Jester
This embryonic period is most susceptible to teratogens
Fertilization age Weeks 3-8
Where t cells form periarterial lymphatic sheaths and where B cells reside in lymphatic nodules
White Pulp
The stretch of the aorta signals this reflex to make alterations in blood pressure via PNS and SNS
Barorecptor Reflex
The sympathetic nervous system flows out of these levels
T1-L2/3
This type of cell growth is characterized by the increase in the number of cells. Seen in the endometrium during the menstrual cycle
Hyperplasia
name the three B symptoms
Fever night sweats unintentional weight loss
Sometimes considered the 4th germ layer, these cells arise from the lateral edges of the neural plate and migrate away to form many different tissues
Neural crest cells
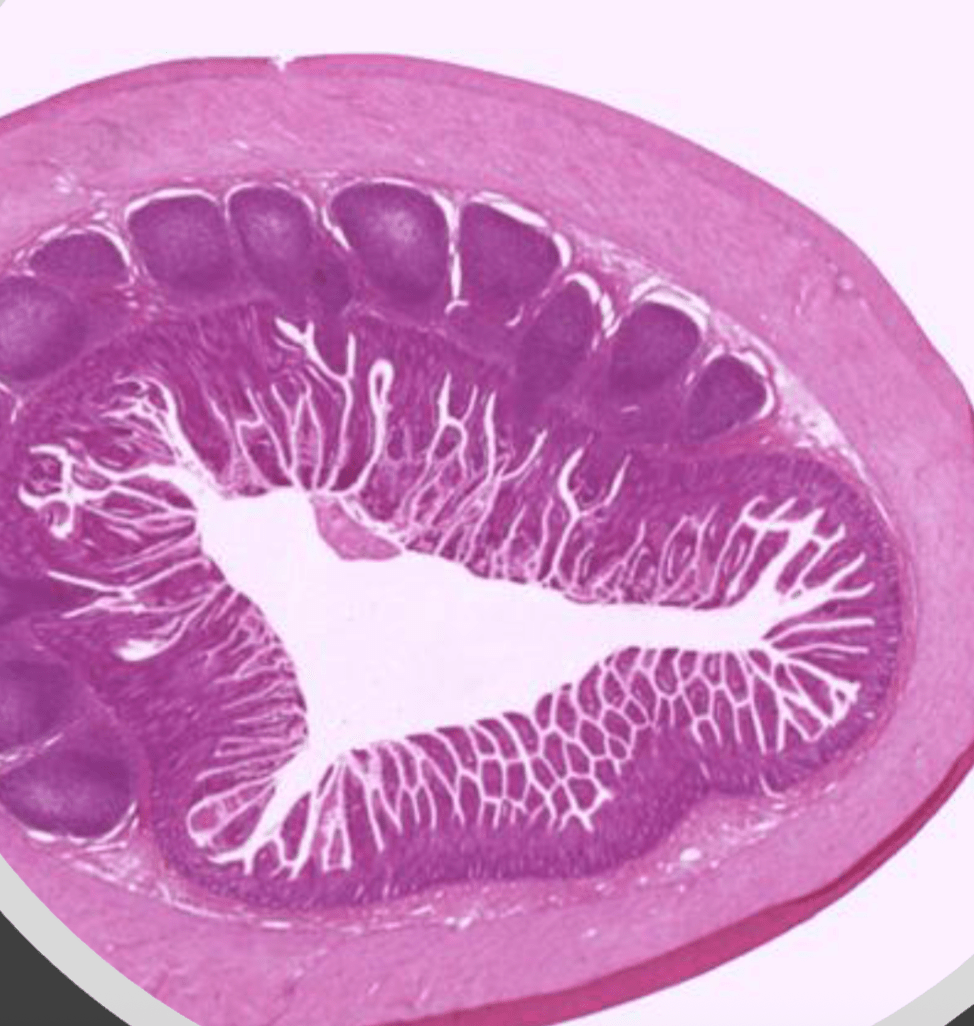
The areas of the body most common to find the above pictured structure
GI, respiratory
Mucosa Associated Lymphatic Tissue
Bonus: Whats the treatment for this condition?
