Name the disorder
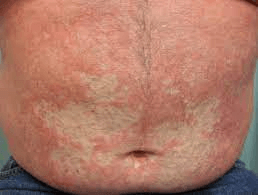
PRP (pityriasis rubra pilaris)
Biphasic incidence: 10-20 yo then 60 yo
Mostly acquired, but inherited forms are associated with what mutations? CARD14 and PSORS2
Clinical features:
Perifollicular hyperkeratosis on an erythematous base (nutmeg grater)
Papules coalesce into orange to salmon plaques with islands of sparing on trunk and extremities- can progress to erythroderma and exfoliation
6 subtypes
What is this, and what is a common trigger?
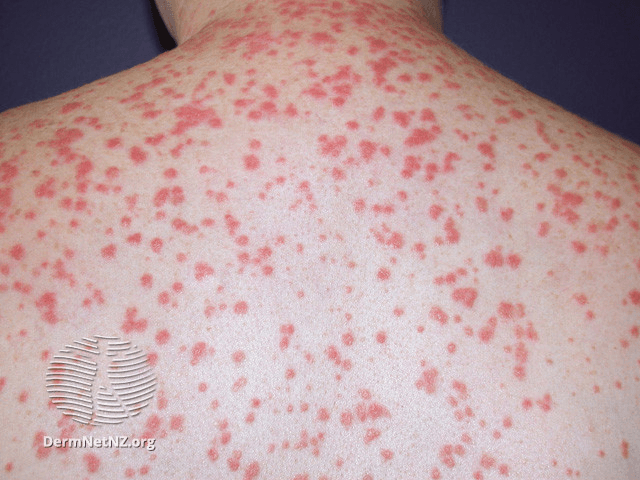
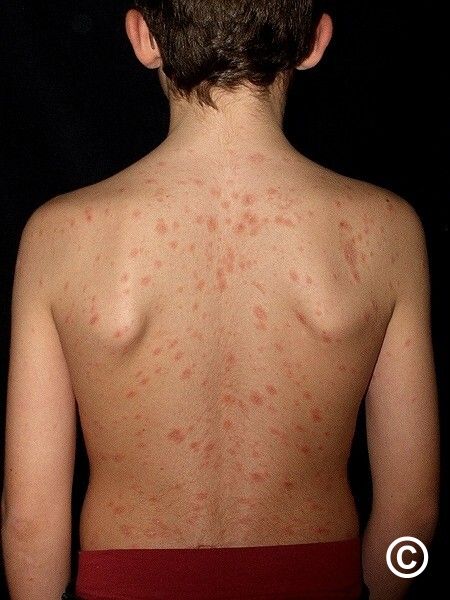
Guttate psoriasis --Group A Strep or URI
-MC in kids. Favors trunk, proximal extremities
-40% will progress to plaque stage
Name a combined IL-12/23 inhibitor
Ustekinumab (Stelara)
What systemic medication for psoriasis is NOT immunosuppressive?
Apremilast (Otezla)
--PDE4-inhibitor
--Side effects of diarrhea, weight loss, depression, and insurance issues
Name 2+ pathology findings in psoriasis
Regular bulbous club shaped acanthosis
Thin suprapapillary plates
Alternating neutrophils and parakeratosis in stratum corneum = sandwich sign
Little to no serum in stratum corneum
Neutrophilic spongiform pustules
Little spongiosis in adjacent epidermis
Strongest HLA association in psoriasis?
