In cases of facial nerve paralysis, after how many months does irreversible muscular atrophy and fibrosis occur?
What is 12-18 months?
Two markers expressed in recurrent metastatic HNC that lead to the greatest benefit in anti-tumor activity associated with anti-PDL-1 agents.
What are PDL-1 and HPV positive (P16+) disease?
Name the following benign lesion noted on CT Scan.
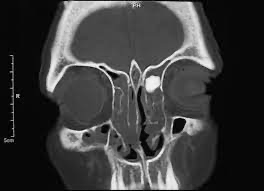
What is osteomata of paranasal sinus?
Name the anatomic space in which dermal fillers may be used for injection laryngoplasty or VF augmentation.
What is the paraglottic space?

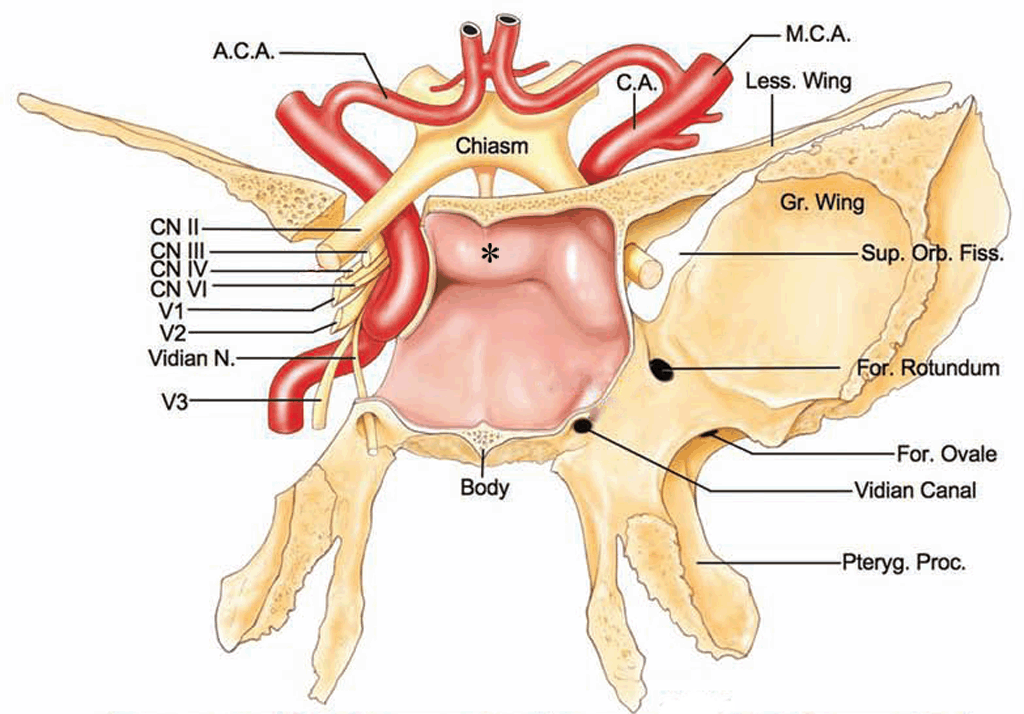
Name the structure highlighted on this CT scan.

