Doesn't mean you're gonna die
Which inhalational anesthetic is the only one to have no effect on MAP but increases SVR?
Nitrous oxide
Following the 'rule of 5's' you would expect a patient with an FiO2 of 60% to have a PaO2 of what?
300
What is normal coronary blood flow in ml/min?
225-250 ml/min
CPAP to the non-dependent lung
A surgeon is about to proceed with a local anesthetic only approach to a carotid endartectomy, but asks you to be in the room in case sedation or conversion to GA is needed. Name 2 advantages to a CEA performed under local anesthesia?
Shorter hospital stay, direct assessment of neuro function/cerebral perfusion, avoidance of intubation, stable hemodynamics
What is the #1 perioperative complication with abdominal aortic repair that requires cross-clamping
Myocardial dysfunction
What are the traditional PaO2 and PaCO2 cut-off values for pulmonary resection?
PaO2 < 60
PaCO2 < 45
What are the 3 classic signs of aortic stenosis?
Syncope
Angina
Dyspnea (on exertion or otherwise)
What is the most common intra-operative complication associated with a double-lumen endotracheal tube
tube malposition
Which medication is best suited to treat hypotension in a patient with severe aortic stenosis
Phenylephrine
Name 2 cardiac related metrics that you would expect to increase with crossing clamping of the aorta during an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair
BP above clamp, SVR, PaOP, CVP, Coronary flow, SVO2
Alveolar pressure is greatest in which West lung zone?
Zone 1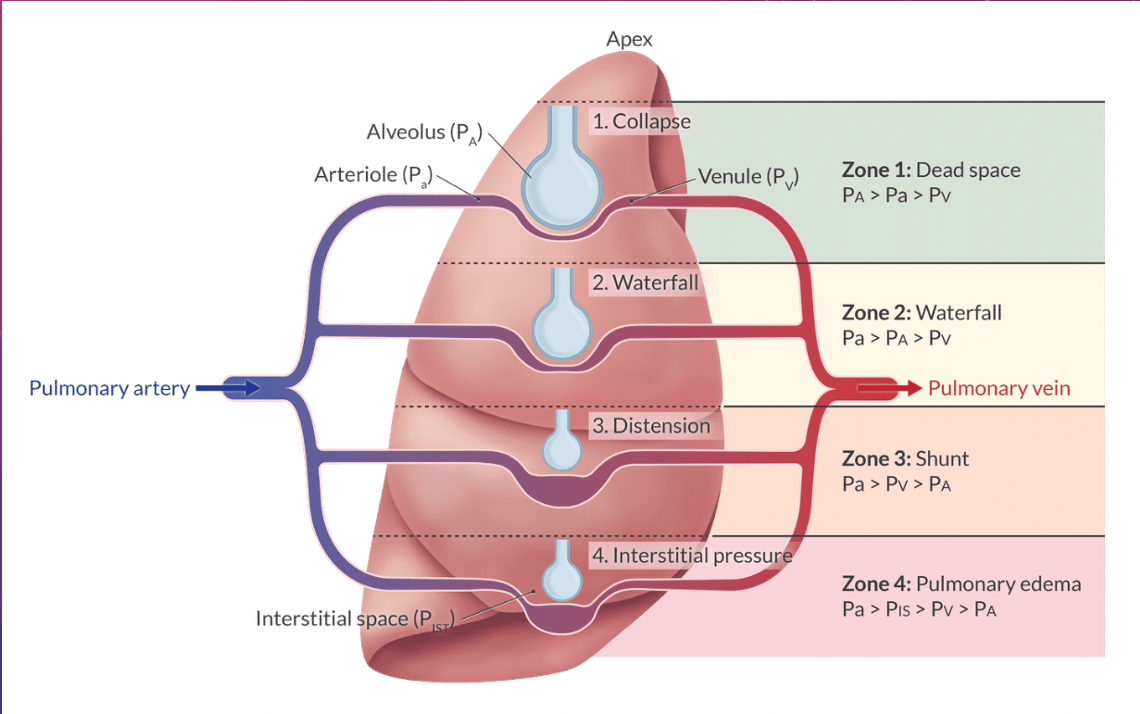
Preload:
Heart rate:
Afterload:
Increased preload
Increased heart rate
Decreased afterload
Name 2 medications (not inhaled anesthetics) that inhibit hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
NTG, beta-agonists, nitroprusside, Ca++ channel blockers, minoxidill, theophylline, PGE1, adenosine, prostacyclin (PGI2), Nitric oxide, Lisinopril, NE, Epi
What is the ppoFEV1 of a patient undergoing a right lower lobectomy with a pre-op FEV1 of 55%
Round to the nearest whole number
ppoFEV1 = pre-op FEV1 (%) x (42-segments removed)/42
55 x (42-12)/42
55 x.71 = 39%
A patient in pacu is having a myocardial infarction of the left ventricular lateral wall - you know you will see ST elevation in which 4 EKG leads?