HLA-Cw6
Name this disease
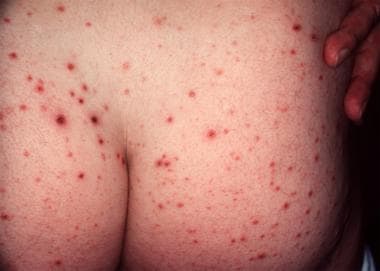
PLEVA (pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta)
Rapid onset of widespread pink papules, evolves in vesicular, ulceronecrotic, purpuric, and crusted papules, heals with varioliform scars
Associated with high TNF-alpha levels
PLEVA and PLC on two ends of disease spectrumAffect children more, male predominance
PLEVA= crusted and occasionally vesiculopustular
Associations with HIV, parvo B19, medications (estrogen, progesterone, TNFi, statin, contrast dye)
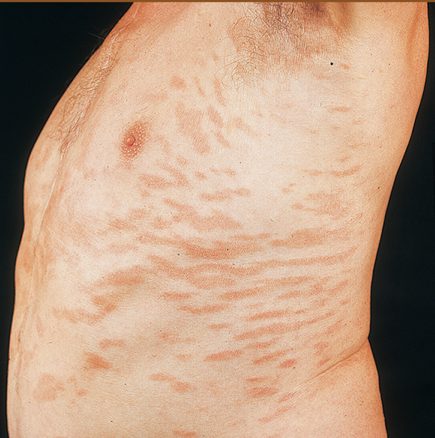
Name this variant:
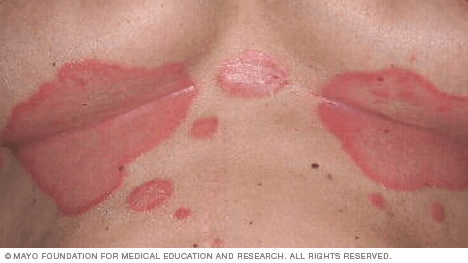
Inverse psoriasis
-breasts, groin, buttock, axillae
Name two IL-17 inhibitors
ixekizumab (Taltz), secukinumab (Cosentyx), brodalumab (Siliq)
Which topical steroid is indicated for ONCE daily use
Mometasone
(the others are BID)
Describe the Auspitz sign
Pinpoint bleeding when you scrape psoriasis scale due to dilated capillaries and suprapapillary plate thinning 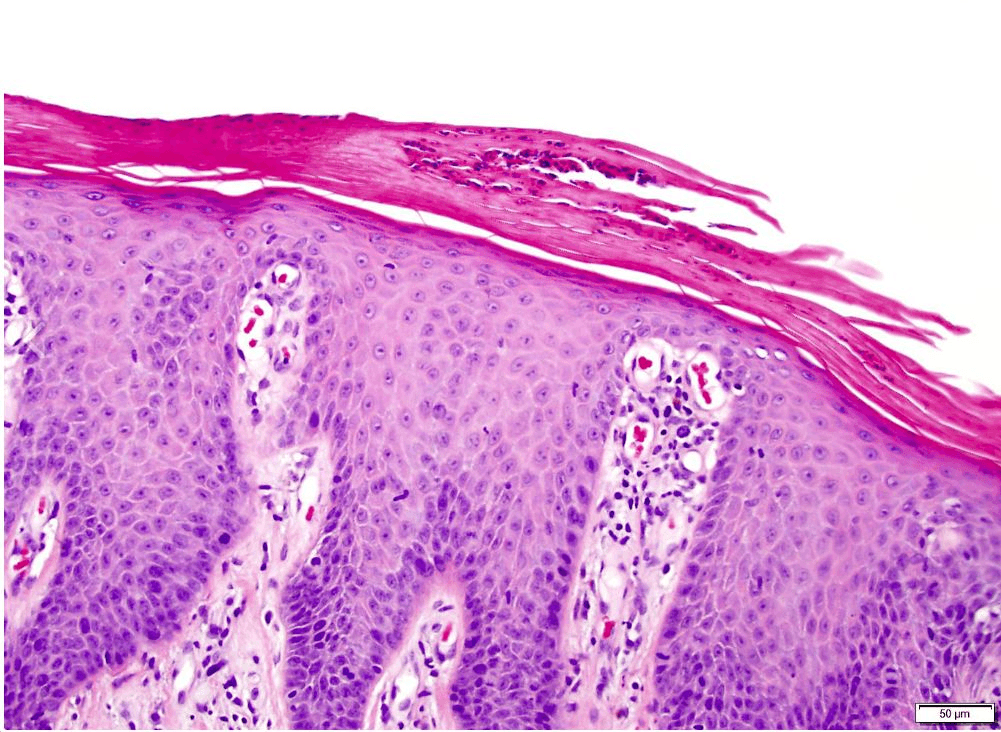
What antimicrobial peptides are secreted from keratinocytes? (name one)
hBD 1-2, cathelicidin LL-37
Name this disease

PLC - pityriasis lichenoides chronica
Widespread, scaly, red-brown scaly papules and plaques
Resolves with hypopigmentation
Lasts longer than PLEVA
More common in adults
Distribution is important
Diffuse distribution = shorter avg duration (11 mo)
Peripheral distribution = longest avg duration (33 mo)
Central distribution = intermediate duration
Name this clinical finding and one disease that causes it!