What is the vidian nerver or vidian canal?
The circled structure is the pterygoid (Vidian) canal, and the nerve that passes through it is the nerve of the pterygoid canal or the Vidian nerve. The foramen rotundum (through which the maxillary division of trigeminal nerve passes) is shown in this image as well but is superior-lateral to the pterygoid canal. Both foramina lead its nerve into the pterygopalatine fossa. The Vidian nerve carries sympathetics from the deep petrosal nerve and parasympathetics from the greater superficial petrosal nerve and supplies both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation of the nasal mucosa.
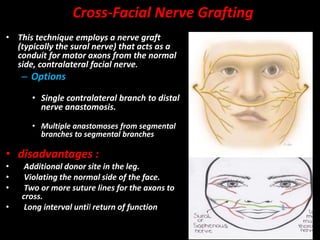
Facial reanimation technique that allows patients a spontaneous smile.
What is a cross-facial nerve graft?
*Other options involve training with use of other muscle function or static slings.
The following pathologic specimen described as having a plasmacytoid morphology with cellular dyshesion corresponds to what type of thyroid neoplasm.
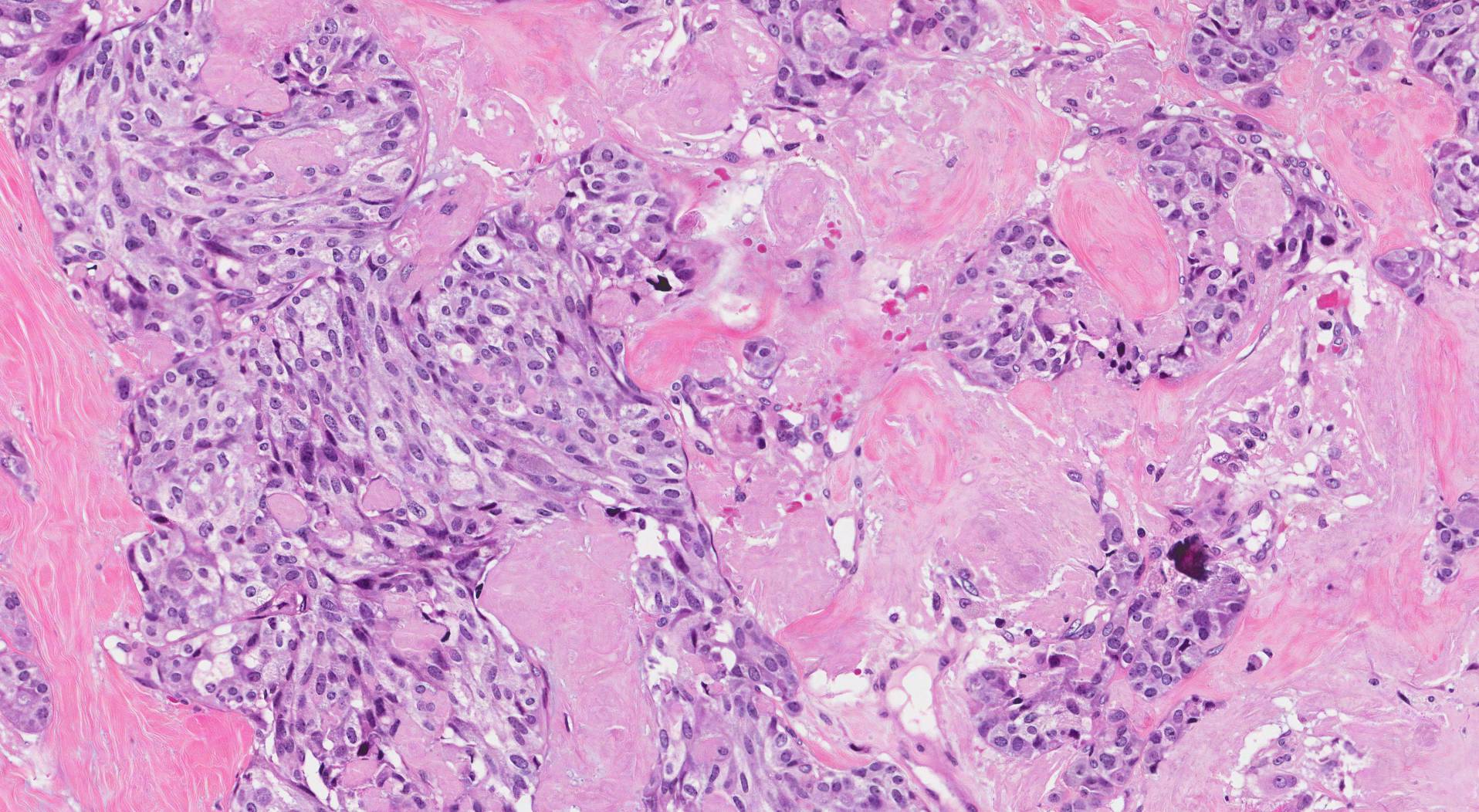
What is medullary thyroid carcinoma?

