In a patient with endometriosis who desires fertility, what type of management would you likely suggest?
Surgical management, but know:
It's controversial to excise endometriomas. A Cochrane review showed that cyst excision was associated with reduced rate of endometrioma recurrence, reduced symptom recurrence, and increased spontaneous pregnancy rates compared with ablative surgery.
There have also been reports that cystectomy could negatively impact ovarian reserve and function.
Schizophrenia is diagnosed based on two categories of symptoms: _____________ symptoms and _______________ symptoms.
1. Positive symptoms: bizarre or confused behavior with hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized speech.
2. Negative symptoms: blunted affect, alogia (i.e., reduction in quantity of words spoken), avolition (i.e., reduced goal-directed activity due to decreased motivation), asociality, and anhedonia
The prevalence of Barrett esophagus is highest among individuals who have this in their medical history.
Family History of Barrett's or esophageal adenocarcinoma (prevalence is 23%)
By comparison, the prevalence of Barrett Esophagus among those with isolated GERD is 3%
In management of PMR, the addition of methotrexate may be warranted in patients who are at high risk of relapse. This includes patients with any of these two risk factors
1. Female sex
2. High baseline ESR (don't ask how high- the article didn't say :-p )
The REAP-S V2 is a validated assessment of nutritional health that evaluates these 5 domains (name at least 3)
Dietary adequacy
Diet Pattern
Intake of calories
Exercise Habits
Motivation for nutrition change
Fill in the blank: the pathophysiologic process of endometriosis is dependent on the hormone ____________, which "promotes implantation of endometrial tissue through proliferative and antiapoptotic effects in endometrial cells and stimulates local and systemic inflammation."
Estrogen
What is the primary side effect of second-generation (atypical) antipsychotics?
A 25 year old Caucasian male patient in your office is newly diagnosed with GERD. His BMI is 35 and he smokes cigarettes and drinks 4 beers a night after working at JBS.
This presence of this risk factor confers the highest odds of him developing Barrett esophagus