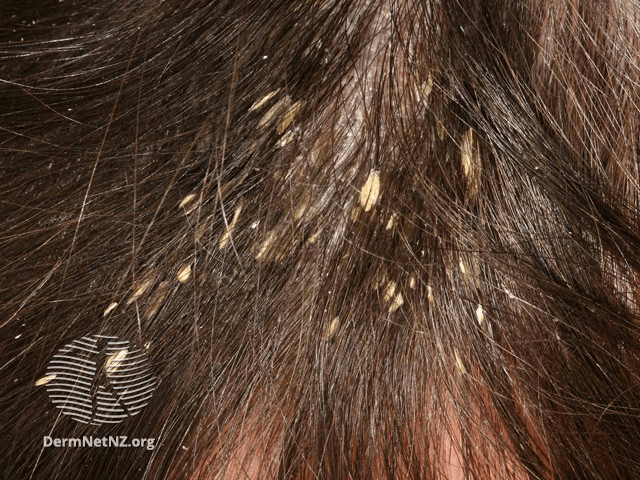
Pityriasis amiantacea
--Psoriasis is the most common cause
Other causes: seborrheic dermatitis, secondarily infected AD, and tinea capitis
Name two IL-23 inhibitors (NOT involving IL-12)
Tildrakizumab (Ilumya), Risankizumab (Skyrizi), Guselkumab (Tremfya)
Name two contraindications to cyclosporine
Immunosuppression
Malignancy history
Active infection
Uncontrolled HTN
Concurrent infection
Differential diagnosis for neutrophils in the stratum corneum (name 4 of 6)
PTICSS
Psoriasis
Tinea
Impetigo
Candida
Seborrheic dermatitis
Syphilis
Through what pathway does coal tar work?
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (taparinof is an upcoming drug to target this)
Name this disease
Small plaque parapsoriasis
SPP: <5cm lesions
LPP: >5cm lesions
Predominantly CD4 T cell infiltrates
Carries risk of progressing into MF: LPP >SPP
Unclear if they are true entities vs condition on the spectrum of clonal dermatitis
M>F 3:1
Fifth decade of life
What is on the differential for this patient? (name 2)

Erythrodermic psoriasis
-DDX includes Sezary, PRP, drug reaction, seb derm
Treatment that (maybe) hastens clearance of pityriasis rosea?
Oral erythromycin
One drug and one infectious trigger of pityriasis rosea?
