This principle involves bundling data and methods that operate on the data within a single unit, keeping the internal representation hidden from the outside world.
What is Encapsulation?
This is the blueprint or template from which objects are created.
What is a Class?
This relationship describes when one class "has a" reference to another class, forming a part-whole relationship.
What is Composition?
This term describes a block of code within a class that performs a specific task and may return a value.
What is a Method or Function?
This example of OOP could involve defining different types of vehicles (cars, motorcycles, etc.) as subclasses of a general "Vehicle" class.
What is modeling a Transportation System?
A woman is born in 2020, but dies in 1995. How can this be?
What is, she was born in 2020 BC?
This allows new classes to obtain properties and behaviors from existing classes, promoting code reusability.
What is Inheritance?
This is an instance of a class, representing a real-world entity with state and behavior.
What is an Object?
This type of inheritance is imposed by Java to avoid complex ambiguity.
What is Single Inheritance?
In Java, this keyword refers to the current object within a method or constructor.
What is "this"?
In a library management system, this OOP principle allows you to treat different types of books (fiction, non-fiction) as the same general type of "Book" object.
What is Polymorphism?
Among timepieces, sundials have the fewest moving parts. Which timepiece has the most moving parts?
What is an hourglass?
This principle allows objects of different classes to be treated as objects of a common type, often implemented through method overloading and overriding.
What is Polymorphism?
This term describes the data that an object holds, representing its current condition.
What is State?
In Java, this keyword is used to indicate that a class is establishing a contract with an interface.
What is "implements"?
This type of error occurs when code breaks while running, like attempting to divide by zero.
What is a Runtime error?
If you have a class representing a "Dog" and it acquires common attributes and behaviors from a "Mammal" class, you're using this OOP principle.
What is Inheritance?
A family has two parents and six sons. Each of the sons has one sister. How many people are in the family?
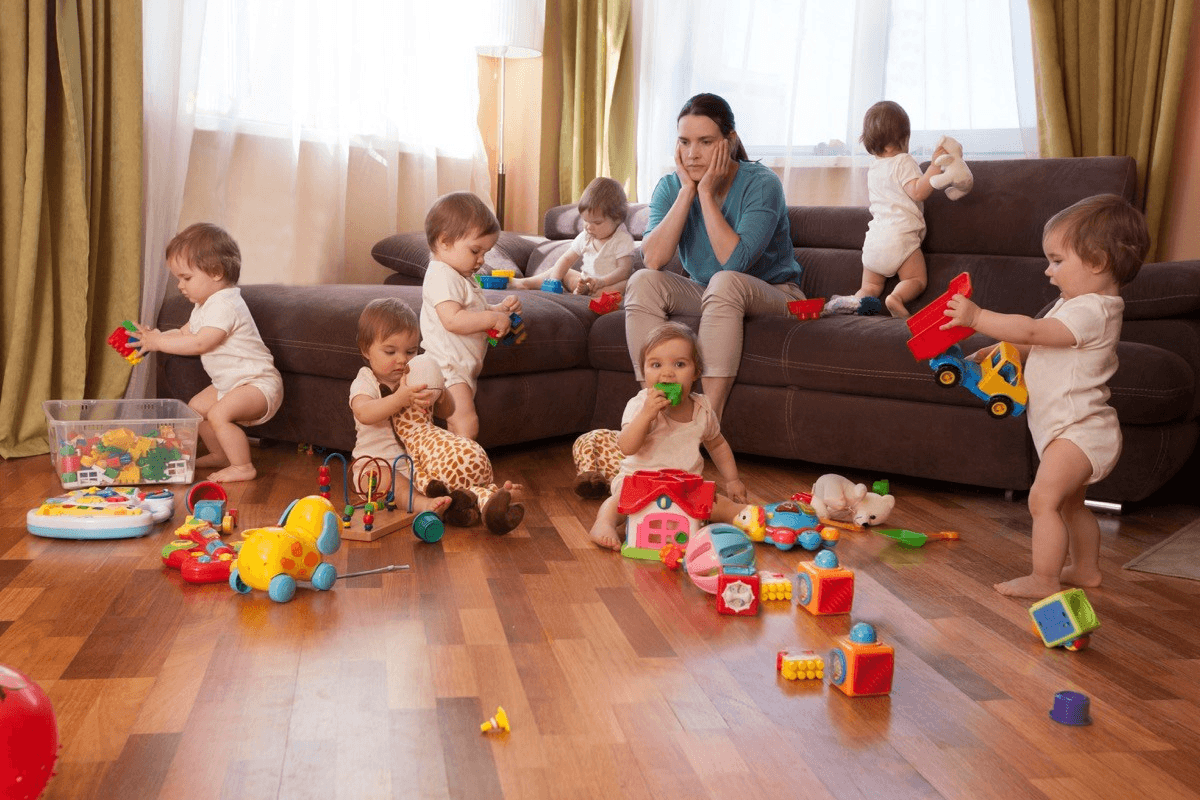

What is nine? Two parents, six sons, and one daughter!
This involves hiding the complex implementation details and only exposing the necessary features to the user, often through interfaces or abstract classes.
What is Abstraction?
This term describes the actions an object can perform, typically implemented through methods.
What is Behavior?
This is a UML term indicating a general connection between two objects, without specifying a specific type of connection.
What is an Association?
This refers to the practice of giving multiple methods the same name, but with different parameter lists, within the same class.
What is Method Overloading?
In a banking system, hiding the complex details of how a transaction is processed and only providing a simple "deposit" or "withdraw" method utilizes this OOP principle.
What is Abstraction?
Which figure should be placed in the empty triangle?
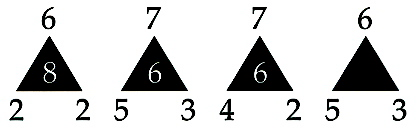
What is 3?
These four principles are often referred to as the foundation of Object-Oriented Programming.
What are Inheritance, Polymorphism, Encapsulation, and Abstraction?
This refers to the uniqueness that distinguishes one object from another, even if they have the same state and behavior.
What is Identity?
This is the process of defining specialized behaviors for a method inherited from a parent class.
What is Overriding?
The water level in a reservoir is low, but doubles every day. It takes 60 days to fill the reservoir. How long does it take the reservoir to become half full?
What is 59 days?
If you have a "Restaurant" class that contains a "Table" object, you are demonstrating this type of relationship.
What is Composition (or "has a" relationship)?
In what number parking spot is the car parked?

What is 87?