Jaw Bone & Facies
Jaw Bone & Facies
Periodontium and Gingiva Cont.
Oral Mucosa
disorder that can cause bilateral facial swelling, interrupt tooth development/eruption, and radiographically presented as "soap-bubble" in the ascending ramus & molar/premolar area (mandible) or tuberositiy (maxilla) ?
what is cherubism ?
developmental bony growths present on the hard palate and/or the lingual aspect of the mandible.
what is torus palatinus ? what is torus mandibularis?
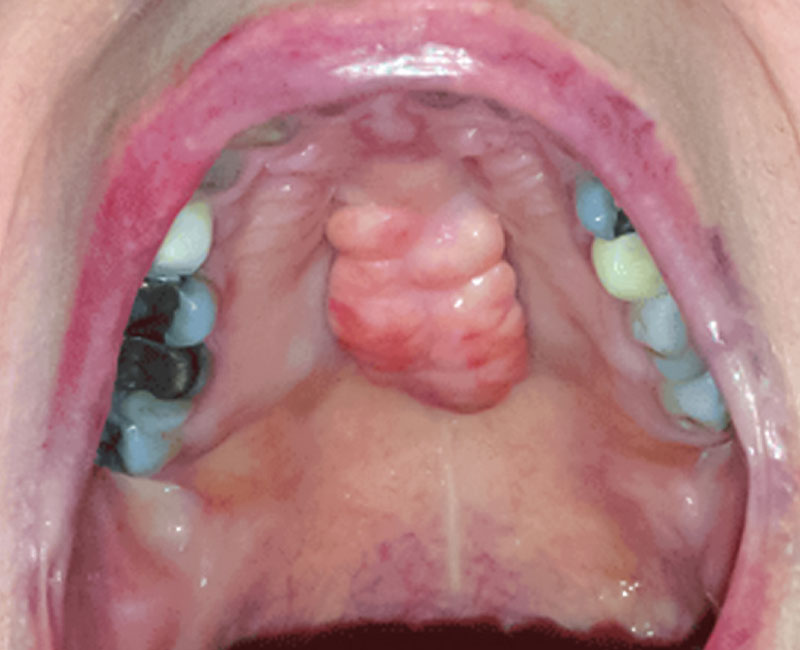
gingival hypertrophy that generally develops early in life and may cause dense connective tissue that overgrow teeth.
what is gingival fibromatosis ?
genetically inherited disorder consisting of both Schwann cells AND perineural blasts. Patients clinically present with multiple neurofibromas on the body and oral cavity. Oral manifestions typically are located on the tongue.
What is Von Recklinghausen's disease? (Neurofibroma)
Hyperpituitarism is most often caused by a benign tumor called a pituitary adenoma, and is most commonly treated by this method.
Pituitary gland surgery/ Transsphenoidal surgery
patient clinically presents with a small face, prominent enlargement of (occipital, parietal, frontal bones), long/narrow neck, and hypoplasia of clavicles. These individuals present w/ supernumerary teeth.
what is cleidocranial dysplasia?
disorder characterized by a cyclic decrease in the number of circulation cyclic neutrophils.
what is cyclic neutropenia?
treatment of gingival fibromitosis
what is surgical removal of tissue? what is proper hygiene care to reduce the risk of secondary inflammation and infection in deep pseudopockets?
A Cleft lip and cleft lip/palate requires a multidisciplinary team consisting of these specialties.
Pediatrician, Oral and Maxillofacial surgeon, pedodontist, orthodontist, and speech pathologist.
Disorder defined by enlargement in the face, hand, feet, lips, and tongue in adults due to an increase of growth hormone. Name the gland affected and the disorder.
What is the pituitary gland and Acromegaly?
autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Disease presents with multiple osteomas, odontomas, and/or intestinal polyps that may become malignant at the age of 30 or above.

What is Gardener Syndrome?
clinical radiopraphic presentation AND treatment of Papillon Lefevre Syndrome.
what is the radiographic presentation of marked alveolar bone resorption with vertical pockets and tooth loss in the same sequence as they were erupted? What is no treatment?
oral manifestations of gingival fibromatosis
what is gingival hypertrophy that overgrows teeth, firm tissue w/ a granular corrugated surface, pale gingiva, and lip protrusion?