DRUG: ACE-inhibitors, NSAIDs, gold, bismuth, B-blockers, barbituates, isotretinoin, metronidazole, clonidine
INFECTIOUS: HHV-6, HHV-7
Differential for this finding: (name 4 of 7)

Subcorneal pustules: CATPISS
Candida
Acropustulosis of infancy
Transient neonatal pustular melanosis
Pustular psoriasis
Impetigo
Sneddon-Wilkinson (and IgA pemphigus)
Staph scalded skin syndrome
Name two systemic diseases associated with psoriasis
Increased risk for cardiovascular disease, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, NASH, and IBD (share HLA-B27 type)
This patient had erythrodermic psoriasis and then developed this finding. What was the medication?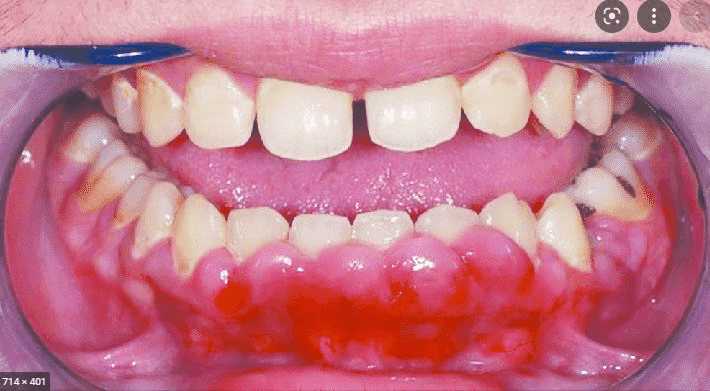
Cyclosporine
Side effects include:
-nephrotoxicity
-HTN
-gingival hyperplasia
-hair growth
- Increased K, decreased Mg
-GI , neuro symptoms
Name the disease and 2+ findings in this photo
:focal(899x812:901x814)/nail-pitting-psoriasis-91da8c37245d49f384238700c36ca22a.jpeg)
NAIL PSORIASIS
Proximal matrix: pits
Distal matrix: leukonychia, hyperkeratosis
Nail bed: oil spots, onycholysis, hyperkeratosis
Laser wavelength that can treat small areas of psoriasis
308nm
Excimer laser
-good for small areas, nail psoriasis
Lab abnormalities in generalized pustular psoriasis? (give me one of three)
Hypocalcemia, hypoalbuminemia, leukocytosis
Name the disease 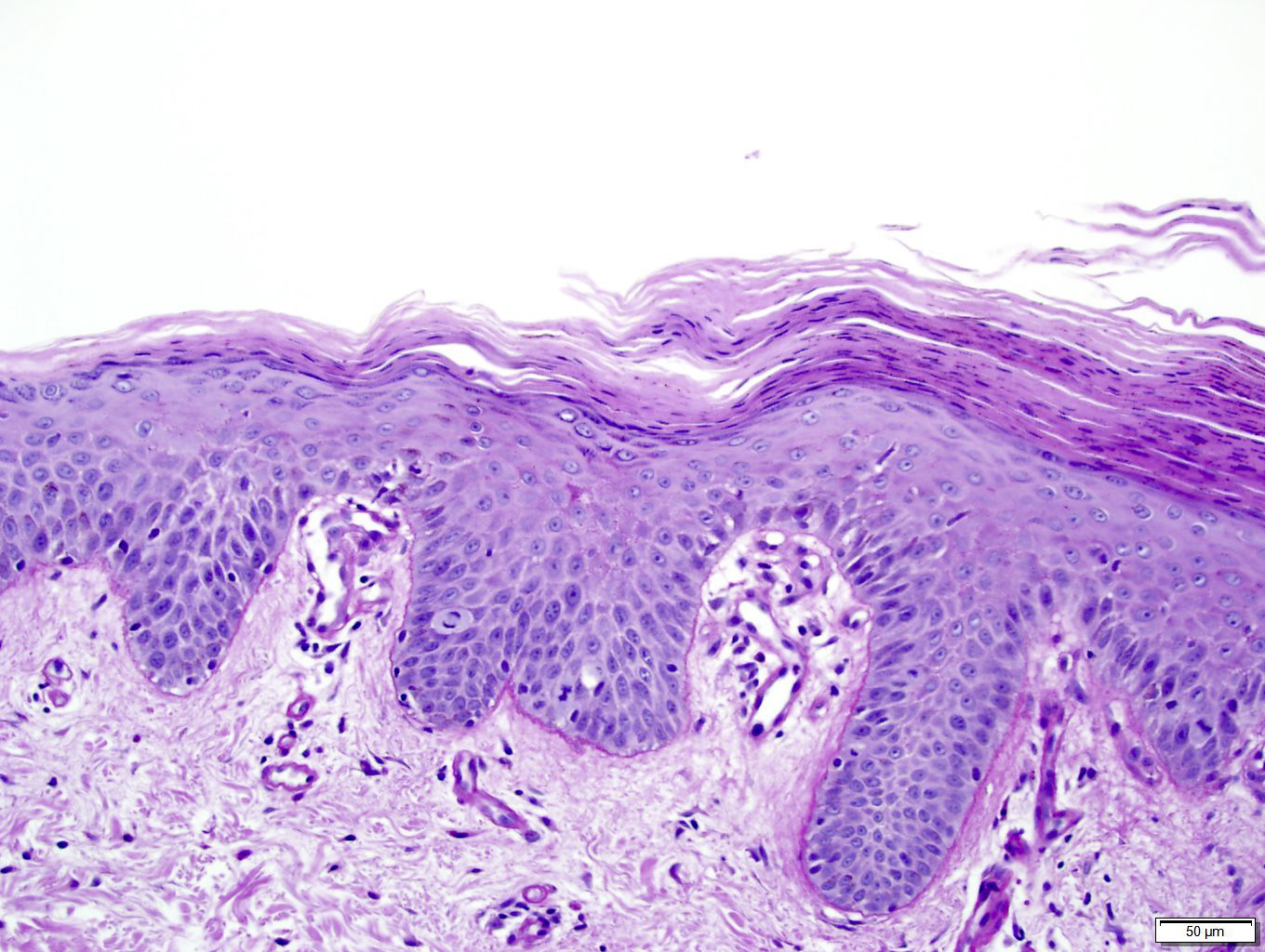
PRP
Checkerboard alternating ortho and para
Follicular hyperkeratosis with parakeratosis in shoulder of follicular plug
What is the most important song to listen to today?
What is this disorder?

