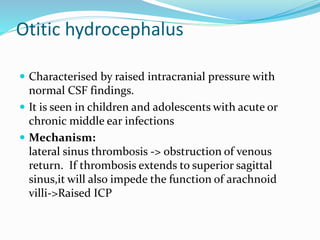
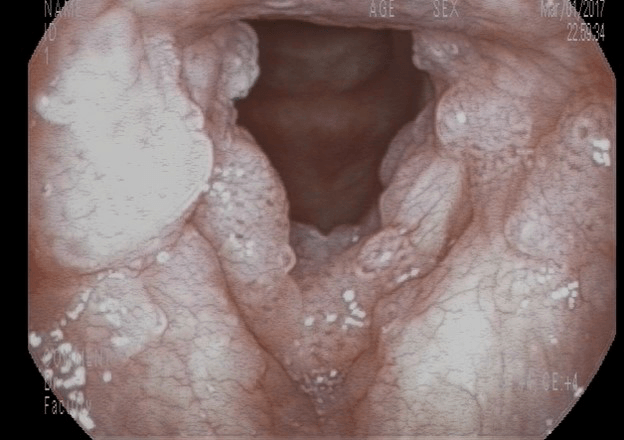
A 30 y/o M patient presents with progressive shortness of breath and chronic dysphonia. On videostroboscopy, the following findings are observed. The patient is diagnosed with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. What two subtypes of HPV are associated with this condition?
What is HPV 6 and 11?
What testing modality is required to establish diagnosis of narcolepsy?
What is multiple sleep latency test?
What is the most commonly affected structure in BPPV?
What is the posterior semicircular canal?
Most common affected SCC is the posterior canal followed by the horizontal and very rarely the superior SCC.
A 65 y/o woman presents to your clinic due to concerns of “tired appearing eyes”. She is diagnosed with dermatochalasia and is subsequently taken to the OR for upper eyelid blepharoplasty. How much of the upper eyelid skin must be preserved during surgery to prevent lagopthalmos?
What is 20mm?
What is the location of electrode array placement in cochlear implantation.
What is scala tympani?
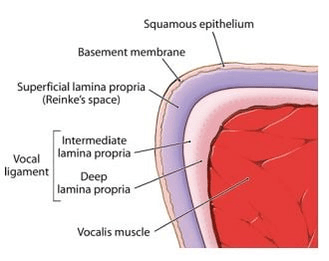
52 y/o F chronic smoker with dysphonia presents to your clinic. The following findings are observed on videostroboscopy. What potential space is affected in this condition?
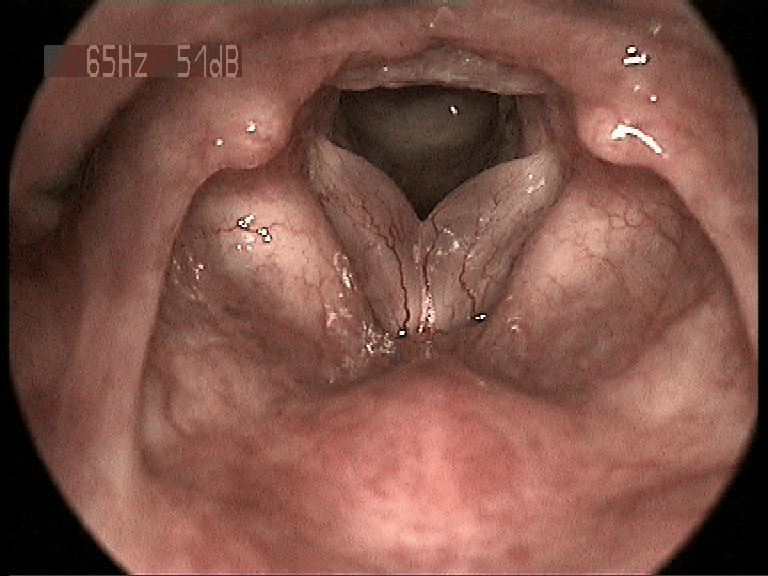
What is superficial lamina propia?
What scoring system may be used to predict the need for use of an oronasal vs a nasal CPAP mask?
What is NOSE score?
NOSE score > 50/100 was independently associated with the use of an oronasal mask at 4 months indicating it could be utilized as a decision-making tool in deciding on the choice of a mask in CPAP initiation.
What is the Glassock-Jackson classification of this lesion?

What is type I?