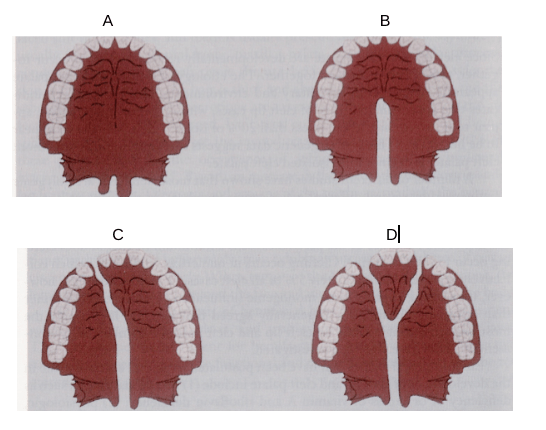
A. Cleft Uvula
B. Incomplete Cleft Palate
C. Unilateral Cleft Palate and Cleft Lip
D. Bilateral Cleft Palate and Cleft Lip
An excess in thyroid hormone increases the metabolism of all tissues. It’s main cause is an ___ disease identified by this key sign of the eyes. Name the disease, disease type and key feature.
Graves Disease, an autoimmune disease associated with exophthalmos/bulging eyes
autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Clinically presents w/ a hypoplastic nose, hypoplastic malar bones with hypoplasia or absence of zygomatic process. Patients may also have misplaced ears, receding chin, clefting of lower eyelids and/or deafness.

what is mandibulofacial dysplasia?
Disorder presenting with decreased neutrophils. Patients clinically present severe destruction of periodontal tissues, loss of both primary and permanent teeth, and red scaly keratosis of palms of hands and soles of feet.
what is Papillon Lefevre Syndrome ?
abnormal pattern growth of cells (cells are mildly atypical), not able able to metastatize, and considered "low grade" dysplasia.
what is mild dysplasia?
Numerous scattered red macules commonly on tongue and buccal mucosa. This Syndrome can also cause _______.
What is Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia/ Osler-Rendu-Parkes Weber Syndrome?
What are nose bleeds/epistaxis?
A patient with history of hyperthyroidism comes into the office for a cleaning. During treatment they start suddenly convulsing, experiencing tachycardia, and have a very high fever.
What is a Thyroid Storm?
inheritance pattern is autosomal dominant. Disease clinically presents with increased distance between eyes - basal cell carcinomas over the (eyes, cheeks, neck, arms, etc.). Orally presents w/ multiple odontokeratocysts (may develop as early as 5 or 6 years old)
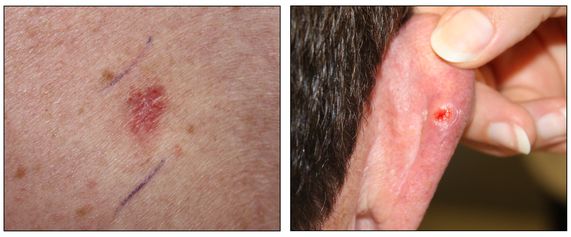
what is Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome?
the amount of days in cyclic intervals for cyclic neutropenia. The amount of days for a neutropenia episode. Best time to treat cyclic neutropenia.
what is the cyclic interval of 21-27 days? what is the neutropenia episode of 2-3 days? When is neutrophil count normal?
Give a differential diagnosis:
Inherited Gingival Fibromatosis
Myxedema
Gingival hyperplasia due to chronic gingivitis
Pregnancy induced gingivitis
Drug induced gingival hyperplasia (Phenytoin, Cyclosporine, CCBs)
Gingival hyperplasia due to Leukemia
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia is treated by either of these two options. HHT has this risk for the hygienist.
What is None or electrocautery?
What is Gingival bleeding?
Decreased output of thyroid hormone can lead to these two diseases. Both diseases are characterized by the age they effect and their clinical signs. (Name the two diseases, who they affect, signs/symptoms of each, and treatment of both)
What is Cretinism; children; delayed mental and physical development, delayed dental eruption and exfoliation; Thyroid hormone replacement therapy/ Levothyroxine
What is Myxedema; Older children/adults; myxedematous swelling in soft tissues (non-pitting edema, thickened lips, macroglossia); Thyroid hormone replacement therapy/ Levothyroxine