Mutation of Fibrillin-1 results in this syndrome, characterized by a wide arm span, long thin fingers, pectus carinatum.
What is Marfan's syndrome?
The 5th step of Spencer's Technique
What is Abduction & Adduction with External Rotation?
Every Fancy Cat Takes An Indoor Poo
Extension, Flexion, Compression with circumduction, Traction with circumduction, Abduction And Adduction with External Rotation, Internal rotation, GH Pump
Paget’s disease primarily involves overactivity of this type of bone cell
What is an osteoclast?
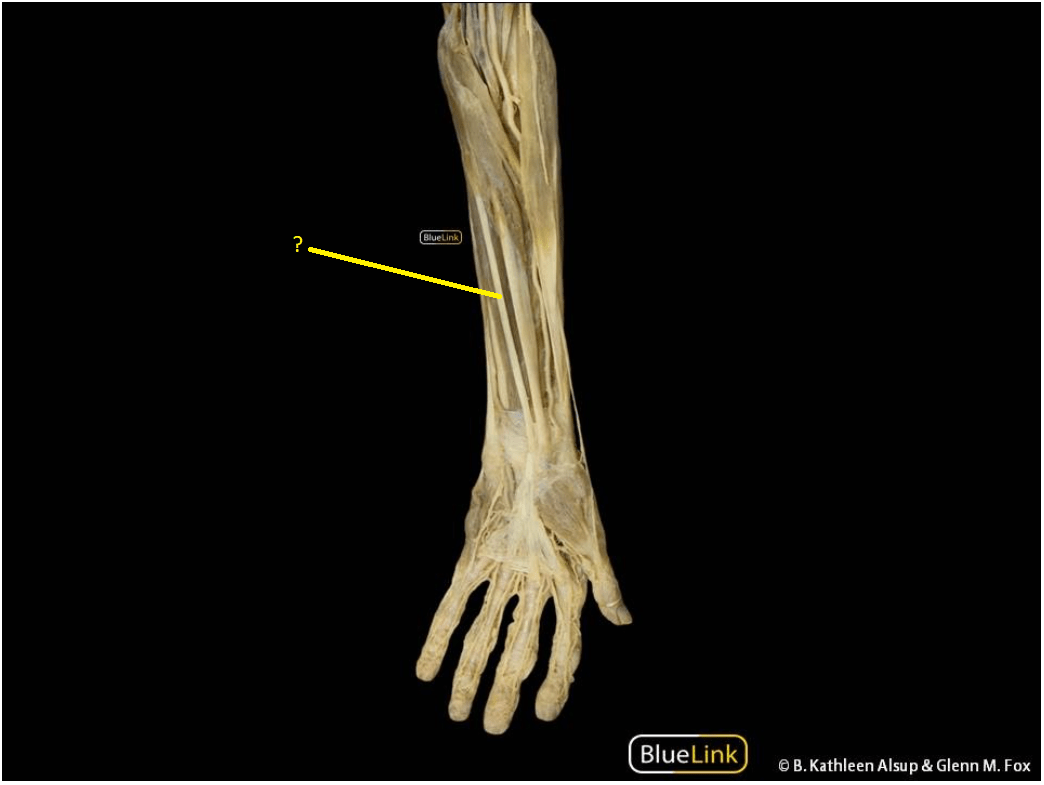
anterior view
What is the Palmaris Longus?
When comparing trigger points versus counterstrain points, this point has no radiating pain, no characteristic pain pattern, and no taut band.
What is a counterstrain point?
The myotome that controls thumb extension
What is C8?
C8, you're great
The skeletal sites most frequently affected by Paget's disease of bone
What are the skull, femur (long bones), pelvis, spine?
A 45-year-old farmer presents with bradycardia, miosis, excessive salivation, and muscle fasciculations after insecticide exposure. He is treated with atropine but continues to exhibit muscle weakness. This drug should be administered to reactivate AChE
What is pralidoxime?
The A subunit of botulism toxin cleaves all 3 SNARE proteins to prevent the docking of ACh-filled vesicles for exocytosis. The A subunit of tetanus toxin cleaves this SNARE protein.
What is synaptobrevin?
This test evaluates for pain or pathology at the acromioclavicular joint
What is the cross-body adduction test, scarf test, cross arm flexion test?
This gene is commonly mutated in patients with familial Paget Disease of Bone.
What is the SQSTM1 gene?
The thenar muscles are innervated mainly by this.
What is the recurrent branch of the median nerve?
The muscle spindle contains 2 types of sensory fibers that can sense changes in the length of muscle. This type of sensory fiber is sensitive to the amount of stretch a muscle has and its rate of stretch.
What are group 1a sensory afferent fibers?
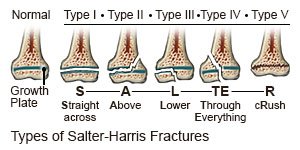
A 13-year-old boy presents after twisting his ankle during football practice. He has tenderness and swelling over the distal lateral malleolus. X-ray shows a fracture extending through the metaphysis, physis, and epiphysis into the articular surface. Growth plate alignment is disrupted.