Onset of GERD before age 30 (OR 15.1)
Other Risk factors:
- Caucasian (OR 6.03)
- Hiatal hernia (OR 3.94)
- GERD (OR 2.9)
- Male sex (OR 2.13)
- Central obesity (2.04)
- Tobacco (OR 1.42)
*Drinking etoh does NOT increase risk
Lower relapse rates and lower cumulative glucocorticoid dose are associated with the early addition of this therapy in the treatment of PMR.
Methotrexate (multiple RCTs)
When asking a patient about their nutrition insight and motivation, the clinician should evaluate for these types of barriers to access.
Social and economic barriers (i.e, food deserts, transportation, etc)
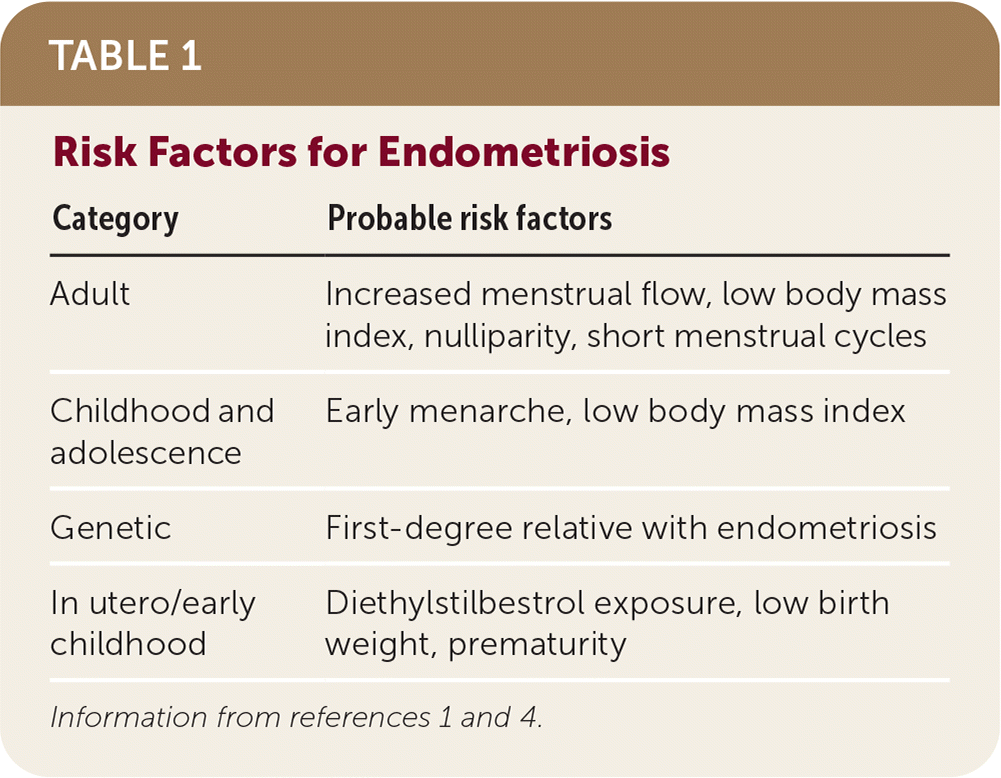
Name three risk factors for the development of endometriosis.
Second-generation antipsychotics have a lesser sided effect profile when compared to first-generation antipsychotics, especially when it comes to what constellation of symptoms?
Extrapyramidal symptoms
- Pseudoparkinsonism
- Akathisia
- Dystonia
- Tardive dyskinesia
A patient with a diagnosis of Barrett's who has undergone a second endoscopy confirming the absence of dysplasia on biopsy should wait for at least this duration of time before undergoing a follow up exam
Minimum 3 years (American Gastroenterological Association)
Regarding glucocorticoid treatment of giant cell arteritis, clinicians should plan for a taper over this period of time
1-5 years (individualized)
While evaluating a patient's dietary intake pattern, you might realize that most Americans do not adhere to these guidelines.
The USDA 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans
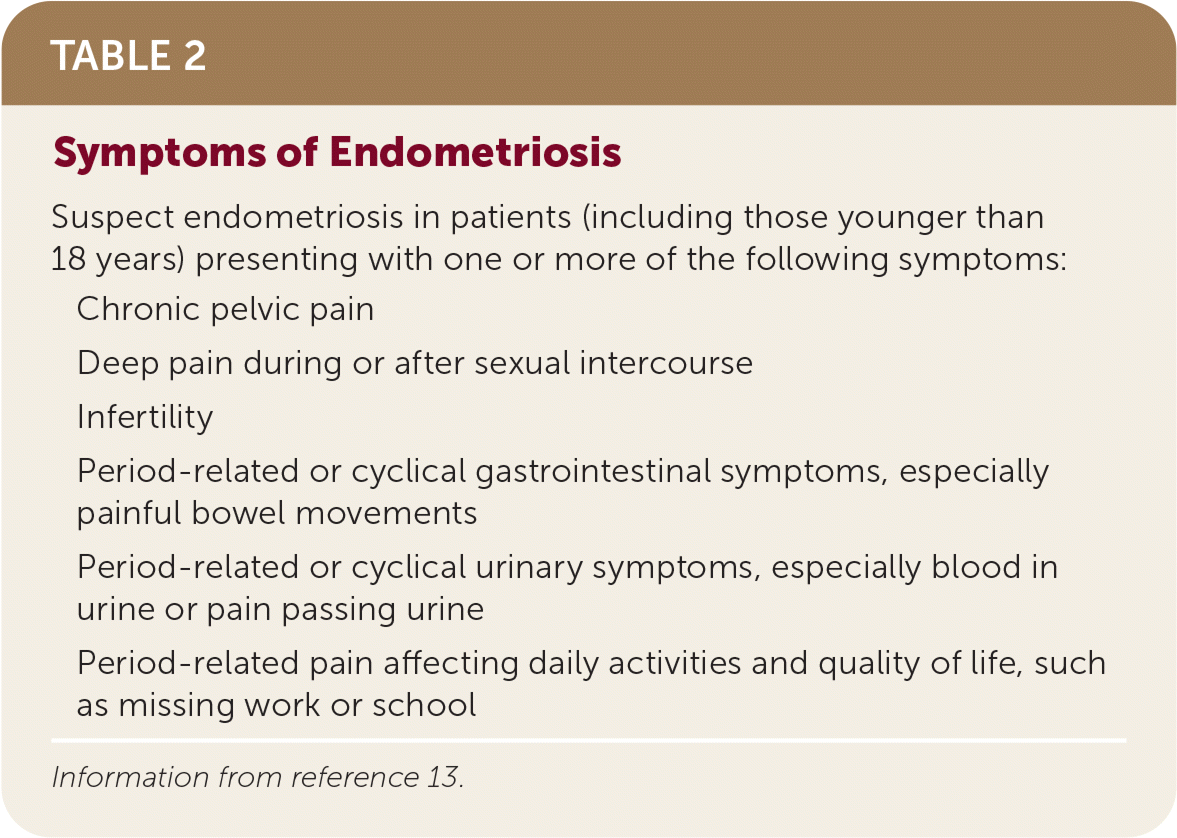
How do you diagnose endometriosis?
It's a clinical diagnosis! Suggestive findings are below. You should also do a pelvic exam.
Laparoscopy with biopsy is becoming less the standard for definitive diagnosis, and ACOG even recommends treating symptoms before to help improve quality of life.
Name the medication used to treat treatment-resistant schizophrenia and its major scary side effect.
Clozapine and severe neutropenia (agranulocytosis).
Based on expert opinion, selective screening for Barrett esophagus should be reserved for this defined group of patients
People with chronic/frequent GERD symptoms
Plus two additional risk factors, including age > 50