A 43 y/o F pt with HB 6 left sided facial paralysis since 2 years ago presents for evaluation for facial reanimation. After careful consideration, the patient and surgeon decide to pursue a gracilis muscle free flap. What is the name of the nerve that provides motor function of the gracilis muscle?
What is the obturator nerve?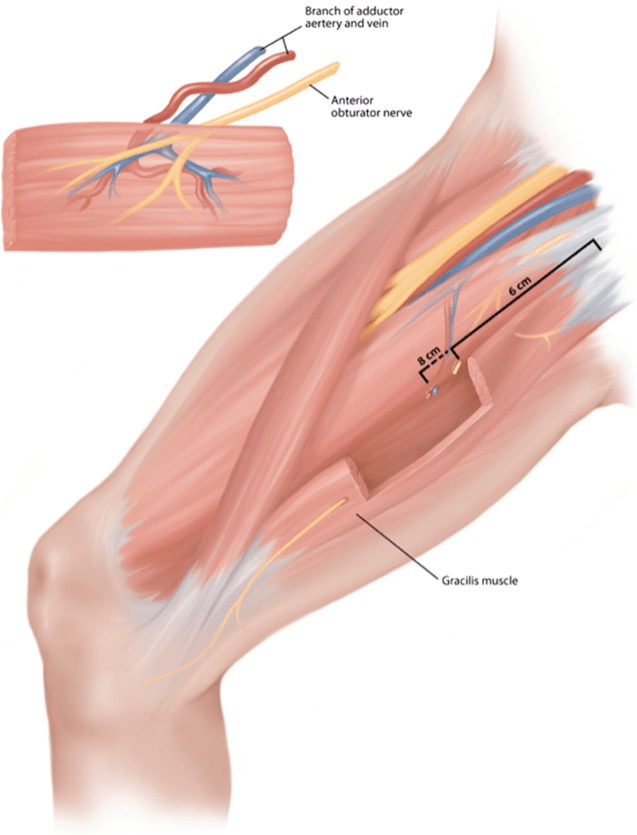
A 15 y/o M pt with acute mastoiditis is noted on imaging to have a hypodense fluid collection within the digastric triangle. What is the name of this condition?
What is Citelli's abscess?


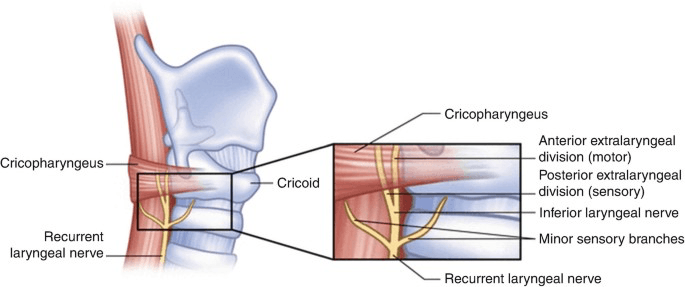
In the case of extralaryngeal recurrent laryngeal nerve branching, which branch contains motor innervation for the intralaryngeal muscles?
What is anterior branch?
What is Stage 2 and REM?
A 40 y/o M pt presents to your office after right stapes prosthesis placement with complaints of with sudden onset vertigo and hearing loss in right ear 2 weeks after surgery. What potential complication should you suspect?
What is reparative granuloma?
Reaction to the packing placed at the oval window after stapedectomy (typically gelfoam or fat).
A 67 y/o F pt presents to your clinic for injectable treatment with PLLA (poly L-lactic acid) filler for the temple region due to volume loss of the temporal fat pad. In what plane should the filler be placed in order to avoid subcutaneous nodule formation?
What is subperiosteal plane?
Name the Schaeffer classification grade of the following laryngeal injury.