If untreated, this injury carries the highest risk for growth arrest due to physeal circulation compromise
What is a Salter-Harris type IV fracture?
This phase of Paget disease is characterized by excessive osteoclastic bone resorption followed by a compensatory, chaotic increase in osteoblastic activity, resulting in a mosaic pattern of lamellar bone with irregular cement lines
What is the mixed phase?
Osteoclastic and osteoblastic activity
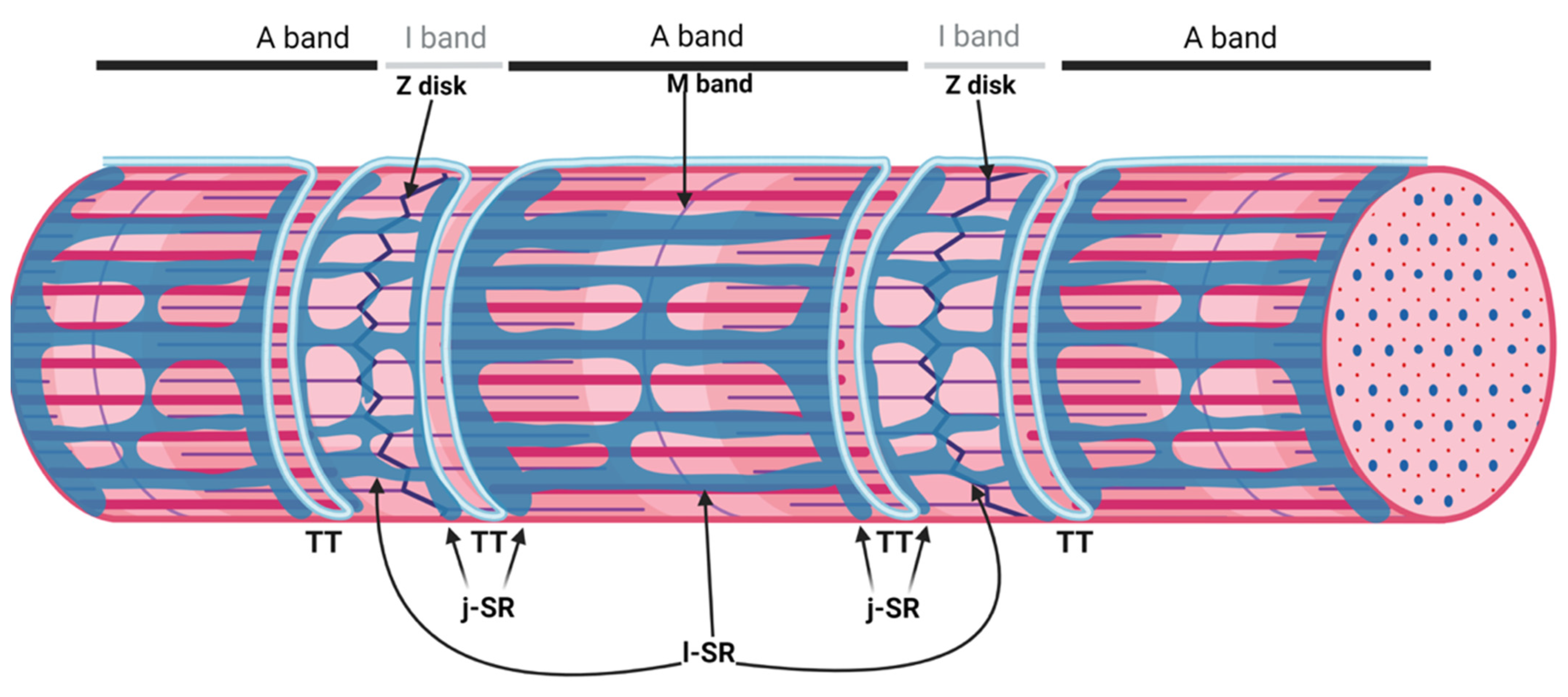
A transverse tubule and two terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticuli form a triad around each myofibril. This triad is located at the junction of these two bands of the sarcomere.
What are the A band and the I band?
In this autosomal recessive disorder, a mutation in the SLC22A5 gene results in the loss of OCTN2, which normally transports extracellular carnitine into the cells
What is primary carnitine deficiency?
To treat this tender point with counterstrain, one must flex the shoulder to 90-120 degrees and abduct the arm. It may require external or internal rotation.
What is the Upper Infraspinatus counterstrain technique?
A 72-year-old woman presents with right hip pain and progressive bowing of her femur. she denies trauma. Imaging shows cortical thickening and trabecular enlargement of the proximal femur. Laboratory studies reveal an isolated elevation in alkaline phosphatase. These are likely complications to develop if her disease remains untreated.
What are osteoarthritis, bone deformities, hearing loss, heart failure, osteosarcoma?
What is the flexor pollicis brevis?