Sneddon-Wilkinson / Subcorneal pustular dermatosis
-crops of sterile subcorneal vesicles/pustules with erythematous base, often annular, on flexural skin
-different from pustular psoriasis! *Has subcorneal pustules in the ABSENCE of spongifrm pustules and epidermal changes of psoriasis
-*great response to dapsone
Biopsy: subcorneal pustule with neutrophils. Normal surrounding epidermis
What is name of this variant?
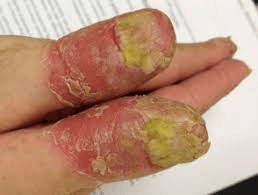
ACRODERMATITIS CONTINUA OF HALLOPEAU
-rare
-lakes of pus
-leads to scale, crust, nail shedding
Treatment of choice for Sneddon-Wilkinson (subcorneal pustular dermatosis)?
DAPSONE
--resolution usually within 4 weeks, then taper
Name two CONTRAINDICATIONS to Acitretin
Acitretin (soriatane) is an amazing option for pustular psoriasis and is great in older patients. Takes 3 months to see effect.
Do not use if:
PREGNANCY
Severely impaired liver function
Chronically elevated blood lipids
In combo with tetracyclines or MTX
What is this disease?

Granular parakeratosis
Affects intertriginous areas including axillae > inguinal fold, inframammary area, abdominal folds
Infantile form – diaper area
Pathogenesis: likely irritation induces parakeratosis and failure of degradation of keratohyalin granules in patients with underlying cornification defects
Has been linked to defect in processing of profilaggrin to filaggrin
Most commonly middle-aged women
Pruritic
Pathology:
Marked compact parakeratosis
Small blue-gray granules in stratum corneum = keratohyaline granules
What cytokine is decreased in psoriasis?
