A 5 day fever, red eyes and lips in a child is indicitive of what condition?
Kawasaki disease
8 year old with severe abdominal pain has had oral paracetamol, oral ibuprofen, and oral oxycodone - still in significant pain
What can we give next if mom is refusing an IV?
intranasal fentanyl (1.5mcg/kg) max dose 100mcg
What is bronchiolitis most commonly caused by?
RSV
Early morning vomiting is suggestive of....
raised ICP
What differential can cause any presentation in neonates and should therefore always be considered
Sepsis
How can you diagnose epilepsy without any imaging?
2 unprovoked seizures occurring more than 24 hours apart
Most common cause of fever in children?
viral infections
8 month old presents with intermittent abdominal pain, drawing knees up to chest and some red mucus in stool........what is the definitive management of this condition
gas enema
Medical Managemnent of a child presenting with barking cough, increased WOB and stridor?
1. Oxygen
2. Steroids (PO/IV/IM Dexamethasone)
3. Nebulised adrenaline
4. PRN Pulmicort (Budesonide)
What fluid is used for rapid bolus in hypovolemic shock from dehydration
rapid bolus of 10-20mL/kg NS
Name 2 risk factors for TTN
1. C section
2. precipitous birth
3. maternal asthma / DM
4. Late premie
5. SGA or LGA
What gastroentestinal virus can cause a benign seizure?
rotavirus
Five month old previously well with no medical history appears acutely unwell and not feeding in the last 8 hours. His pulse rate is 136/min, blood pressure 85/50 mmHg, respiratory rate 44/min, SpO2 98% on room air, and temperature 38.8°C. He responds sluggishly to voice and appears irritable. His peripheries are warm with capillary refill time of one second. His anterior fontanelle is full but not bulging. There is no rash or focal neurological signs.
What is the most important investigation to confirm the diagnosis ?
Lumbar Puncture
features concerning for bacterial meningitis including fever, irritability, lethargy and a full fontanelle. While several investigations are important in the work-up, lumbar puncture is the most important diagnostic test as it provides definitive evidence of meningitis and identifies the causative organism to guide specific therapy.
What is the most common extra-intestinal manifestation of coeliac disease in children?
Anaemia
This is typically due to iron deficiency, resulting from malabsorption in the small intestine. The chronic inflammation and damage to the intestinal mucosa impair the absorption of essential nutrients, particularly iron.
What is the next step in management of preschool wheeze after the patient has been given oxygen, salbutamol, and oral prednisolone and is still showing iWOB?
- Ipratropium bromide
- should be added to salbutamol, oxygen, and steroids in the initial management of severe paediatric asthma exacerbations.
7 day old boy presents to the Emergency Department with failure to pass meconium since birth, progressive abdominal distension, and bile-stained vomiting. What is the definite treatment for this condiditon?
Pull through surgery
For suspected GBS sepsis what antibiotics do you give and for how long?
- Benzylpenicillin 60mg/kg q12h (or ampicillin) PLUS Gentamicin 2.5mh/kg daily
- Positive = 5-7 days
- negative = 36 hours
Child having a seizure has already received two doses of Midazolam....what do you give next?
Second Line: IV Levetiracetam (Keppra)
4 year old boy with a two-day history of fever and rash. He initially developed a low-grade fever two days ago, which his parents treated with paracetamol. His temperature has now spiked to 38.9°C. A diffuse, erythematous rash appeared around his mouth and groin two days ago and has since spread to involve his arms, legs and trunk. He has no significant medical history and takes no regular medications. On examination, he appears irritable but not in acute distress. His pulse rate is 110/min, blood pressure 100/60 mmHg, respiratory rate 24/min, SpO2 98% on room air, and temperature 38.9°C. The rash resembles sunburn, with some skin peeling, particularly in the axillary and groin areas. What is going on?
Staphylococcus scalded skin syndrome
3 year old was playing with television remote and mom saw him putting an object in his mouth. The boy appears well, however he is drooling and has excess saliva in his mouth. He does not appear to be in distress or complaining of any abdominal pain.
What is the next step in management?
a) lactulose
b) Refer to ENT or gastro immidietly
c) reassurance and observation
d) chest xray
e) drink lots of water to flush object down
answer: a chest X-ray to confirm the location and diagnosis.