What is Grade III?
A 35 y/o female patient with chronic dysphonia presents to your clinic and undergoes videostroboscopy that demonstrates the following findings. You observe “bamboo nodules” on both vocal folds. What serologic test is most specific to diagnose the patient’s condition?
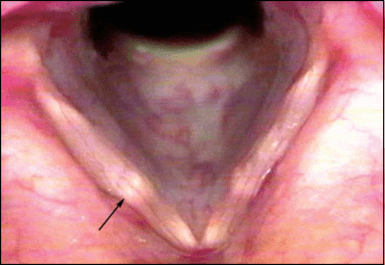
What is anti-CCP antibodies?
Periodic limb movement disorder is associated with repetitive contraction of which muscle?
What is anterior tibialis?
What is the most common cause of facial nerve stimulation after cochlear implantation?
What is cochlear otosclerosis?
Thought to be due to increased bony transmission of electrical stimulation from the intracochlear electrode due to pathologic changes in the bone related to otosclerosis.
Name the nasal deformity observed in this patient.
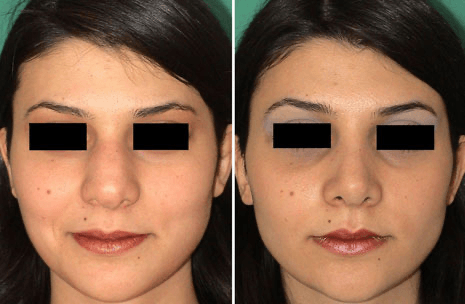
What is parentheses deformity?
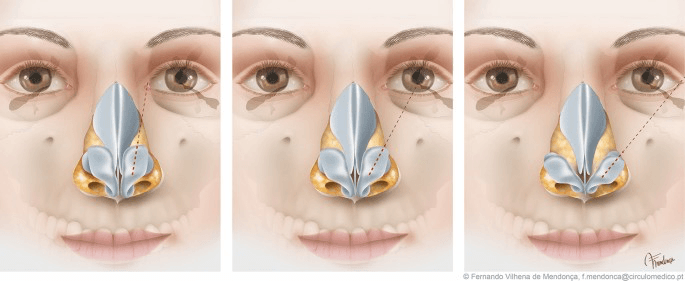 When the lateral cruras of the alar or lower lateral cartilages are oriented too vertical (instead of their canonically normal wide or even close to 90º square angle with the superior septum or nasal midline), having a too narrow angle with the superior septum or nasal midline above them, severely or mildly (all the possible given combinations might be present) a typical deformity called parenthesis tip is present making the tip is prone to look boxy.
When the lateral cruras of the alar or lower lateral cartilages are oriented too vertical (instead of their canonically normal wide or even close to 90º square angle with the superior septum or nasal midline), having a too narrow angle with the superior septum or nasal midline above them, severely or mildly (all the possible given combinations might be present) a typical deformity called parenthesis tip is present making the tip is prone to look boxy.
Abnormal development of which aortic arch is associated with pulmonary artery sling?
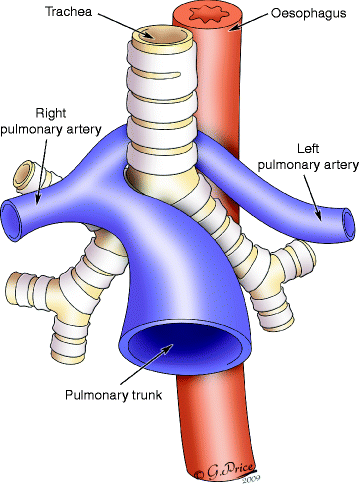
What is 6th aortic arch?
A 73 y/o M pt with history of congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation presents to your clinic due to chronic dysphonia. The following is the patient’s videostroboscopy. What is the name of the condition?
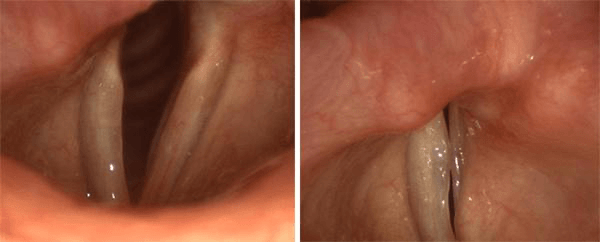
What is Ortner (cardiovocal) syndrome?
A 41 y/o F pt has frequent arousals, sleep fragmentation and excessive daytime sleepiness. PSG demonstrates no true apnea or hypopnea but demonstrates 20 RERAs per hour. What syndrome does she present?
What is upper airway resistance syndrome?


A patient with dysphagia, loss of taste in posterior 1/3 of tongue, hoarseness and neck weakness has what syndrome?
What is Vernet syndrome?
What artery is at risk of injury during SMAS elevation?
What is the transverse facial artery?
Transverse Facial A. (at risk of transection during SMAS elevation, courses through SMAS).

A 10 y/o M pt with acute otitis media presents to the ED due to worsening symptoms along with intractable headaches and blurry vision. On physical examination, the fundoscopic exam reveals papilledema. What potential complication do you suspect?
What is otic hydrocephalus?