Organophosphate poisoning
Atropine, Pralidoxime
These fibers convey information from the outside environment to the body via a two neuron pathway. Their ganglia are in the periphery.
visceral sensory fibers
Cannot assess temporality, causality, possible reverse causation, incidence prevalence bias are examples of limitations for what kind of study.
cross sectional study
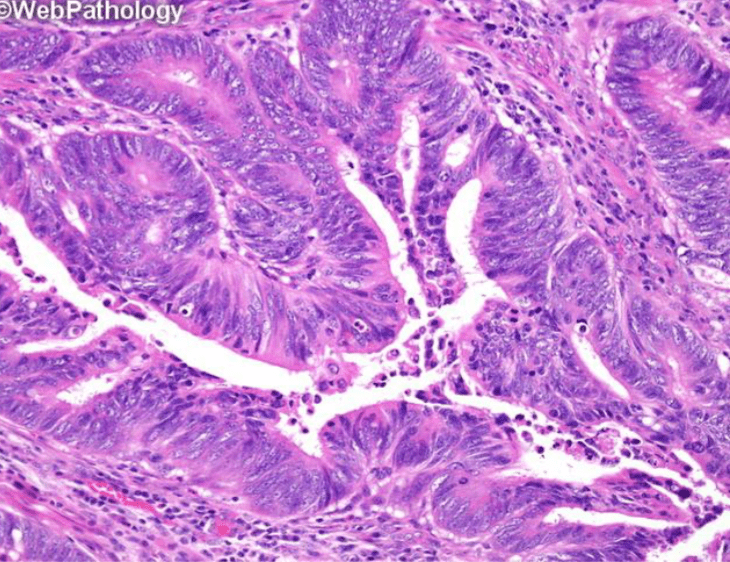
Which image shows malignant colonic mucosa
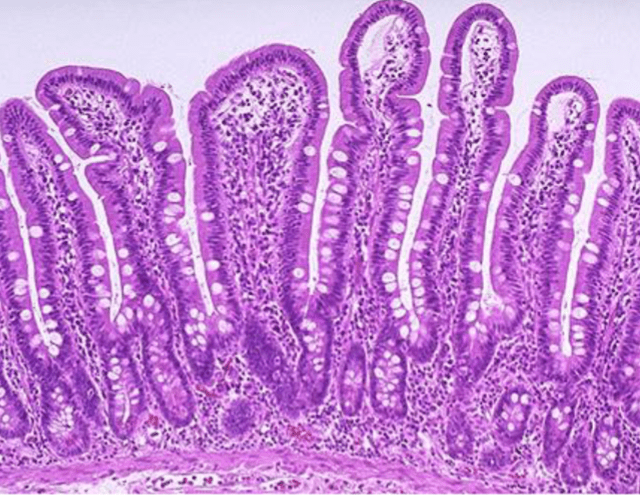
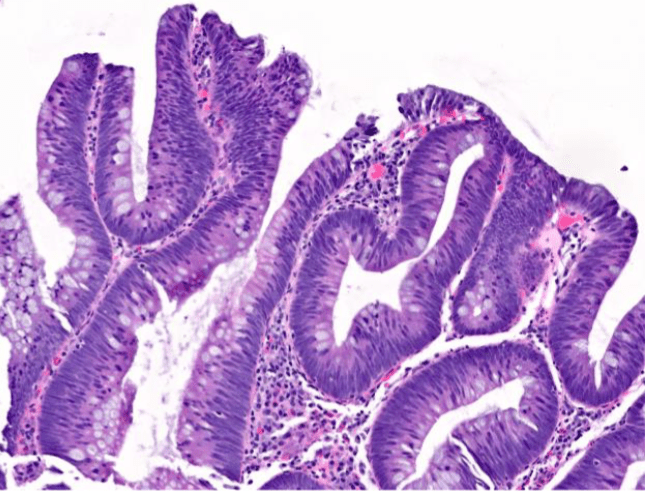
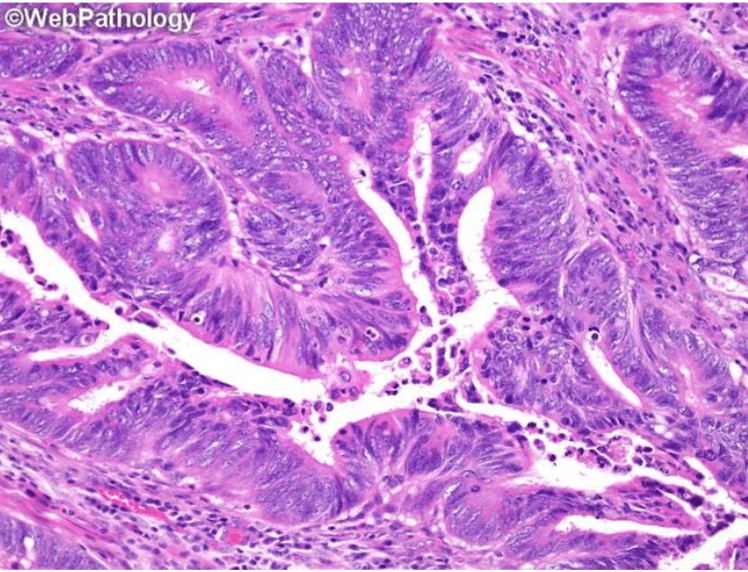
Lymphatic drainage from the breast primarily goes to
axillary lymph nodes (approx 75%)
Other part is the parasternal lymphnodes
This group of cells migrates second into the primitive streak and gives rise to the following structures
supportive structures such as blood, muscles, bones, heart, spleen kidney ureter
mesoderm
Positive selection of T cells occurs in the ()
whereas negative selection of T cells occurs in the ()
Double Jeopardy!!!!
