fatty acids, triglycerides, butter/oil are all types of this macromolecule group.
lipids
uses energy from the sunlight to make energy-rich food molecules by photosynthesis
Chloroplast
Small mini-organelle in the cell where PROTEINS are synthesized
ribosomes
The macromolecule shown below is: 
What is a lipid (triglyceride)?
short “hair-like” structures that help some cells MOVE
Cilia
Poly means _____
What is many/multiple?
a network of protein filaments to help the cell maintain its shape and help the cell with movement
Cytoskeleton
a thin flexible outer layer that protects and surrounds the cell and REGULATES what enters and leaves the cell
Cell membrane
The monomer shown below is:
What is an amino acid?
a tiny hole in the membrane that surrounds the nucleus of a cell and allows material to move in and out of the nucleus “mini doorway”
Nuclear pore
Lipids have longer lasting energy than Carbohydrates. (True or False)
true
ASE means
Enzymes which are proteins
A strong layer around the cell membrane in plants, algae, and some bacteria
Cell wall
The monomer shown below is: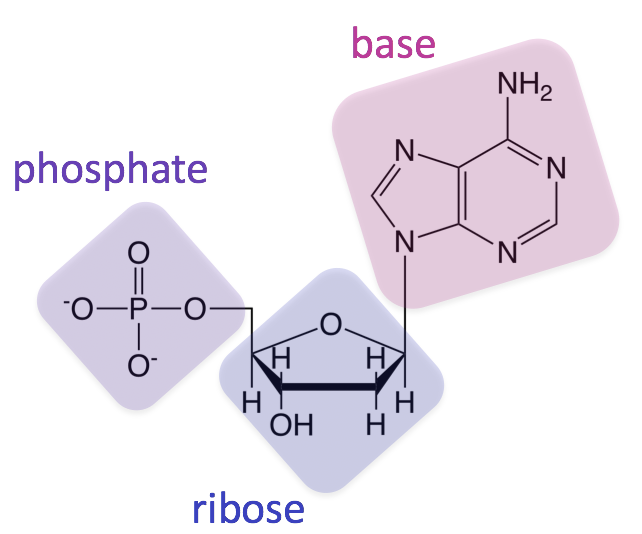
What is a nucleotide, DNA?
a “whip-like” structure that helps some cells MOVE
Flagellum
Sugars end in what three letters?
OSE
filled with digestive enzymes that surround and break down worn out cell parts
Lysosome
Control center inside a cell contains the cell’s genetic DNA material
Nucleus
C6H12O6 is its chemical formula
monosaccharide
enzymes attach carbohydrates and lipids to proteins and ship them to different parts of the cell.
Golgi Apparatus
Glycerol is needed to build this macromolecule.
What is a lipid?
Name for a carbohydrate that has many monomers.
polysaccharide
Small region in the nucleus where rRNA is made.
Nucleolus
The structure below is an example of this.
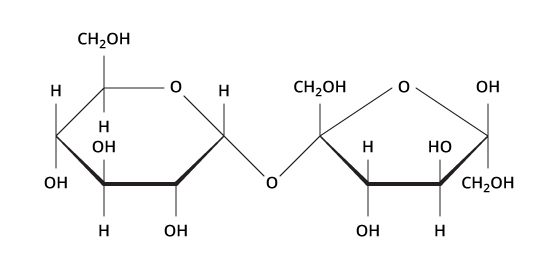
What is a carbohydrate?
releases energy and produces ATP from molecules of glucose
Mitochondria