After induction, patient develops severe hypotension, skin blanching, and increased inspiratory airway pressures noted.
What is Anaphylaxis?
Intraoperatively, ST segment elevation, irregular rhythm, tachycardia, and hypotension. Name the pathology.
What is Myocardial Ischemia?
Audible O2 failure alarm sounds. Inappropriately low FiO2 value on gas analyzer. Flow meter reads abnormally low.
What is oxygen failure?
This class of drugs is the most common cause of anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions in the OR.
What is non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockers (rocuronium?)
Rapid response is called to Endo Room 1. You find a sedated patient with severe bradycardia. You push a medication.
What is atropine?
Upon induction, increased EtCO2 seen on monitor, with tachycardia, respiratory rate, hyperthermia. Masseter spasm and associated muscle rigidity noted. This medication is administered.
What is Dantrolene or Ryanodex?
Your patient has sudden hypotension and the ECG below.
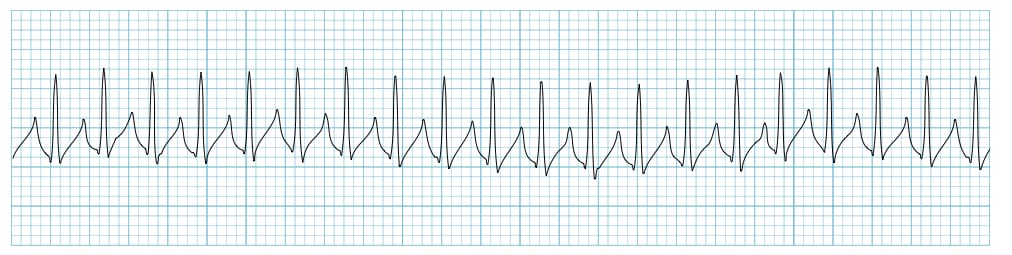
What is SVT?
Your patient is undergoing tonsillectomy. Suddenly you hear a pop and smoke fills your nostrils. Describe your next steps.
What is remove ETT?
Increasing pressure on this nerve will result in elevated parasympathetic activity and may resolve stable SVT.
What is vagus nerve?
Your patient is suddenly hypotensive and SpO2 is flat. However, there is a strong rectal pulse. Name the problem & your next step.
What is hypotension & vasopressors?
You’re starting an induction and subsequently have two failed attempts of laryngoscopy. Suddenly you can’t ventilate with the mask. You ask for these items.
What is a scalpel, bougie, and a lubed 6.0 ETT?
On abdomen insufflation your patient is hypotensive and ECG suddenly changes (below). You're immediate reaction is to:
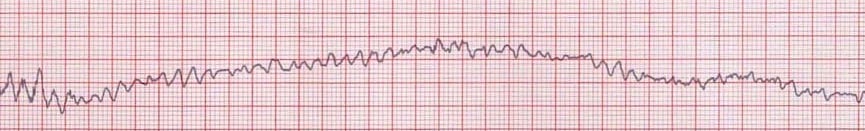
Patient has notable wheezing and up-sloping waveform. Increased EtCO2 noted on monitor. Increased peak airway pressures noted to be 40. Name the pathology & medication you push.
What is bronchospasm & propofol?
This medication may be used to quickly address demand ischemia intraopertively.
What is esmolol?
You are able to intubate but not ventilate. The bag won't re-inflate, FiO2 shows <21% O2, and the patient is desaturating. Describe your next steps.
What is connect to ambu & back-up O2 tank?
Patient with sudden increase in peak inspiratory pressures. Tachycardia and hypotension. Decreased breath sounds on left side. You place a needle here.
What is the 4-5th intercostal space between anterior and mid-axillary line?
Patient in PACU has dyspnea, dizziness, right upper abdominal discomfort. Patient’s O2 sat drops to low 80s. Hypotension noted on monitor with MAP 50. ECG shows right bundle branch block and right axis deviation. Name the pathology & best first choice vasopressor.
What is right heart failure & epinephrine?
This is most likely seen on lung ultrasound in a patient with a pneumothorax.
What is lack of lung sliding (or lung point)?
The code blue button in the OR is located here.
What is behind the nursing computer?
You heard the surgeon mutter something about bleeding as they left the room. Your patient is suddenly tachycardic & profoundly hypotensive. Describe your priorities & next steps.
What is temporize with fluids & blood?
Heme is noted after injection of bupivacaine. Patient immediately begins to seize and is unstable. You bolus a medication. Name the medication & dose.
What is 100 mL of intralipid over 2-3 min?
You see a petechial rash, profound hypotension, and new tachycardia during a hip arthroplasty in a 91 yo F. Name the pathology & next steps.
What is cement embolism & supportive care?
Your morbidly obese patient is breathing 900 mL on manual w/ an LMA in place. You remove the LMA and the patient is now completely obstructed. Name the most likely pathology to be seen in PACU (other than hypoxemia) if the obstruction is not removed immediately.
What is negative pressure pulmonary edema?
During a take-back for post c-section hemorrhage you are transfusing the patient. The patient becomes hyperthermic, tachycardic, hypotensive, and appears you lost the IV. Name the most likely pathology.
What is hemolytic transfusion reaction/DIC?
During CVC exchange under MAC the patient suddenly becomes extremely tachycardic with loss of p-waves and hypotensive. Name the medication and initial dosing.
What is adenosine and 6 mg?