1. Thymic Cortex
2. Thymic Medulla
In sympathetic nervous system relies of adrenergic receptors and the neurotransmitter norepinephrine to send messages. There are two exceptions to this rule:
Adrenal glands, use acetylcholine on nicotinic receptors
Sweat glands: use acteyl choline on M3 receptors
The main difference of the Sympathetic nervous vs Parasympathetic nervous system in terms of post ganglia nerve fiber distribution
SNS: widely distributed to reach all vascular parts, including skin, organs, glands, and cardiac muscle
ANS: limited distribution to smooth muscle in organs and glands and cardiac muscle DOES Not go to skin
What are the characteristics of a grade C for a particular screening and give an example
Prostate cancer
breast cancer-->lung, liver brain lymph nodes
Prostate cancer-->lymph nodes and bones
Lung cancer---> bone brain lymph nodes, pleura diaphragm,
kidney Cancer--->Lung liver bones
These represent examples of what phenomenon
Metastatic Organotropism
This condition is a form autonomic nervous system dysfunction that is characterized by an increase in HR by 30 BPM after 10 min of standing or a HR >120
Orthostatic intolerance without orthostatic hypotension
commonly treated with high salt diet
POTS
Postural orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome
Fun Fact: COVID-19 infection was linked to potential development of POTS
The formation of this establishes uteroplacental circulation and occurs during the 2nd week after fertilization
trophoblastic lacunae
The main histological difference between pharyngeal and palatine/lingual tonsils
Palatine/lingual tonsils have non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
The contraction of this part of the bladder contributes to urinary filling and is innervated by what receptor
alpha 1 receptors
internal urethral sphincter;
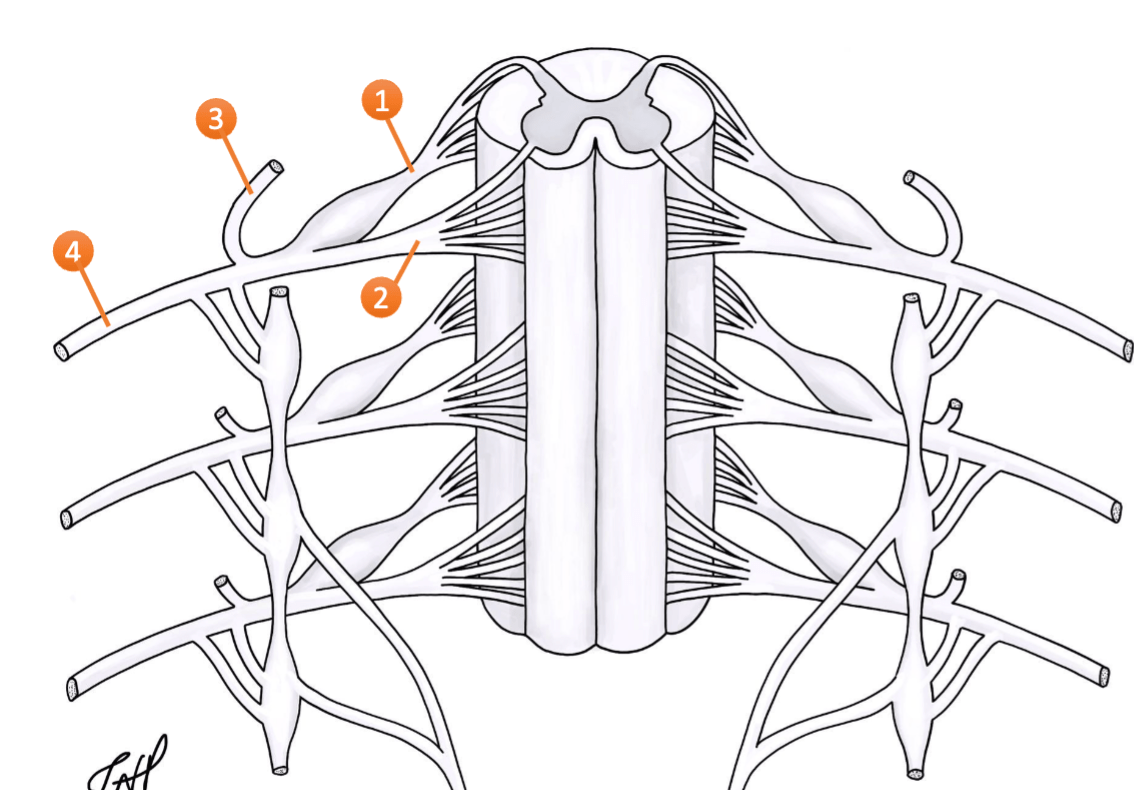 The structure in number 2 has cell bodies in what location of the spinal cord
The structure in number 2 has cell bodies in what location of the spinal cord
spinal cord grey matter (anterior and or lateral horn)
anterior ventral root-motor fibers
The ways to mitigate cofounding factors in the study's design process
restriction, matching, randomization,
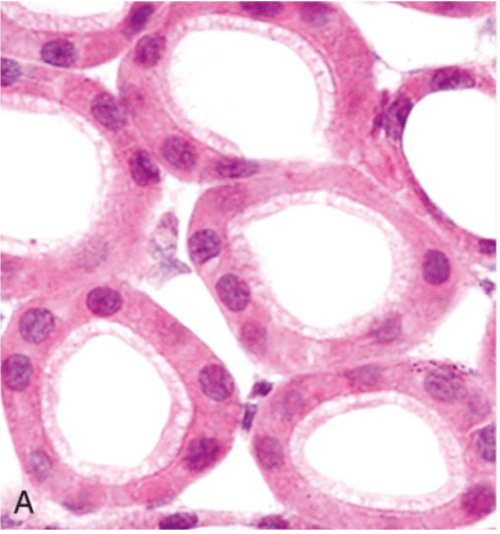
