What is the annual stroke risk beyond which anticoagulation for AF is a class 1 indication?
>2%
Dx?
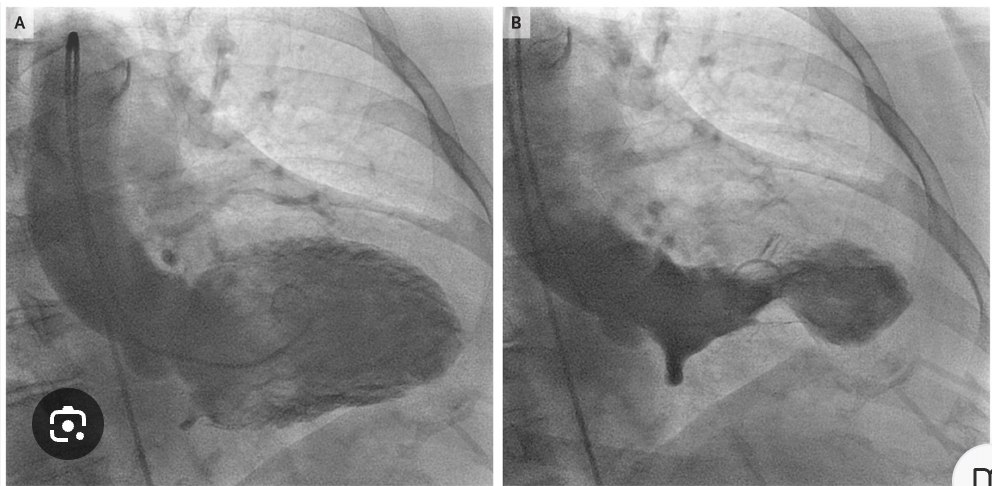
Stress/Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
A 25/M is diagnosed with HCM. His LVOT gradient is 40. NBS?

DX
Subaortic membrane
Define recurrent pericarditis
New signs and symptoms of pericardial inflammation after a symptom-free interval of 4 to 6 weeks
Complete coding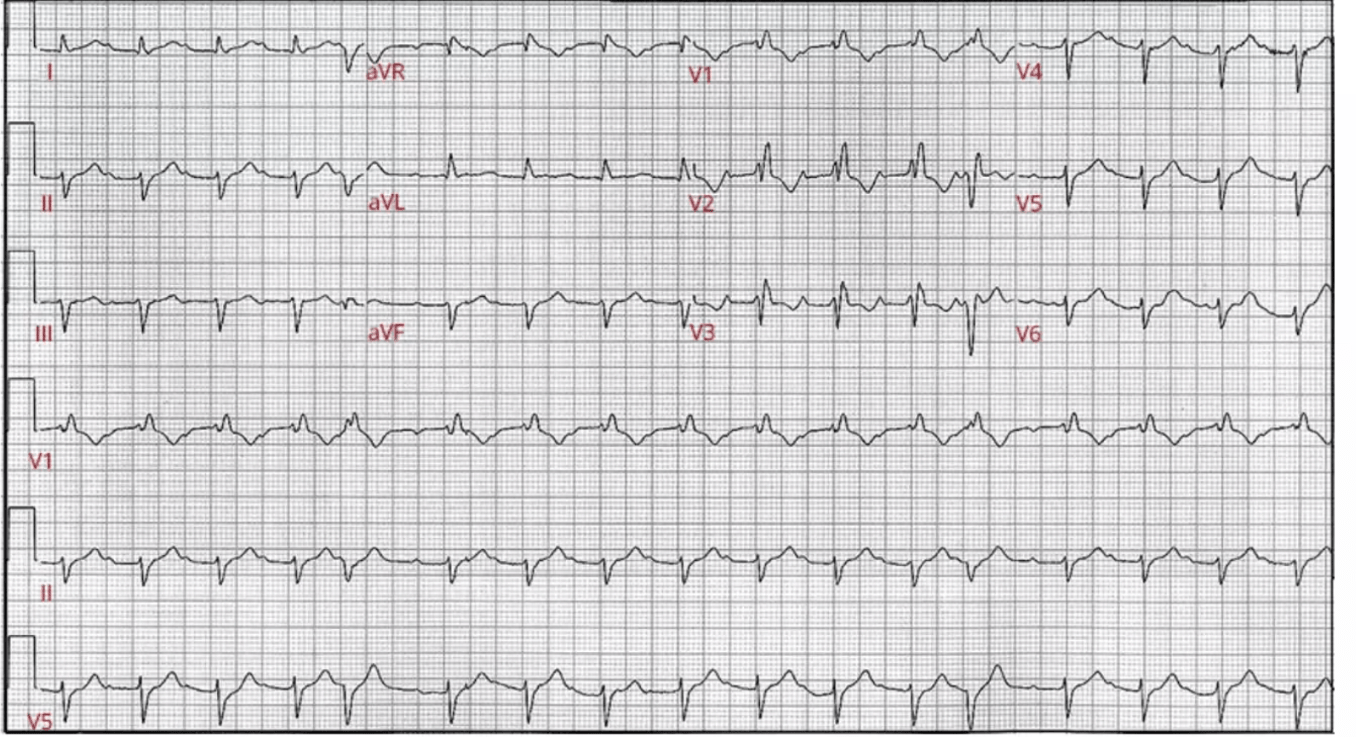
Sinus rhythm
1st degree AVB
LAFB
RBBB
PVC
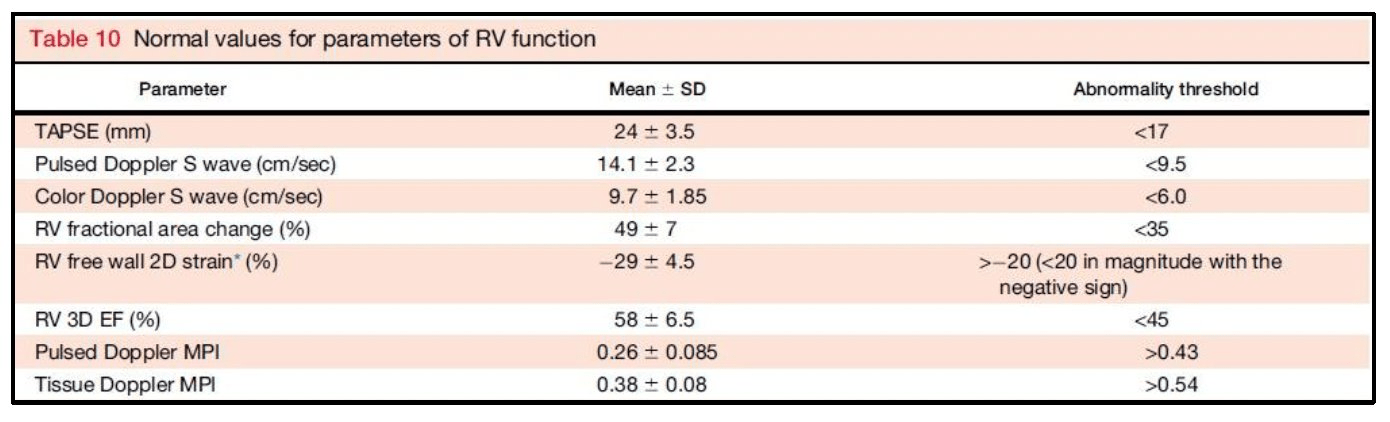
Name any 3 markers of RV function with their abnormal values
What is the mechanism of action of disopyramide in HCM?
2.Class 1A anti-arrythmics>prevention and treatment of AF
3. Vagolytic action-decreases HR
Give any 3 indications for treatment in subaortic membrane
ALL symptomatic patients
Asymptomatic patients with peak gradient ≥50 mm Hg and/or mean gradient ≥30 mm Hg
Patients with peak gradient <50 mm Hg but with evidence of LV dysfunction
Patients with progressive aortic insufficiency
Which drug was used in The AIRTRIP trial of patients with recurrent pericarditis resistant to colchicine and dependent on corticosteroid therapy?