I, aVL, V5, V6
Calculate the A-a gradient using the following parameters (at sea level) round to the nearest whole number:
PaO2: 90 mmHg
PaCO2: 60 mmHg
FiO2: 50%
192 mmHg
Which of the following cardiac pressure/volume loops is indicative of increased afterload?
A B C
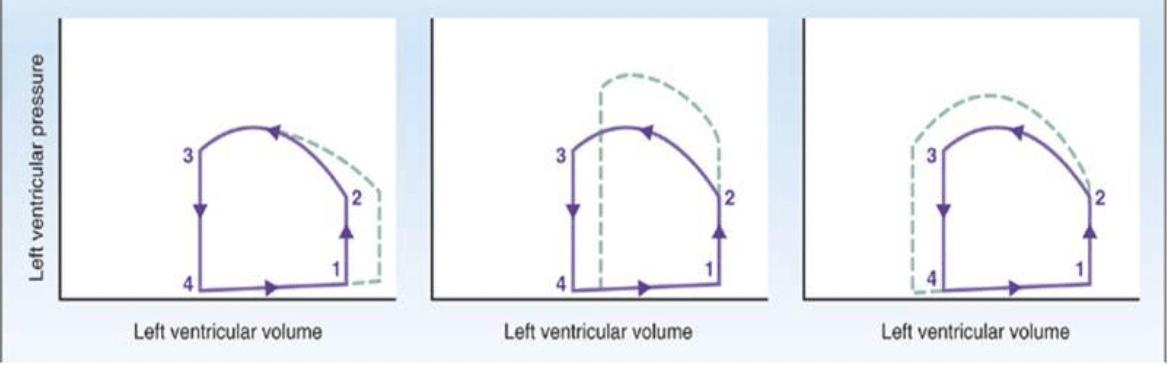
B
A = increased pre-load
C = increased contractility
What are 3 ways we can help treat/mitigate the effects of pulmonary edema?
Nitroglycerin, O2, Diuretics, Prone positioning
An TEE is ordered under anesthesia for suspected regional cardiac wall abnormalities. What region of the heart would you expect to have wall abnormalities from occlusion of the right marginal artery?
Lateral right ventricle
2 = 2.4% chance of major cardiac event
Draw the flow/volume loop you would expect to see from a patient with a tracheal tumor
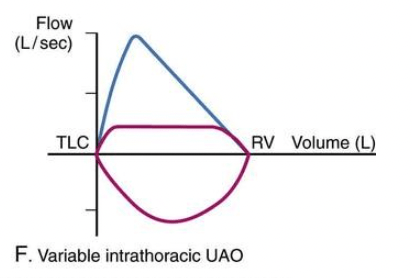
C
Name all 4 bronchial blockers in this picture
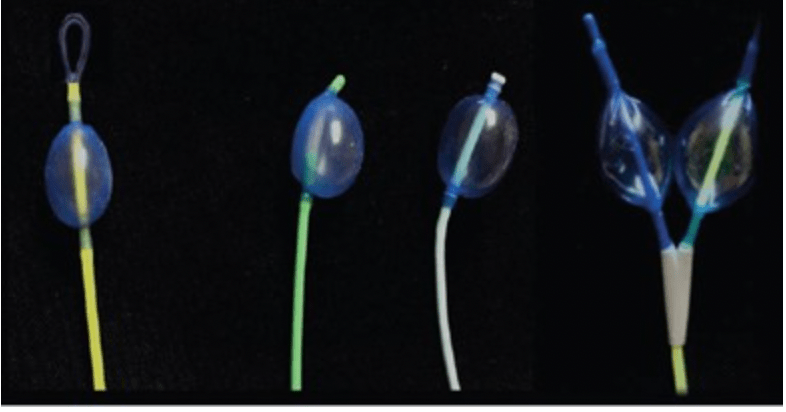
From Left... Arndt, Cohen, Uniblocker, EZ blocker
Calculate this patients SVR using the following parameters:
mean arterial pressure: 75 mmHg
central venous pressure: 8 mmHg
cardiac output: 4.5 L/min
1190
((MAP-CVP)/CO) x 80