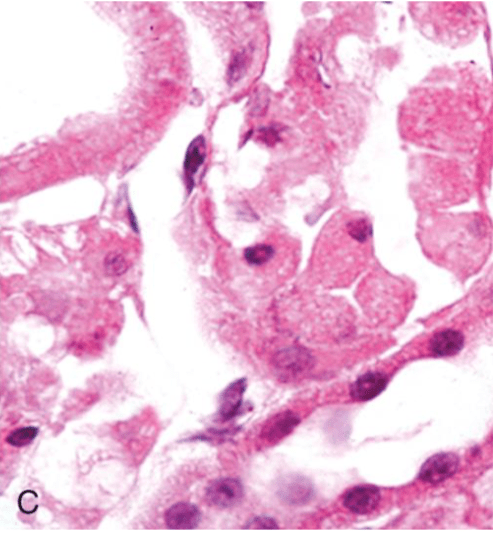
A normal Kindey Tubule
C Abnormal Kidney tubules
This shows what kind of cellular injury
Necrosis
Characterized by the severe deficiency of protein, this disease is classified into three different categories. The severe form of this disease is categorized by
Kwashiorkor,
generalized edema or moderate edema +facial edema (moon facies)
muscle atrophy, abdominal distension
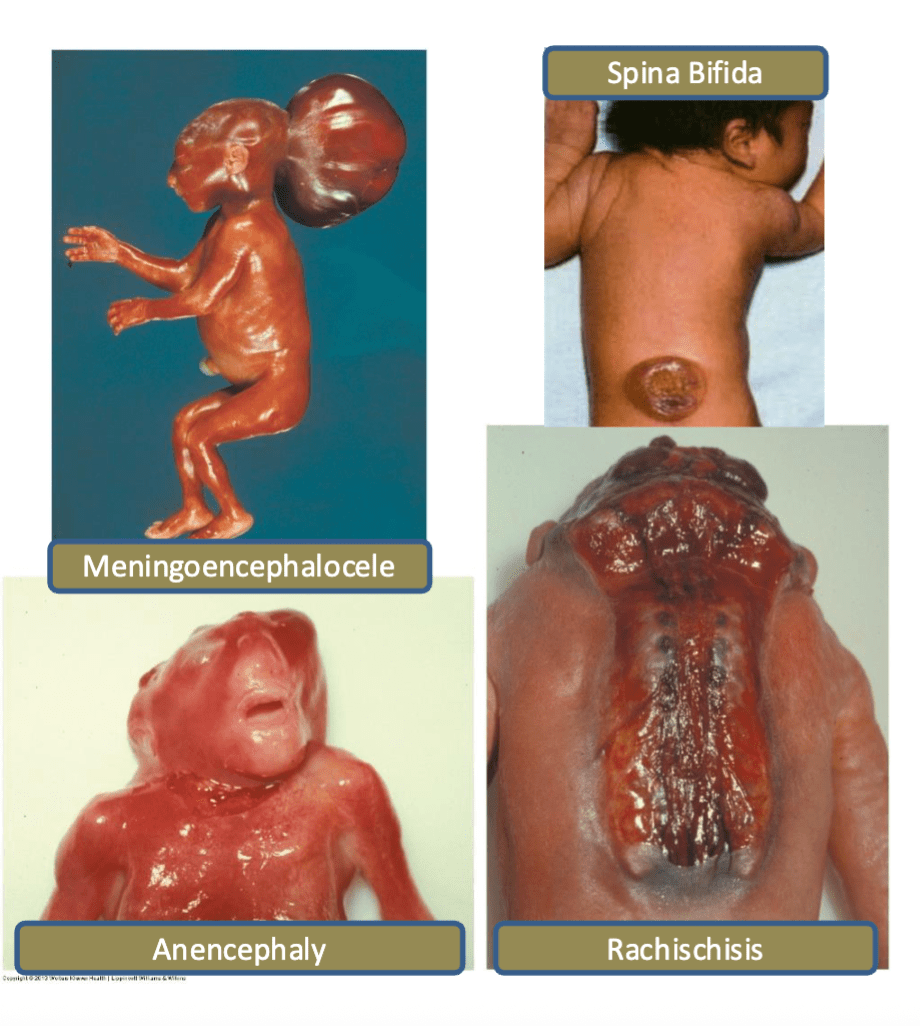
These defects are prevented by supplemental folic acid and are detected through 2 methods:
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein levels measured at 16-18 weeks
Ultrasound
Neural Tube defects
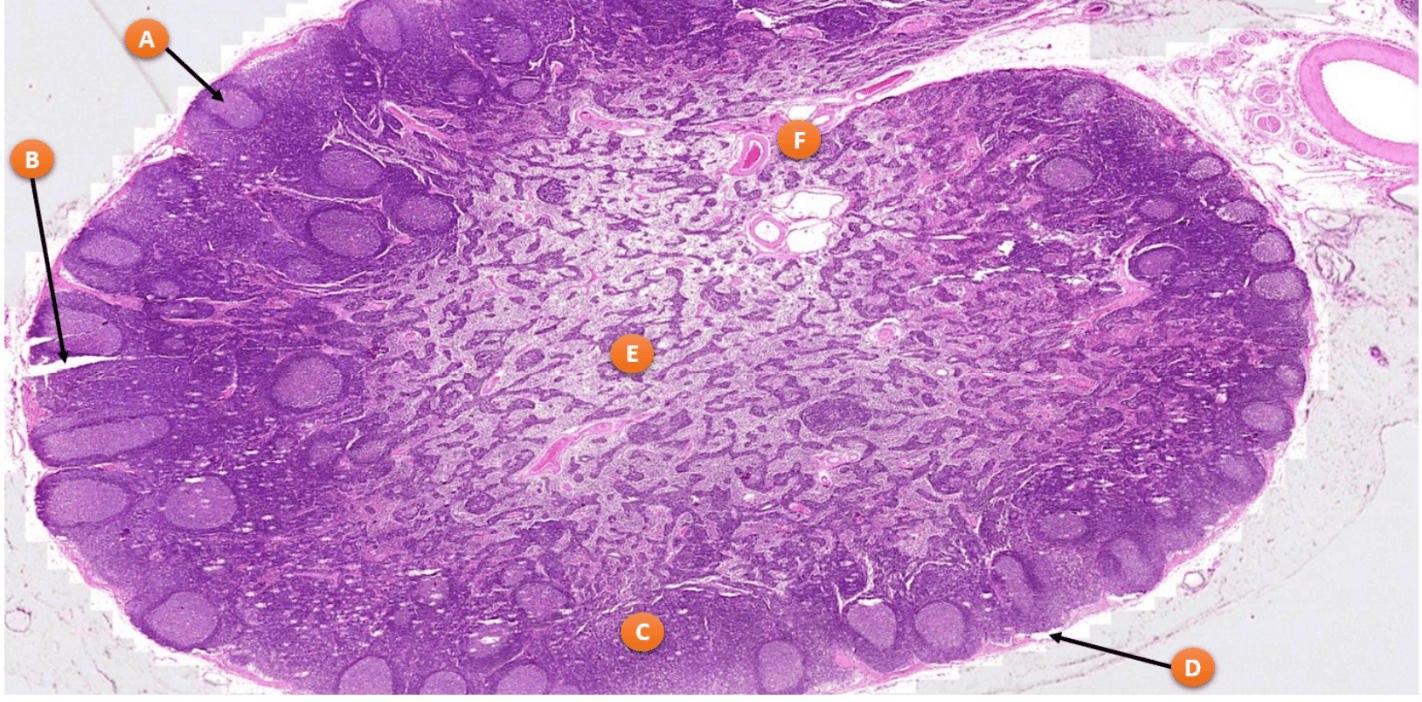 What is the function of the area highlighted by E
What is the function of the area highlighted by E
Medulla of Lymph Node
Medullary sinuses- antigens are removed by macrophages from slow flowing lymph
Medullary cords: store b cells, plasma cells, dendritic cells and macrophages in reticular fibers
Your patient is given an unknown drug that causes an increase in hr, but a decrease in mean arterial pressure and diastolic pressure. This drug most likely acted on what type of receptor.
