Meningitis after cochlear implantation is most commonly caused by what organism?
S. pneumoniae
Kids 2-4 yo: prevnar series; >5 yo: pneumovax
Temporal bone anomalies, syndactyly, craniosynostosis, midface anomalies (hypertelorim, high arch palate, proptosis)
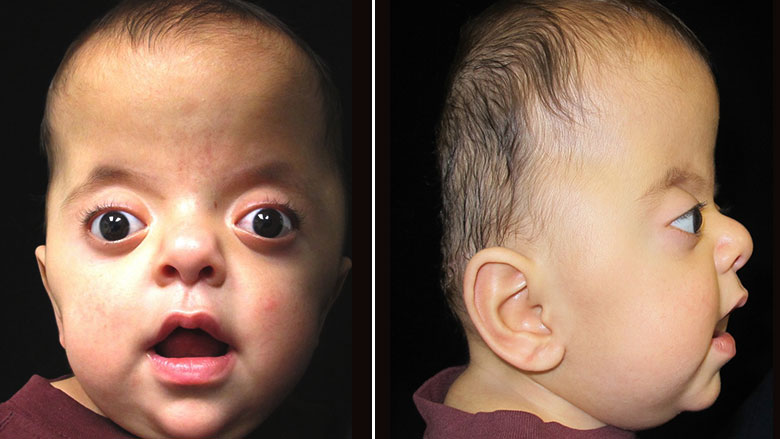
Apert syndrome
Causes of hearing loss: recurrent middle ear effusions (partially due to ETD), stapes fixation
Increased vascularity of the promontory in otosclerosis

Schwartz sign
Most common cause of genetic hearing loss
Connexin 26 mutation
(Autosomal recessive)
4 year old presents with recurrent middle ear effusions and TM perforations despite appropriate otic drops and PO abx. Stain of otorrhea shown below. What is the next best test?
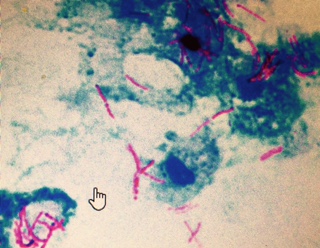
PPD or quantiferon
(concern for mycobacterial infection)
Myopia and cataracts, hypermobile joints with early arthritis, cleft palate, and hearing loss
Stickler syndrome
Autosomal dominant: COL2A1, COL11A1, and COL11A
Autosomal recessive: COL9A1
Triad of diplopia, retro-orbital pain, and otorrhea
Gradenigo's syndrome (petrous apicitis)
Name one syndrome associated with congenital aural atresia
Treacher Collins, Crouzon, Goldenhar