Anakinra
Code this
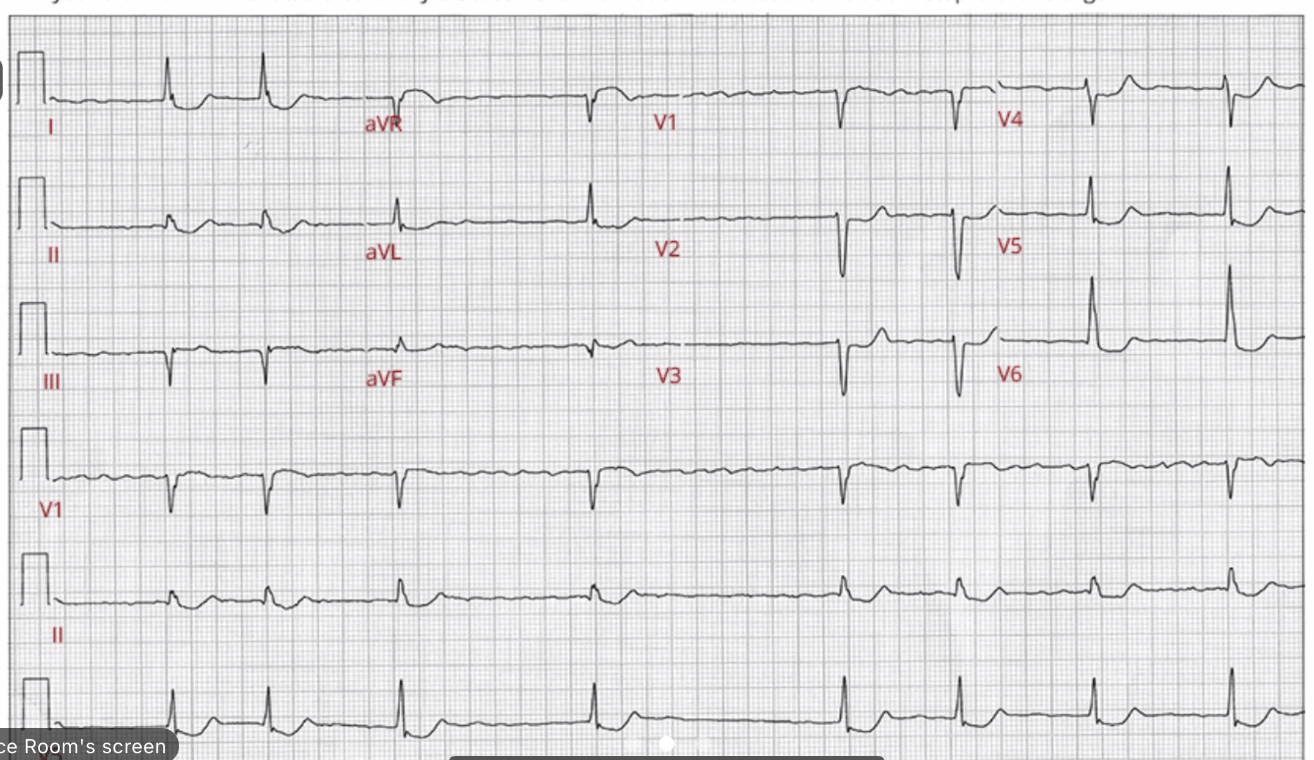
AF with slow ventricular response
Digoxin effect
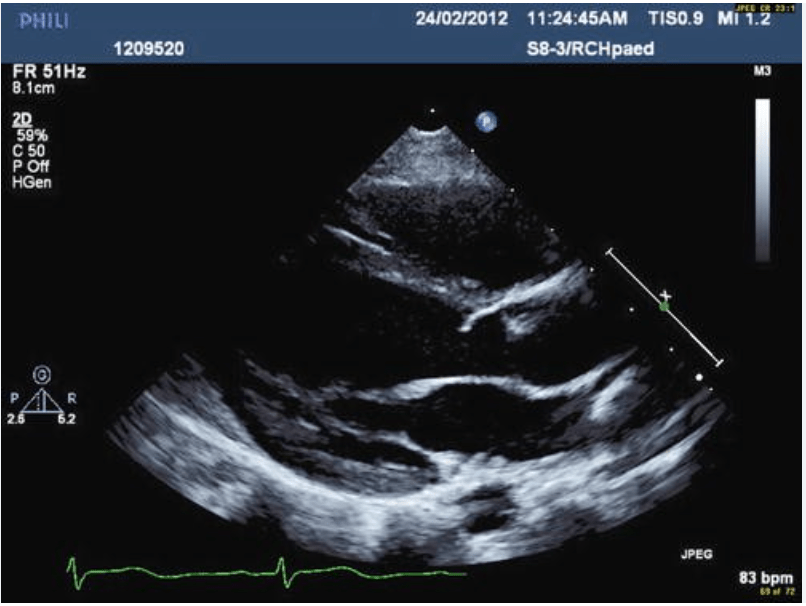
Pulmonary doppler. Findings?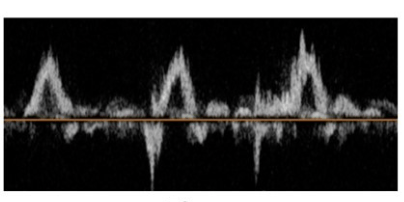
Blunted or Reversed S-wave:
- Normally, the S-wave is positive, indicating forward flow from the pulmonary veins into the left atrium during ventricular systole.