- No evidence that screening in patients with GERD improves mortality or quality of life
- Life expectancy should be taken into account with screening
For patients newly diagnosed with GCA, they should undergo noninvasive MRI/CT imaging to evaluate for this complication.
Large vessel involvement
Aortic aneurysm and TIA are associated with giant cell arteritis
Regarding the myriad of diets that patients may follow, this key factor is more closely associated with weight loss after one year than the diet pattern itself.
Adherence to the diet
*Energy restriction is also a key factor in successful weight loss
What is the first-line treatment for endometriosis?
Combined hormonal contraceptives, including oral pills, transdermal patches, and vaginal rings.
You can also utilize progestin-only methods in those who can't tolerate additional estrogen exposure.
You are the PCP for a patient with schizophrenia. What are some screenings and interventions you should do for this patient?
You should screen for cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome, and assist with smoking cessation.
FYI:
- 2-4X increased mortality rate for people with schizophrenia compared to those without
- Some factors that contribute to this are comorbid psychiatric disorders, substance use disorders, and higher rates of suicide
- Most deaths are related to higher rates of CV disease with comorbid renal disease, respiratory diseases, stroke, cancer, and thromboembolic events
[ Daily Double!! ]
In the presence of Barrett esophagus, medical therapy with these three medications should be considered for preventing progression
- Once daily PPI (twice daily if needed for symptoms).
- ASA 300-325 mg daily
- Statin (based on retrospective observational studies
* High dose PPI (40mg) performs better in preventing adenocarcinoma and high grade dysplasia NNT= 37 over 8 years. ΑSA tx has similar outcomes
To improve chances of successful remission, patients with newly diagnosed Giant Cell Arteritis should be treated with high dose oral steroids and this monoclonal tx.
Tocilizumab (IL-6 antagonist)
based on 2 high quality RCTs
For patients who are athletes, physicians should routinely screen them for this nutrient-reducing activity
Disordered eating behaviors