Bonus Points: What kind of drug would cause this kind of response?
Beta 2 receptor
Albuterol (beta 2 agonist)
B2 causes peripheral vasodilation, BP falls, results in reflex tachycardia
This is the path pre ganglionic fibers take in the viscera within the abdominopelvic cavity
pass through the sympathetic trunk without synapsing and branch from the paravertebral ganglia and travel to the pre-vertebral ganglia and synapse there
Study had 200 participants
50 in the treatment group developed migraines
20 in the placebo group developed migraines
What is the risk difference of developing migraines?
0.15 risk difference
(50/200)-(20/200)=
0.25-0.1=0.15
The 3rd stage of cancer according to TNM system
Large tumors that have spread to nearby lymph nodes but not to other areas of the body
T1-T4, N1-N3 M0
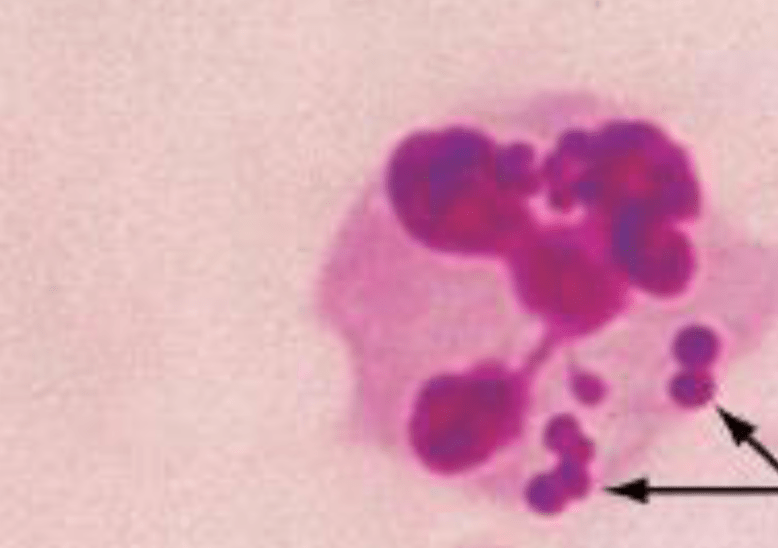
A genetic defect in these cells presents what symptoms.
Bonus Points for name of disease
Presents with chronic infections and inflammation in tissues exposed to the outside world i.e skin, oral cavity, GI tract, respiratory tract.
Chronic Granulomatous Disease