- In severe MR, the S-wave becomes blunted, markedly reduced, or even reversed.
- This is due to the significant regurgitant flow from the left ventricle into the left atrium during systole, which increases left atrial pressure and impedes forward flow from the pulmonary veins.
Increased D-wave:
- The D-wave, which represents forward flow during ventricular diastole, may be increased or dominant in severe MR.
- This is because, during diastole, the regurgitant volume is no longer opposing the pulmonary venous inflow, so the diastolic wave may appear more prominent relative to the systolic wave.
In HCM, Name any 3 advantages of surgical myectomy over alcohol septal ablation.
1.Superior reduction in gradients
2.Less need for re-do
3.Lower rates of PPM/CHB
What is the syndrome associated with this
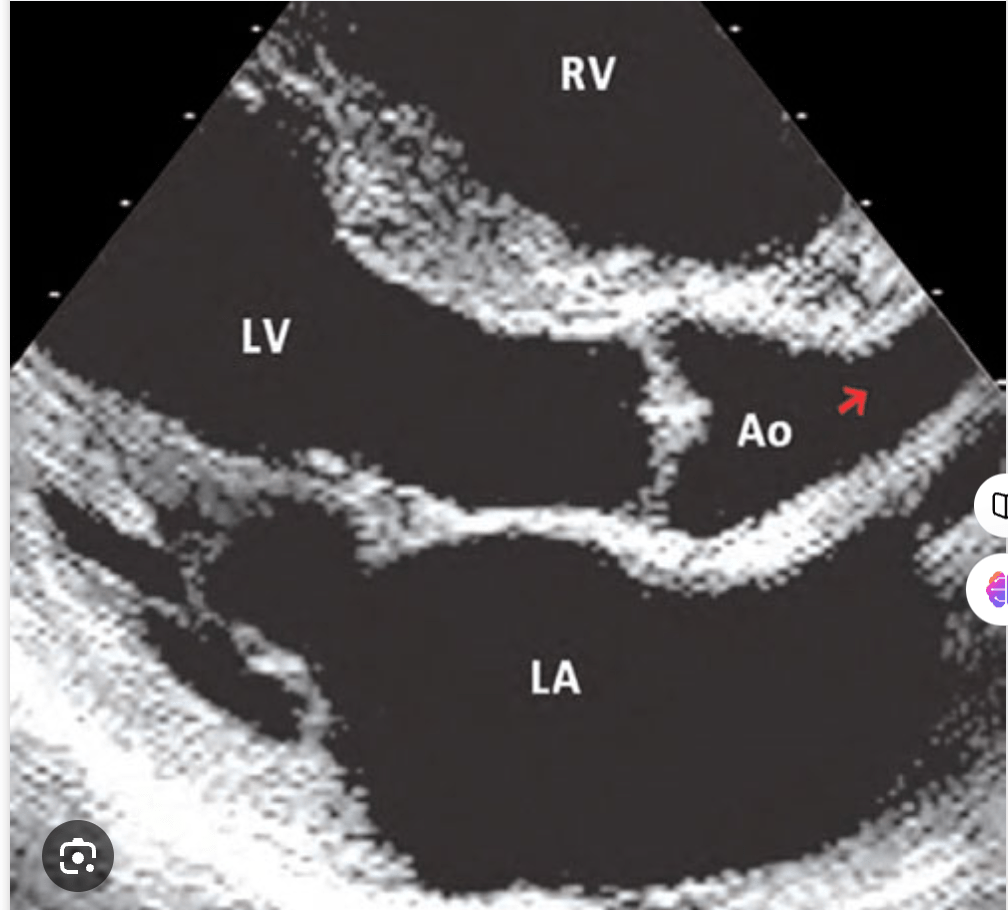