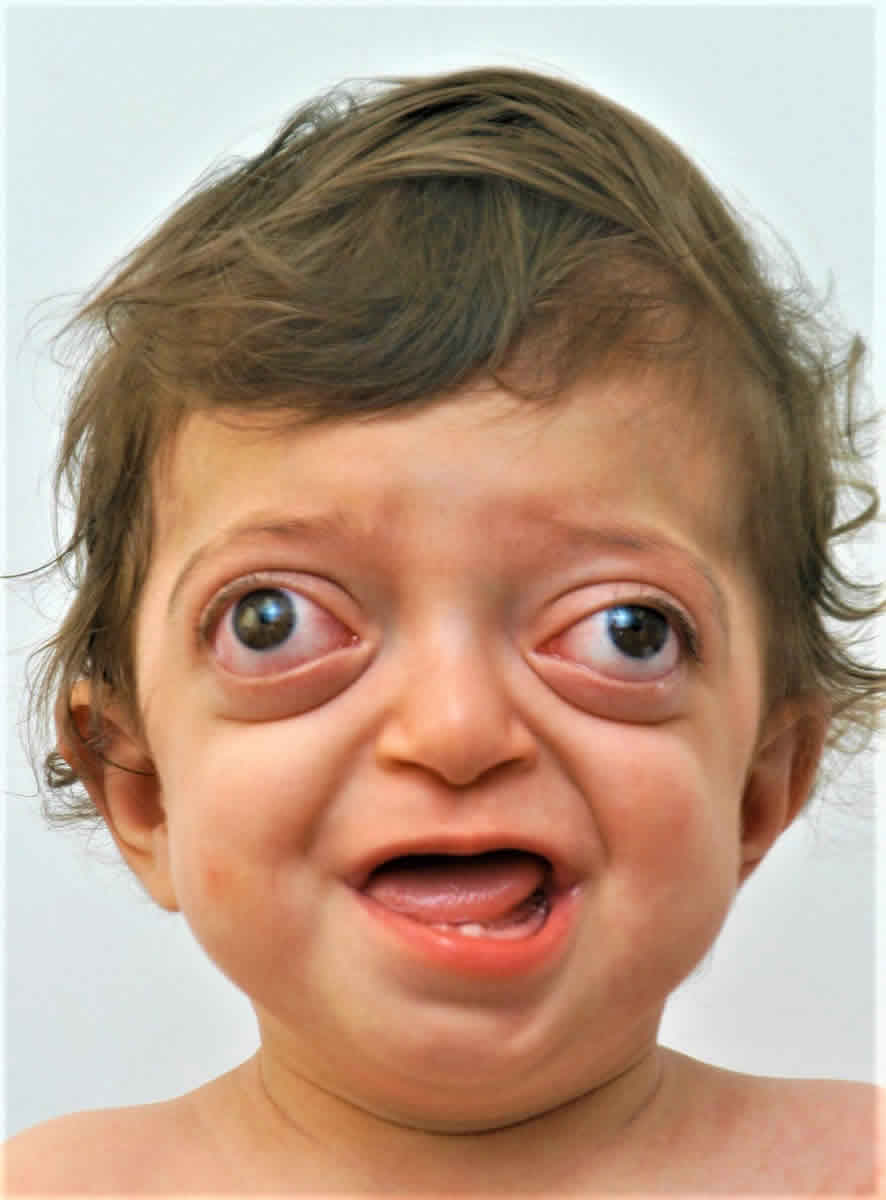

What other physical exam finding may this patient present with?

Facial paralysis
Ramsey Hunt is the second most common cause of acquired facial paralysis/paresis; 40% can have SNHL
Retinitis pigmentosa and congenital deafness
Usher syndrome (autosomal recessive)

Hearing loss is due to atrophy of the organ of Corti; most likely of all congenital deafness to manifest with vestibular symptoms
The anatomic space bounded by pars flaccida and neck of the malleus and enclosed by the lateral malleolar fold
Prussak’s space (most common site of an acquired epitympanic cholesteatoma)

An infant fails their newborn hearing screen and also has cataracts and cardiac anomalies. What does this constellation of findings suggest?
Congenital rubella
(1) Abnormal central incisors (2) Interstitial keratitis of the eye (3) Deafness
This triad is associated with what infection?
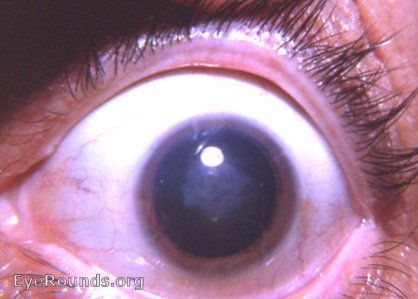
Syphilis (Hutchinson’s triad)
Sensorineural hearing loss and enlarged thyroid (euthyroid goiter)
Pendred syndrome (autosomal recessive)
enlarged vestibular aqueduct, Mondini cochlear hypoplasia, and often atrophy of organ of corti
Tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Jacobson nerve (neuroendocrine cells from here give rise to glomus tympanicum)

The most severe congenital malformation with complete absence of the bony and membranous labyrinth
Michel aplasia
Associated with thalidomide exposure

Name the imaging modalities to (1) confirm and (2) clinically follow malignant otitis externa?
(1) CT and technetium-99 scans (high sensitivity for osteomyelitis)
(2) CT and gallium-67 scans (uptake decreases as infection is cleared)
Profound sensorineural hearing loss and prolonged QTc with risk of life-threatening arrhythmias
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome (autosomal recessive)
Blanching of this lesion with pneumatic otoscopy

Brown's sign: blanches glomus tympanicum, most common tumor of the middle ear
Most common symptom is pulsatile tinnitus. May also cause hearing loss (conductive > sensorineural).
What is the most common middle ear abnormality associated with aural atresia?
Fusion of the malleus and incus