What are the three major phytoplankton growth strategies?
Survivalist: N:P>30
Bloomer: N:P <10
Generalist: N:P near redfield
Where are nutrients typically highest?
Upwelling zones and coast
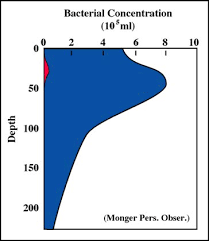
At what depth are bacteria largely found (in the highest concentration?
What is the Redfield Ratio?
The ratio of carbon to nitrogen to phosphorus
C:N:P
106:16:1
This strategy shows a lighter underside and darker topside of a nekton organism
Countershading
What is SVR and how does it affect phytoplankton?
Surface-to-Volume ratio
Large cells >SVR
Small cells <SVR (better in low-nutrient zones)
What is iron (Fe) fertilization, how is it affected, and why is it controversial?
Fe is a micronutrient. Phytoplankton need minuscule amounts for it to have a massive impact. Fe fertilization can play an important role in reducing additional impacts associated with climate change, but it would take over a century. Carbon removed from the atmosphere would have to sink deep into the ocean and remain there for a long time. Since some diatoms release toxins that can contribute to harmful algal blooms, this can pose a challenge with Fe fertilization. Additionally, Fe fertilization could shift where and how nutrients are distributed in the marine environment.
Whats a stromatolite?
Microbial mat
Does CNP vary? Does Redfield vary?
Redfield C:N:P = 106:16:1 [defined]
Does CNP vary? YES
Is this always 106:16:1? NO
Does Redfield vary? NO
Singular species of similar size and age use this strategy maintained by various cues
Schooling
Which species are silicious?
diatoms and radiolarians
DOM vs POM?
Dissolved vs particulate organic matter
DOM: mostly produced as waste by phyto
C-cycle, N-cycle, and CaCO3-cycle. What are they, and what are their implications?
Fill-in-the-blank figures for each.
Why does Redfield not always apply to diatoms?
Require silica
Masking silhouette with ventral photophores
Counterillumination
What is the trophic role of radiolarians?
Photosynthesizers and mixotrophs
KNOW FOR ALL MAJOR SPECIES
How might a STRONG wind influence surface nutrients?
Input of nutreints from the deep layer
What is NPP and how do you calculate it?
Net Primary Production
NPP = GPP - Respiration
What other nutrients might be limiting?
ANY! But particularly Iron or Silica
Two types of adaptations to maintain position and/or buoyancy.
Hydrodynamic and Hydrostatic
How does climate change affect phytoplankton?
Depends on the species! Have a general idea for them all.
Range shifts, slowed circulation, change of nutrient inputs
Describe nitrification
ammonium to nitrite (NO2-) and then nitrite to nitrate (NO3-)
Increases bioavailable nitrogen
(Know all the steps in this process and how they affect biology)
What is marine snow and what's its role?
Sinking aggregates of material, yummy food, but also export to sea floor (size dependent sinking)
Which nutrients are external "pollutants"?
N and P
This moves an organism through the expulsion of water, ink, waste, or eggs.
Jet Propulsion
Where are cyanobacteria dominant and why?
HNLC zones, can do nitrogen fixation (ie. diazotrophs)
KNOW ALL THE TYPES AND WHY! (Ppt 13)
How is nutrient limitation different in Atlantic vs Pacific?
North Pacific = Blue
North Atlantic = Red
What life strategies do viruses use?
Lytic kill-the-winner (Coral reefs)
Temperate (Algal dominate reefs)
What would a Redfield N:P lower than 16:1 mean for phytoplankton?
Not enough Nitrogen, rely on nitrogen fixation
Shift toward "bloomers"
Cyanobacteria
Having a small, local population makes you more susceptible to disease and decreases this
Resilience