Supravalvular aortic stenosis-william syndrome
Finding and diagnosis?
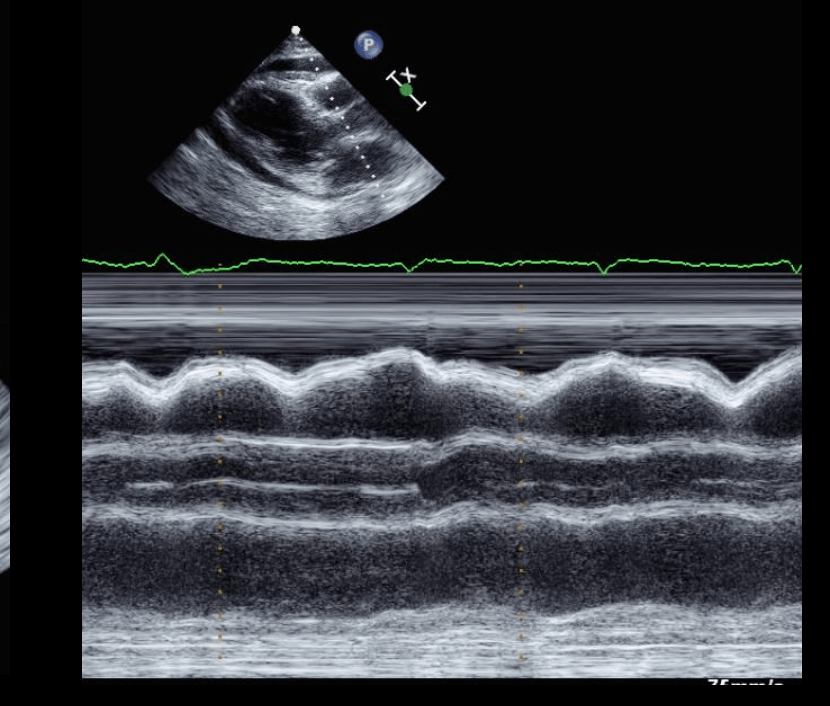
RV diastolic collapse/cardiac tamponade
75/F with this EKG. Full coding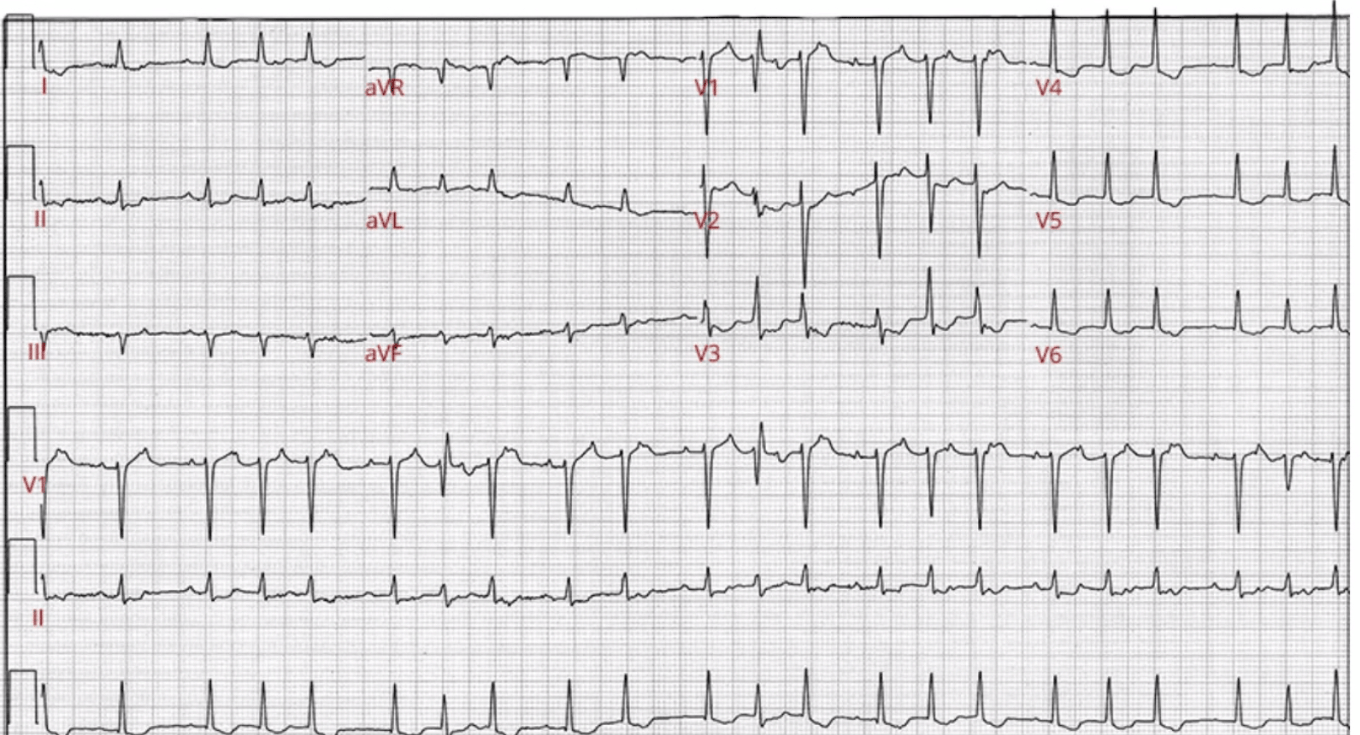
Atrial tachycardia (Atrial rate is 166)
Mobitz type 1 AVB
Non-specific ST-T changes
APC with aberrancy (Ashman)
What is the most common risk factor for this condition?