21 month old with SpO2 of 89% on room air and a temperature of 37.4°C increased WOB and auscultory findings........what lobe is the issue in?
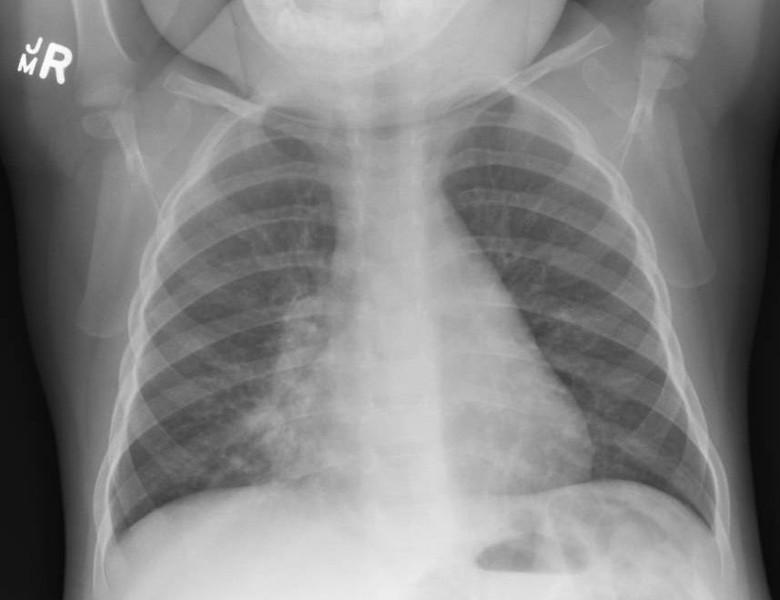
R middle lobe consolidation / collapse
The chest X-ray shows obliteration of the right heart border in keeping with right middle lobe consolidation or collapse obscuring the r heart border
A 5-week-old infant with persistent vomiting for the past week. The vomiting occurs shortly after feeding and is described as forceful and non-bilious. On examination, the infant appears dehydrated and underweight. A firm, movable, olive-shaped mass is palpable in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen.
Considering the most likely DDX - What electrolyte and acid–base abnormalities are typically seen in this condition?
Hypochloremic, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis
In neonatal respiratory distress how should fluids be adjusted
↓requirement (by ~30 mL/kg/day) for infants in respiratory distress
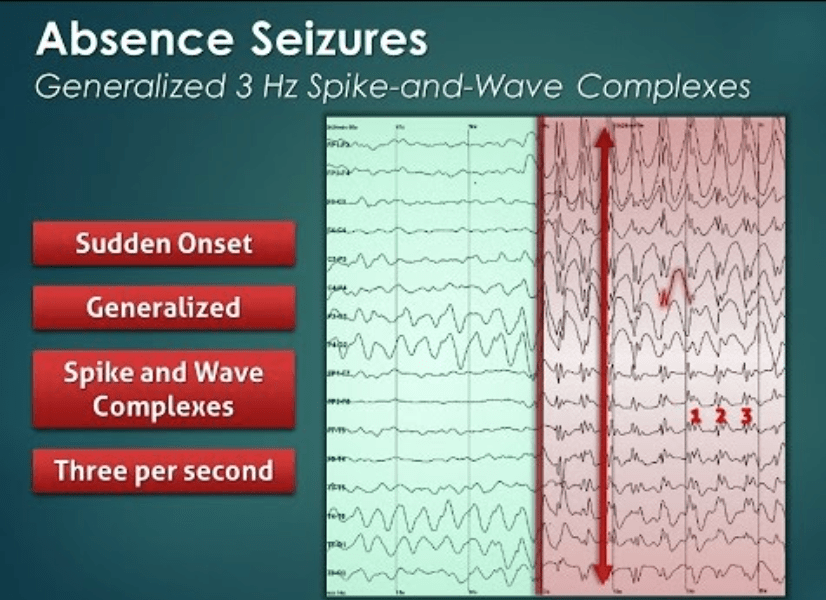
What finding would you see on EEG for absence seizures?