Term that corresponds to the abnormally large wheel preceded by negative wheels.
What is flash response?
Must sop testing as this may herald anaphylactic reaction.
Condition that affects women primarily that presents with dysphagia and iron deficiency anemia.
What is Plummer Vinsen syndrome?

Type of collagen targeted by relapsing polychondritis.
What is Type II collagen?
Name one of three major tip support mechanisms.
What is
- size, shape, resilience of LLC?
- attachment of LLC to ULC (Scroll region)?
- attachment of LLC to caudal septum?


Anatomic variation associated with this condition.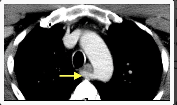
What is a right non-recurrent laryngeal nerve?


Nam the test of choice to evaluate anosmia or hyposmia.
What is the UPSIT score?

<10 consider malingering
The University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test (UPSIT) is a test that is commercially available for smell identification to test the function of an individual's olfactory system.
Known for its accuracy among smell identification tests it is considered to be one of the most reliable (r=.94) and trusted.
Name the condition/tumor noted on the imaging provided.

What is chondrosarcoma of the larynx?
Laryngeal chondrosarcoma is rare, comprising less than 1% of laryngeal cancer. It mainly develops (75% of cases) in cricoid or more rarely in thyroid (20%) or arytenoid (3%) cartilage.
The most typical CT image is of so-called “popcorn” intratumoral calcification, found in some 80% of cases. The tumor is centered on the affected cartilage, and presents as hypodense. Contrast medium uptake is generally moderate.
A patient with GPA of the skull base is most likely to have which cranial nerve involvement?
What is the trigeminal nerve?
Dermal filler that requires skin testing 1 month prior to use.
What is poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) filler?
Skin testing required due to bovine collagen content.
Vascular variant that is considered a contraindication for TORS resection.
What is retropharyngeal ICA?
What is the frontal and sphenoid sinus?
Name the condition noted on stroboscopy for a 70 y/o patient complaining of chronic dysphonia and difficulty being heard in loud environments.

What is presbyphonia?
Vocal fold atrophy and glottic insufficiency with relative prominence of the vocal processes on laryngeal exam would be consistent with this diagnosis.
Name the inner ear finding in the following CT Scan.

What is an enlarged vestibular aqueduct (EVA)?
Chemical peel consisting of phenol, croton oil, water and septisol.
What is Baker Gordon solution?

What is succinate dehydrogenase?
Mutations in the SDH gene are associated with hereditary paragangliomas. There are four subunits to the enzyme: SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, and SDHD. Mutations in these subunits increase angiogenesis and make the cell less susceptible to hypoxia
Stage of an inverted papilloma that involves the OMC.
What is a T2 inverted papilloma?
Name the diverticula noted in figure B.

What is a Laimer's diverticulum?

Name the microbial organism that causes the following lesions.
 A biopsy shows papillomatous and polypoid squamous hyperplasia with mixed inflammation. The specimen stains positively with GMS and PAS stains.
A biopsy shows papillomatous and polypoid squamous hyperplasia with mixed inflammation. The specimen stains positively with GMS and PAS stains.
What is coccidiomycosis?
Although this is primarily a pulmonary disease, approximately 0.5–1.0% of infected individuals develop disseminated disease affecting skin, subcutaneous tissue, bone, joints and meninges. These lesions are frequently seen in the head and neck. Diagnosis is typically made by cultures and serological testing. Tissue specimens may reveal the double-walled spherule of C. immitis containing numerous endospores, surrounded by a granulomatous reaction.