The physiological cause of late decelerations.
What is uteroplacental insufficiency?
A primary source of liability is?
What is Poor Communication?
Your monitor tracing shows fetal tachycardia. What should be your initial nursing intervention/assessment?
What is check a maternal temperature?
Identifies a fetus who is well oxygenated.
What is the primary value of EFM?
What 4 things are assessed when doing a contraction assessment.
What are frequency, intensity, duration, and resting tone/time?
The location where maternal-fetal oxygen transfer takes place.
What is the intervillous space?
What is a company's hierarchy of reporting relationships?
What is the Chain of Command?
The primary intervention for a fetal monitor tracing that suddenly shows frequent, early decelerations.
What is do nothing? (Vaginal exam may be performed to evaluate cervical progression.)
A pH of 7.21, PCO2 57, and PO2 18 are considered this.
What is normal acid base?
This medication relaxes uterine smooth muscle and increases maternal cardiac output.
What is Terbutaline?
Name 3 of the most common causes of uteroplacental insufficiency.
What is hypo/hypertension, diabetes, smoking, IUGR, tachysystole, AMA, IVF, postdates?
Name 2 strategies for improving communication among healthcare workers
What is SBAR, SBAR3 (SBARRR), CUS, I-SBAR-Q
Intervention to consider for repetitive variable decelerations, despite fluid bolus and position change.
What is an Amnioinfusion?
Identify this tracing.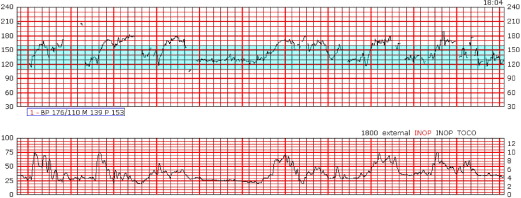
What is signal ambiguity?
The total pressure in mm Hg for all uterine contractions within a 10-minute time frame using an IUPC.
What are Montevideo units?
The primary pathophysiology associated with a true undulating pattern.
DOUBLE JEOPARDY
What is Fetal Anemia?
Common root causes in adverse outcomes include: (list two)
What is Communication Failure, Poor Teamwork, Systems Failures
These interventions would be indicated for a Category III tracing.
What is reposition the patient, administer oxygen, increase IV fluids, notify the provider, prepare for imminent delivery?
This is an extrinsic factor and common cause of variable decelerations.
What is Cord Compression?
This shunt allows well-oxygenated blood to directly enter the fetal heart.
What is the ductus venosus?
Cord blood interpretation:
pH: 7.01
Co2: 80
Po2: 22
BE: -18
What is mixed acidosis?
Name 3 teamwork practices that enhance communication.
What are briefings, huddles, debriefings, multidisciplinary rounds, multidisciplinary fetal heart monitoring education?
Supportive measures that may decrease maternal catecholamine release.
What are maintain a calm environment, minimizing maternal pain, anxiety, and fear, and assist with coping with labor?
This is an intrinsic physiologic response by the fetus in response to a variable deceleration.
What is stimulation of fetal baroreceptors?
34 week patient presents to triage post MVA. What is the underlying physiology for this tracing? 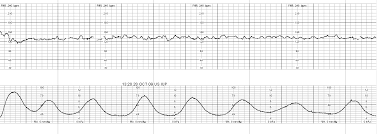
What is a placental abruption?