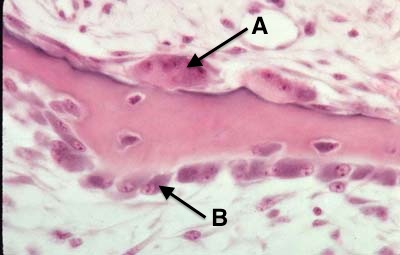
What are Osteocytes?
At this stage chondroblasts invade the haematoma
What is stage 2 - Fibrocartilaginous (Soft) Callus Formation?
What is osteopenia?
This starts the formation of Endochondral Ossification.
What are Mesenchymal Stem Cells?
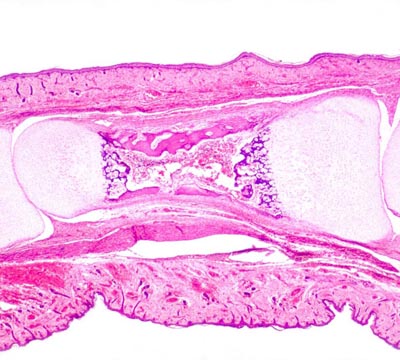 This slide depicts...
This slide depicts...
What is Endochondral Ossification?
This type of exercise uses force to make bones work harder.
What are weight-bearing exercises?
This disease is due to a deficiency.
What is Osteomalacia?
This hormone increases blood calcium levels by stimulating bone resorption and kidney reabsorption.
Parathyroid Hormone
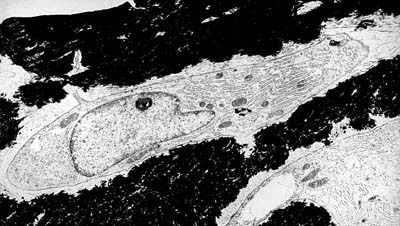 What is the precursor of this cell?
What is the precursor of this cell?
What is an Osteoblast?
This is the first phase of bone fracture healing.
What is hematoma formation?
A decrease in this is characteristic of both osteopenia and osteoporosis, and can be spotted on TEM. (A quantity that can be calculated - and measured)
What is Bone Mass Density?
This hormone is the main regulator of phosphates.
What is FGF-23?
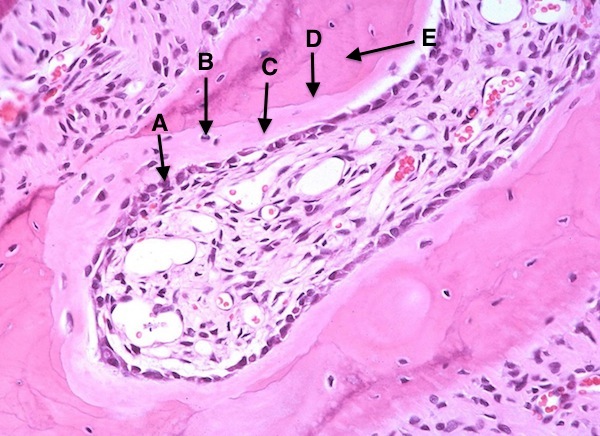 A
A
What is an Osteoblast?
The idea of converting cartilage to bone is found in what other important aspect of bones (name the process)
What is Endochondral Ossification?
Compared to compact bone, this structure in osteoporotic bone is thinner and more porous.
What is trabecular bone?
The type of bone, based on what was presented, likely to result from Endochondral Ossification
What is a long bone?