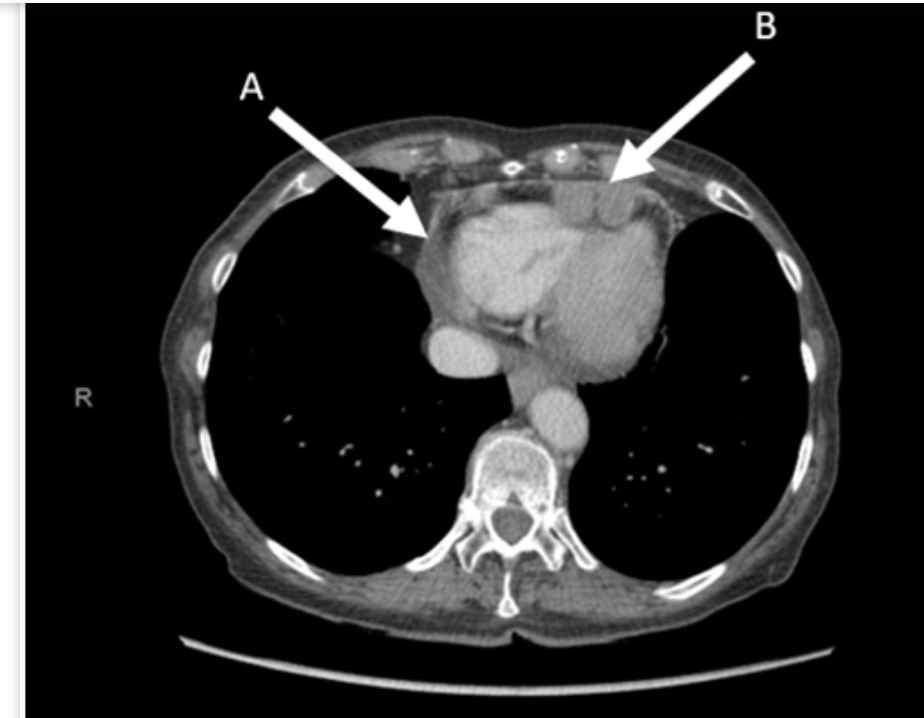
Mesothelioma-Asbestos
What were the inclusion criteria of the explorer trial for HCM?
Inclusion Criteria for EXPLORER-HCM Trial:
Age:
- ≥18 years.
Diagnosis:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) with LV hypertrophy unexplained by other cardiac or systemic conditions.
- Obstructive HCM (oHCM) was defined by a resting or provoked LVOT gradient of ≥50 mmHg.
Symptoms:
- Patients had to be symptomatic, with at least NYHA Class II or III symptoms, indicating mild to moderate heart failure related to HCM.
Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF):
- LVEF ≥55%, indicating preserved systolic function.
Background Therapy:
- Patients were permitted to be on a stable dose of background therapy, such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers, provided the dose had been stable for at least 30 days prior to randomization.
- Patients could also be on disopyramide, provided it was stable, although very few were on this drug.
Heart Rate:
- A resting heart rate of ≥50 bpm to ensure safety during treatment with mavacamten, as the drug can reduce contractility.
Explain the 4 images