IL-10
This patient has high fever, LAD, arthritis, GI, pulm involvement. What is the eponym?

Mucha Habermann (febrile ulceronecrotic) variant of PLEVA
-fevers, LAD, arthritis, GI/pulm involvement
What psoriasis variant has this associated finding?
(extra credit- what is this presentation called?)

Associated with pustular psoriasis
Annulus migrans of the tongue
Treatment of choice for this condition: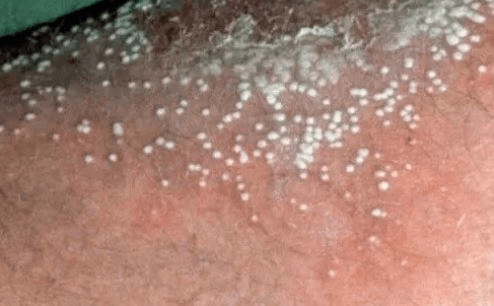
ACITRETIN
Best for Pustular (von Zumbusch) variant (better than cyclosporine, MTX, biologics)
In addition to topical steroids, what are two topical medications that can be used for psoriasis (separately or in combination)
Calcipotriene + tazarotene has similar efficacy as clobetasol
Synergistic effect by combining drugs with different mechanisms of action
(JAAD 2002)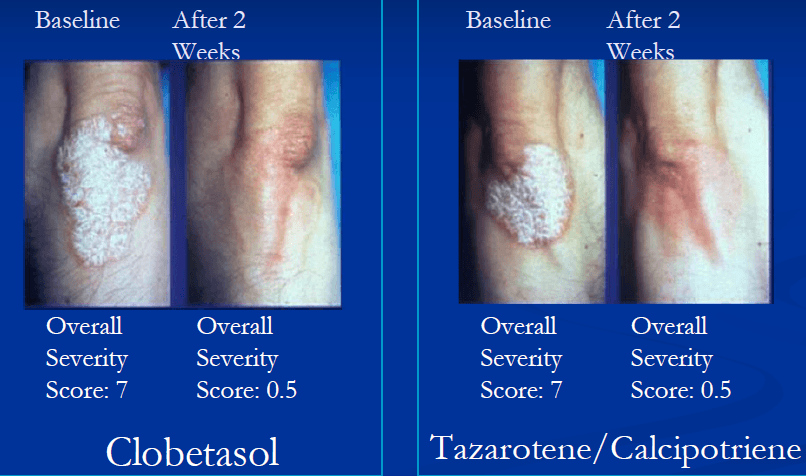
Also true for calcipotriene + betamethasone (works better together than separate) = taclonex
What is this and what might you see on path?
Pityriasis rosea
Herald patch: initial solitary lesions appears on the trunk and enlarges over several days; may be multiple
In the next few days, numerous small thin papules and plaques
“Christmas tree pattern” or “fir tree pattern” – long axis of oval lesions following Langer’s lines of cleavage on back
May see minute pustules
Involves trunk and proximal extremities, spares face, palms and soles
+/- HHV6, HHV7
PATH: focal mild spongiosis, mound-like (focal, non-confluent) parakeratosis, and extravasated erythrocytes are characteristic and a clue to this diagnosis when considering other causes of spongiotic dermatitis that may appear similar clinically, such as nummular dermatitis
Name three medications associated with development of psoriasis:
Short latency <4 weeks? Terbinafine, NSAIDs
Intermediate latency 4-12 weeks? Antimalarials, ACE-I
Long latency >12 weeks? Beta-blockers, lithium
Which trigger pustular psoriasis or plaque psoriasis flares? Lithium, Beta-blockers, IFNs, TNF-alpha inhibitors, antimalarials, taper of systemic steroids
What can TNF alpha inhibitors induce? May lead to plaque psoriasis and/or palmoplantar psoriasis