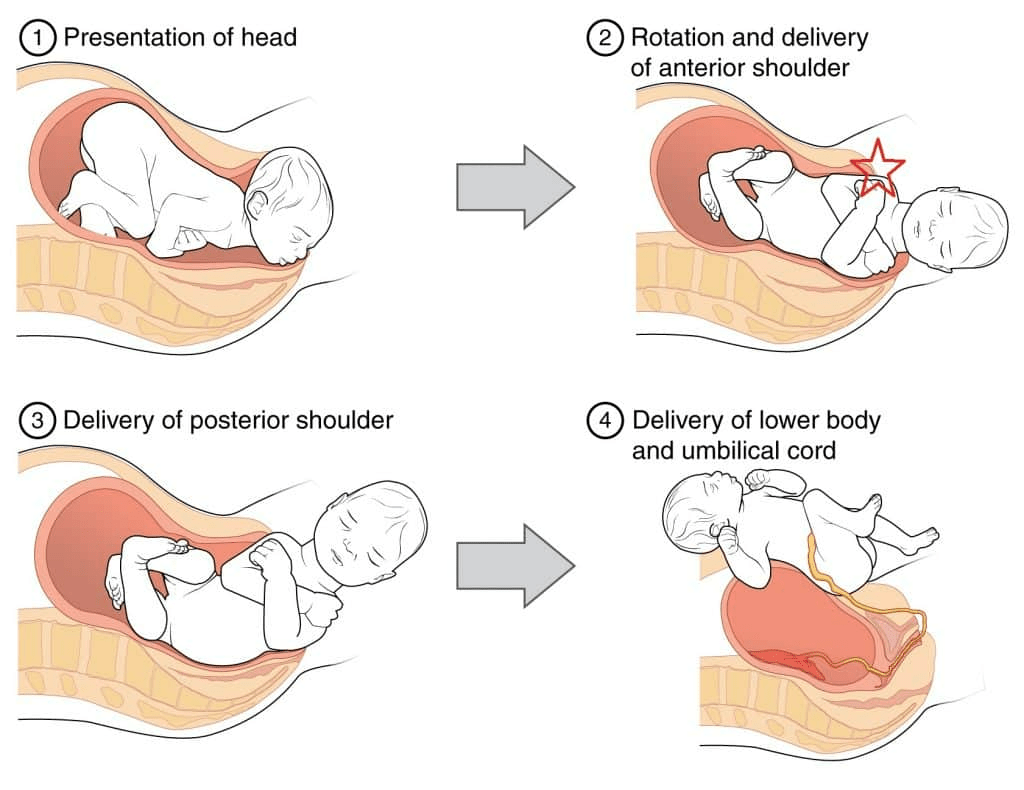
The name of the maneuver shown in the image below that is used to deliver babies with shoulder dystocia:
What is McRoberts Maneuver?
Excessive umbilical cord traction or fundal pressure in the setting of a relaxed uterus are risk factors for this cause of primary postpartum hemorrhage.
What is uterine inversion? (Image from Anderson et al. Am Fam Phys 2007.)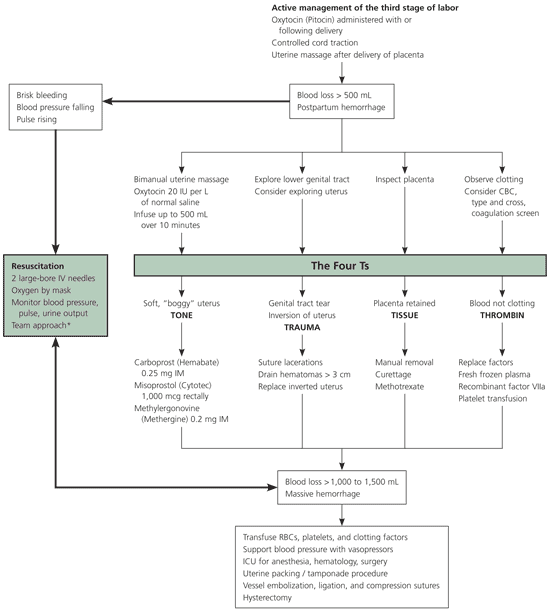
These are the 3 criteria for performing a perimortem cesarean.
What is a visually gravid female in cardiac arrest without ROSC in 4 minutes? (ACOG, AHA)
What are changes in vitals that are associated with acute blood loss anemia? (name at least 4)
Low UOP, hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea, decreased pulse pressure
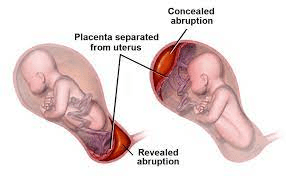
A sudden cause of uterine contractions and pain with or without vaginal bleeding that strikes patient's with hypertension, smoking, cocaine use, or trauma in the second half of pregnancy.
What is placental abruption?
After the fetal head delivers and turns towards the maternal thigh, the physician should apply traction in this direction.
What is gentle downward traction?
Close examination of the placenta may provide clues that this diagnosis is present in the patient with primary postpartum hemorrhage.
What is retained placenta?

These three medications are appropriate antihypertensives for the management of pre-eclampsia.
What is labetalol, hydralazine, or nifedipine?
What is the two biggest risks to the fetus caused by shoulder dystocia?
This entity can present much like placental abruption, with vaginal bleeding, discomfort, and fetal distress.
What is uterine rupture?
(Image from NEJM 2016 Bouet et al.)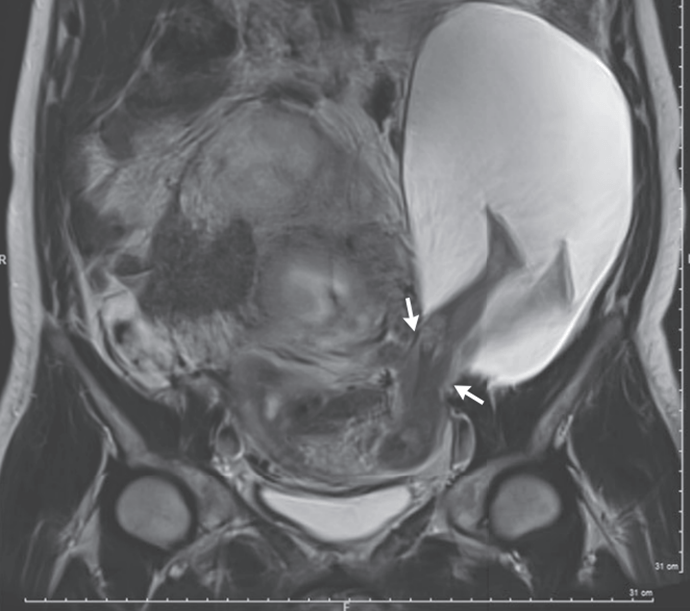
The maneuver to be utilized to deliver the head in a breech vaginal delivery.
What is the Mauriceau-Smellie-Veit maneuver?
A readily available adjunct that may be used to physically try to stop postpartum hemorrhage.
What is packing or the use of a catheter with balloon (Bakri / Cook balloon can hold 500 cc)?

This imaging modality must be considered in any postpartum patient presenting with severe headache.
What is CT head? - consider venogram to rule out venous thrombus