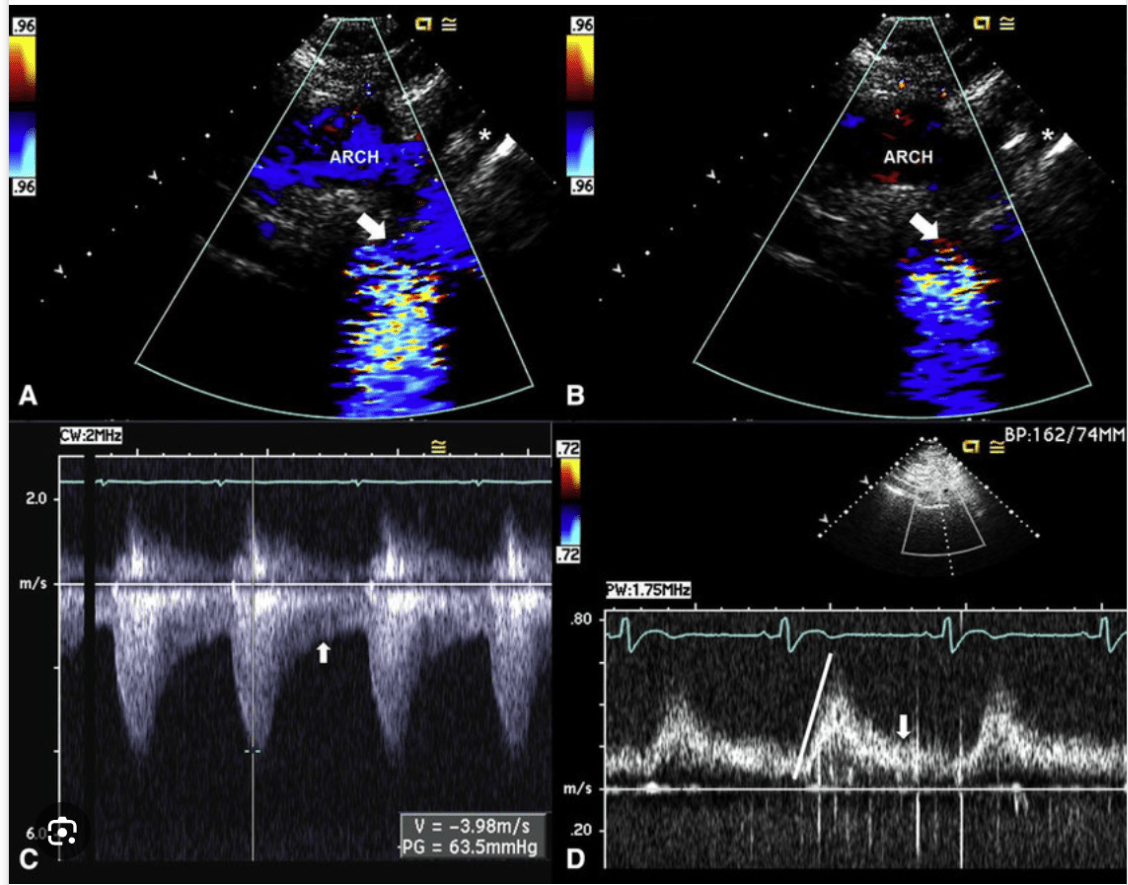
Transthoracic assessment for aortic coarctation. A, Echocardiogram of a 31-year-old woman with BAV and severe aortic coarctation. Suprasternal systolic still frame shows laminar Doppler flow through the proximal portion of the arch (''ARCH'') before becoming turbulent flow across a tight coarctation (arrow) just distal to the left subclavian (asterisk). B, Suprasternal diastolic still frame shows no Doppler flow through the proximal portion of the arch but persistent diastolic turbulent flow across the coarctation (arrow) just distal to the left subclavian (asterisk). C, Continuous-wave Doppler signal across the coarctation shows a systolic (measurement) peak gradient of 64 mm Hg through the coarctation, with persistent flow in diastole (arrow). D, Pulsed-wave Doppler signal of the abdominal aorta shows a delayed peaking of the systolic signal (line) with prominent persistent flow in diastole (arrow), pathognomonic of coarctation.
Which 2 diseases gives rise to this finding?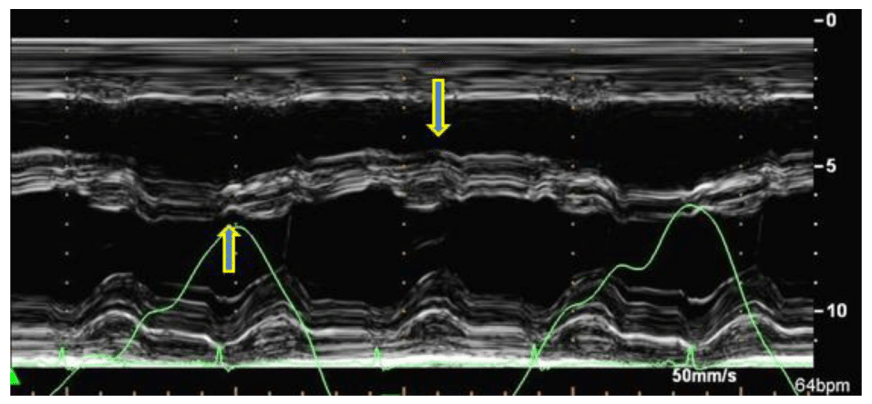
Ventricular interdependence-constrictive pericarditis and cardiac tamponade